Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 92501. |
24.8÷12.4-? The correct answer to this problem in proper number of significant digit is |
|
Answer» `2` |
|
| 92502. |
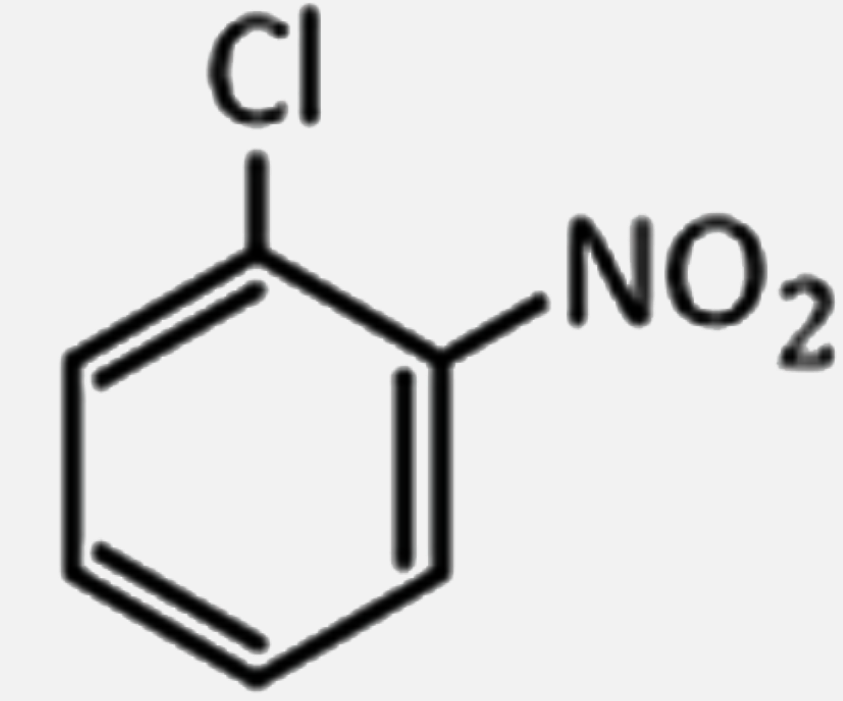
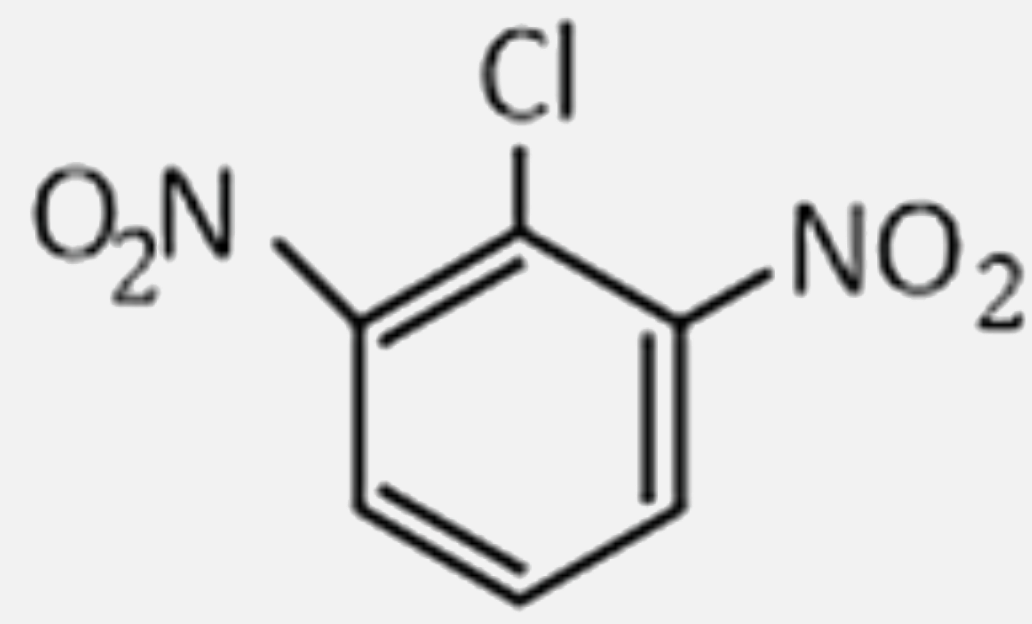
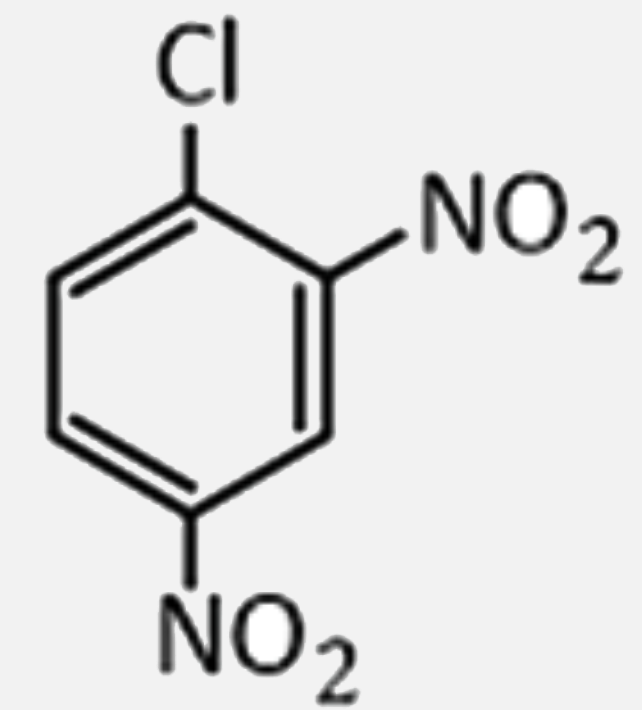
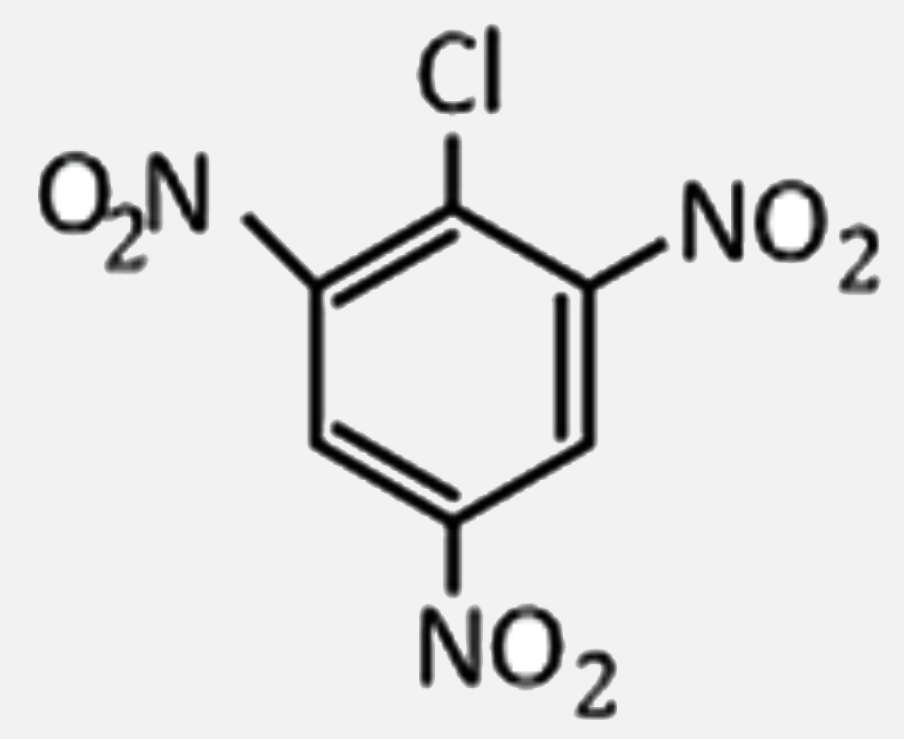
2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene on warming with water produces: |
|
Answer» chlorobenzene  . .
|
|
| 92503. |
2,4,6-tribromo aniline is a product of : |
|
Answer» Electrophilic ADDITION on `C_6H_5NH_2` |
|
| 92504. |
245 gm of KClO_(3) on heating yielded 64 gm O_(2).Find % yield of reaction. (K = 39 , Cl = 35.5 ) |
|
Answer» `66.67` |
|
| 92505. |
24 g of CH_4 at NTP occupy a volume of : |
|
Answer» 33.6 litre |
|
| 92506. |
2,4 - DNP is obtained by reacting hydrazine hydrate with which of the following ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 92507. |
2,4- DNP gives an oragne - red coloured precipitate with |
|
Answer» Carbonyl COMPOUNDS |
|
| 92508. |
.^(23)Na is the more stable isotope of Na. Find out the process by which ._(11)^(24)Na can undergo radioactive decay |
|
Answer» `beta^(-)` emssion `._(0)n^(1) rarr ._(+1)P^(1) + ._(-1)e^(0) or beta^(-)` The proton will stay inside the nucleus whereas electron which cannot EXIST in the nucleus, will be emitted out as `beta-` RAY |
|
| 92509. |
""^(23)Na is more stable isotope of Na. Find out the process by which ""_(11)^(24)Na can undergo radioactive decay. |
|
Answer» `BETA^(-)`-EMISSION |
|
| 92510. |
2.38 g of uranium was heated strongly in a current of air. The resulting oxide weighed 2.806 g. Determine the empirical formula of the oxide. (At. Mass U = 238 , O = 16) |
|
Answer» Solution :Step 1. To calculate the percentage of uranium and OXYGEN in the OXIDE. `2.806g` of the oxide contain uranium = 2.38 g. `THEREFORE"Percentage of uranium"=(2.38)/(2.806)xx100=84.82` Hence, the percentage of oxygen in the oxide= `100.00-84.82=15.18.` Step 2.To calculate the empirical formula  Hence, the empirical formula of the oxide is `U_(3)O_(8)`. |
|
| 92511. |
23g of sodium reacts with ethyl alcohol to give |
|
Answer» 12 mole of NaOH |
|
| 92512. |
._(23)^(28)Al+_(1)^(1)P rarr X +_(0)^(0)gamma, type artifical radioactive reaction. |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 92513. |
23 g of sodium will react with methanol to give |
|
Answer» ONE MOLE of OXYGEN |
|
| 92514. |
23 g of sodium will react with ethyl alcohol to give: |
|
Answer» ONE MOLE of HYDROGEN |
|
| 92515. |
23 g of sodium react with CH_3OH to give : |
|
Answer» 1 MOLE of `O_2` |
|
| 92516. |
23 g ofsodium reactwith 1 mole methyl alcohol to give |
|
Answer» half MOLE of `H_2` |
|
| 92517. |
2,3-Dimethyl-2-butene can be prepared by heating which of the following compounds with a strong acid |
|
Answer» `(CH_3)_2CH-undersetunderset(CH_3)|CH-CH=CH_2` 
|
|
| 92518. |
22g of CO_2 at STP will occupy : |
|
Answer» 11.2 litre |
|
| 92519. |
""^(227)Ac has a half-life of 21.8 years with respect to radioactive decay. The decay follows two parallel paths, one leading to ""^(227)Th and the other leading to ""^(223)Fr. The percentage yields of these two daughter nuclides are 1.2% and 98.8% respectively. what is the rate constant in y^(-1), for each of the separate paths? |
|
Answer» Solution :We have, `lamda_(Ac)= (0.6932)/(t_((1)/(2)))= (0.6932)/(21.8)= 3.18 xx 10^(-2) yr^(-1)` `lamda_(TH)=` (FRACTIONAL yields of Th) `xx lamda_(Ac)` `=(1.2)/(100) xx 3.18 xx 10^(-2) = 3.8 xx 10^(-4)yr^(-1)` SIMILARLY, `lamda_(FR)= (98.8)/(100) xx 3.18 xx 10^(-2)= 3.14 xx 10^(-2) yr^(-1)` |
|
| 92520. |
22.7 ml of N/10 Na_(2)CO_(3) solution neutralizes 10.2 ml of a dilute H_(2)SO_(4). Then the volume of water that must be added to 400 ml of same H_(2)SO_(4) to make it exactly N/10 is |
|
Answer» 254 ML |
|
| 92521. |
.^(226)Ra disintegrates at such a rate that after 3160 years only one fourth of its original amount remains. The half-life of .^(226)Ra will be |
|
Answer» 790 years `N = N_(0) ((1)/(2))^(n)...(i), t = n XX t_(1//2)` ...(ii) For `RA^(226) (N)/(N_(0)) = (1)/(4)`, from eq. (i) `(1)/(4) = ((1)/(2))^(n) or ((1)/(2))^(n) or ((1)/(2))^(2) = ((1)/(2))^(n) , n = 2`, from eq. (ii) `T_(1//2) = (t)/(n) = (3160)/(2) = 1580 yrs` |
|
| 92522. |
2.25 g of a Non volatile substance dissolved in 250 g of C_6H_6.This solution shows depression in F.P. by 0.256 K.Which of the following is/are correct : Given that : (K_b and K_f for C_6H_6 is 2.53 "Kmolal"^(-1) and 5.12 "Kmolal"^(-1),BP of C_6H_6=353.3K) |
|
Answer» MOLAR mass of SUBSTANCES is =180 0.256=`2.25/(M.M)xx1000/250xx5.12` M.M=180 g/mol `DeltaT_b=mxxK_b=(g.wt)/(M.M)xx1000/((g.wt.)_"solvent")xxK_b =2.25/(180)xx1000/250xx2.53=0.1265` B.P. of solution =353.3+0.1265=353.425 K `(DeltaV.P.)/P_("solvent")^@=X_B=n_B/(n_A+n_B)=(2.25/180)/(2.25/180+250/75)=0.00388`. |
|
| 92523. |
2.25 C^(14) atom is dissociate from 1 gm carbon of old statue. 15.3 C^(14) atom dissociate from carbon of living statue then how many years statue was old? C^(14)=5730 years. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`1.58xx10^(+4)` YEARS | |
| 92524. |
22.4 mL of CO_(2) at STP was absorbed in 100 mL water at 25^(@)C (assume no volume change). The solution was found to have pH=4. What is the value of pK_(a1) of carbonic acid (assume only first dissociation)? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 92525. |
2.24 L of N_2at N.T.P. contain same number of molecules as are present in |
|
Answer» 8.8 G of `CO_2` |
|
| 92526. |
""^(222)Rn has a half-life period of 3.83 days. What fraction of the sample will remain undecoposed at the end of 10 days? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 92527. |
22.2 gm Sn is deposited on electrode when 2 ampere current is pass through molten tin salt solution for 2 hours. So what is the oxidation state of Sn in salt ? (Sn=119 gm mol^(-1)) |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Required electricity=`Q=Ixxt` `=(2amp.)(5xx3600)` SECOND `=(2xx5xx3600)/(96500)` Faraday `=(72)/(193)` Faraday and 22.2 gm `Sn=(22.2)/(119)` mole Sn (II) So, `(72)/(193)` faraday give `(22.2)/(119)` mole Sn `=(1xx22.2)/(119)xx(193)/(72)=0.50` mole Sn So, 1F GIVES 0.50 mole Sn and 1 mole Sn required 2F. So oxidation state of Sn is +2. |
|
| 92528. |
2.2016 of acetaldehyde produced 13.95 kcal of heat of combustion in O_(2). Calculate the heat of combustion of CH_(3)CHO |
|
Answer» 279 KCAL |
|
| 92529. |
2.20 g of an ammonium salt was boild with 74ml of 1 N NaOH till the emission of ammonia gas ceased. The excess of unused NaOH solution required 70 ml of N/2 sulphuric acid for neutralization. The percentage of ammonia in the salt is: |
|
Answer» 0.31 |
|
| 92530. |
22 g solid CO_2 or dry ice is enclosed in a bottle of one litre properly closed. If temperature of bottle is raised to 25^@ C to evaporate all the CO_2, the pressure in bottle is : |
|
Answer» 13.23 atm |
|
| 92531. |
22 g of dry ice is placed in an evacuated bottle of 1 litre capacity and tightly stoppered. What would be the pressure (in atm) inside the bottle, whenit is heated to 37^(@)C ? |
|
Answer» 12.71 `T=37+273=310` K, P=? Dry ice is solid `CO_(2)` which when HEATED in an evacuated bottle it is CONVERTED into gaseous `CO_(2)` From ideal GAS equation `PV=(WRT)/MimpliesP=(22xx0.082xx210)/(44xx1)=12.71` atm Now PRESSURE inside the bottle is 12.71 atm. |
|
| 92532. |
2.2 g of an alcohol (A) when treated with CH_3 -Mgl liberates 560 mL of CH_4 at STP. Alcohol (A) on dehydration followed by ozonolysis gives ketone (B) along with (C). Oxime of ketone (B) contains 19.17% N. (A) on oxidation gives ketone (D) having same number of carbon atom. Structure of ketone (D) is |
|
Answer» `CH_3-overset(O)overset(||)C-CH_2-CH_2-CH_2` |
|
| 92533. |
2.2 g of an alcohol (A) when treated with CH_3 -Mgl liberates 560 mL of CH_4 at STP. Alcohol (A) on dehydration followed by ozonolysis gives ketone (B) along with (C). Oxime of ketone (B) contains 19.17% N. (A) on oxidation gives ketone (D) having same number of carbon atom. Molecular mass of (A) is |
|
Answer» 74 Number of MOLES of `CH_(4)`= number of moles of alcohol `560/22400=2.2/M rArr`M=[where M =MOLECULAR weight ] Thus molecular formula of alcohol A is `C_(5)H_(11)OH`. 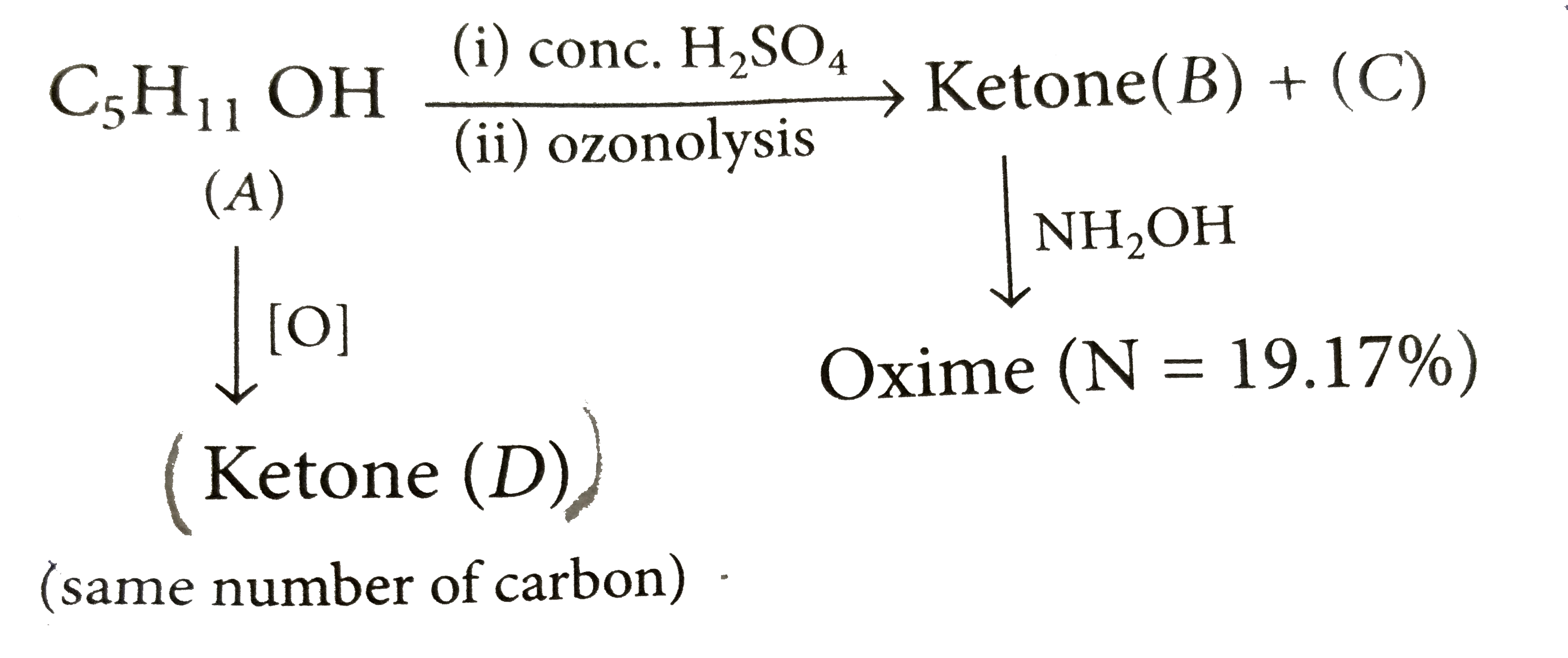 Molecular mass of 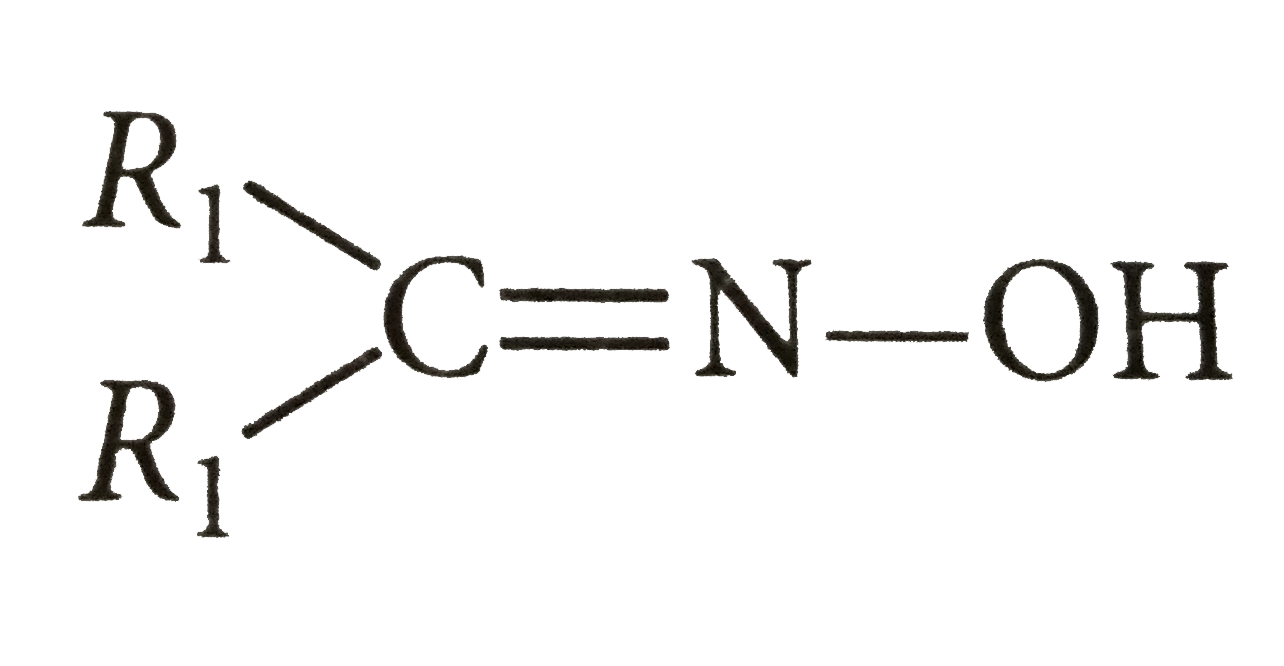 `= 14/19.17 xx 100 =73` `R_1+R_2=73-(12+14+16+1) =73-43=30` `R_1=R_2=15 CH_3` Thus ketone is `CH_3-underset(CH_3)underset(|)C=O` and hence C is `CH_3-CH=O`. on this basic alkene is `CH_3-underset(CH_3)underset(|)C=CH-CH_3`and alcohol A will be `CH_3underset(CH_3)underset(|)"CH"-underset(OH)underset(|)"CH"-CH_3` because it is `2^@` alcohole which on oxidationgives ketone (D) having same number of C -atom. |
|
| 92534. |
2.2 g of an alcohol (A) when treated with CH_3 -Mgl liberates 560 mL of CH_4 at STP. Alcohol (A) on dehydration followed by ozonolysis gives ketone (B) along with (C). Oxime of ketone (B) contains 19.17% N. (A) on oxidation gives ketone (D) having same number of carbon atom. Structure of (B) is |
|
Answer» `CH_3-CH_2-oversetOoverset(||)C-CH_3` |
|
| 92535. |
2.2 g of an alcohol (A) when treated with CH_3 -Mgl liberates 560 mL of CH_4 at STP. Alcohol (A) on dehydration followed by ozonolysis gives ketone (B) along with (C). Oxime of ketone (B) contains 19.17% N. (A) on oxidation gives ketone (D) having same number of carbon atom. Structure of (A) is |
|
Answer» `CH_3-UNDERSET(CH_3)underset(|)CH-CH_2-underset(OH)underset(|)CH-CH_3` |
|
| 92536. |
2,2-Dimethyloxirane can be cleaved by acid (H^(+)). Write its mechanism. |
Answer» Solution :In the acidic medium, the oxygen atom of the oxirane ring gets protonated. The PRESENCE of positive charge on the oxygen atom weakens the C-O bond more on the SIDE of `C_(2)` since the partial positive charge CREATED on `C_(2)` will be stabilized by the +I-effect of the two `CH_(3)` GROUPS in the transition state (T.S.). Consequently, the attac of the nucleophile, i.e., `H_(2)O` PREFERENTIALLY occurs on `C_(2)` yielding 2-methylpropan-1,2-diol. 
|
|
| 92537. |
2,2 -dichlorobutane on boiling with queous KOH gives |
|
Answer» BUTANAL |
|
| 92538. |
2,2- diethoxy butane is obtained from ethanol and what ? |
|
Answer» `CH_(3) - CH_(2) - CH_(2) - CHO` |
|
| 92539. |
2, 2-dichloro propane treated with aq. KOH gives an unstable product. It is |
|
Answer» `CH_(3) COCH_3` |
|
| 92540. |
2.180 gram of a sample contains a mixture of XO and X_(2)O_(3) which are completely oxidised to XO_(4)^(-) by 0.015 mole of K_(2)Cr_(2)O_(7). Calculate the atomic weight of X, if 0.0187 mole XO_(4)^(-) is formed. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 92541. |
2.1 g of Fe combines with S evolving 3.77 kJ. The heat of formation of FeS in kJ/"mole" is |
|
Answer» `-3.77` |
|
| 92542. |
2.1 g of Fe combines with S evolving 3.77 kJ. The heat of formation of FeS in kJ/mol is |
|
Answer» `- 1.79` |
|
| 92543. |
2.1 g of Fe combines with S evolving 3.77 kJ. The heat of formation of FeS (in kJ/mol) is |
|
Answer» `-1.79` |
|
| 92544. |
2.1 g of Fe combines with S evolving 3.77 kJ of heat. The heat of formation of FeS in kJ/mol is: |
|
Answer» `-3.77` |
|
| 92545. |
20mL of solution of 0.1M acetic acid is divided into two equal parts and kept in two beakers separately. To one beaker 0mL of 0.05M NaOH. Two hydrogen the other 10 mL of 0.025 M NaOH. Two hydrogen electrodes are placed in the two solutions which are linked through a salt-bridge. what would be the measured emf? |
|
Answer» 59mV |
|
| 92546. |
20mL of 0.2M NaOH are added to 50mL of 0.2M acetic acid (K_(a)=1.85xx10^(-5)) Take log2=0.3,log3=0.48 (1) What is pH of solution? (2) Calculate volume of 0.2M NaOH required to make the pH of origin acetic acid solution.4.74. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:(,NaOH+,CH_(3)COOHrarr,CH_(3)COONA+,H_(2)O),("Millimole added",20xx0.2,50xx0.2,,),(,=4,=10,0,0),("Millimole after reaction",0,6,4,4):}` `{"Molarity"}=("millimole")/("Total volume")` `[CH_(2)COOH]=(6)/(70)` &`[CH_(2)COONa]=(4)/(70)` rArr Buffer solution consisting of a weak acid & its salt with a strong BASE. (2) Let `V mL` of `0.2M NaOH` is required to make `pH=4.74`,Then `NaOH` should be completely used up (:. final solution is required to be acidic) `{:(,NaOH+,CH_(3)COOHrarr,CH_(3)COONa+,H_(2)O),("Millimole added",0.2xxV,50xx0.2,,),(,=0.2V,=10,0,0),("Millmole after reaction",0,(10-2V),0.2V,0.2V):}` `:.["Acid"]=(10-1.2V)/(50+V),["Salt"]=(0.2V)/(50+V)` `:.4.74=-log1.85xx10^(-5)+log""((0.2V)(50+V))/((10-0.2V)(50+V))` `:.V=25mL` |
|
| 92547. |
20ml of 0.25 N strong acid and 30 ml 0.2 N of strong base are mixed, the resulting solution is |
|
Answer» 0.02 N acidic 1 ml of 1 N acid`-=1ml` of 1 N base 20 ml of 0.25 N acid`-=20xx0.25` ml of a 1(N) acid =5 ml of 1(N) acid 30 ml of 0.2 N base`-=30xx0.2ml` of 1(N) base `=6` ml of 1(N) base `therefore(6-5)=1ml` of 1(N) base STILL remain in the mixture. `50xx x-=1xx1` or `x=(1)/(50)=0.02` The strength of the resulting solution is 0.02 N. |
|
| 92548. |
20ml of 0.1M of an electrolyte could cause flocculation of 980ml of a sol. What is the flocculation value of the electrolyte? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 92549. |
20g of chlorine are evolved in 6 hour from sodium chloride solution by the current of : |
|
Answer» 5 AMPERE |
|
| 92550. |
20^@C aqueous solution of sodium chloride containing ethyl alcohol on electrolysis gives : |
|
Answer» ETHYL chloride |
|