Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 501. |
a.At what distance should the lens be held in Exercise 27 in order to view the squares distinectly with the maximum possible magnifying power ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :a.V = - 25 cm, F = 10 cm `(1)/(v) - (1)/(u) = (1)/(f), (1)/(-25) - (1)/(u) = (1)/(10) ` Solving `rArr u= (-50)/(7) = - 7.14 ` cm |
|
| 502. |
What is resistivity ? What is conductivity ? How they are related. |
| Answer» Solution :RESISTIVITY of a MATERIAL is the resistance offered by a unit cube of that material and CONDUCTIVITY is the RECIPROCAL of resistivity. | |
| 503. |
Find V_(A)-V_(B) in steady state |
|
Answer» 8V |
|
| 504. |
The excess pressure inside one soap bubble is three times that of inside a second one. The ratio of the volumes of the two bubbles is |
|
Answer» |
|
| 505. |
The bias applied for a solar cell is |
|
Answer» forward bias |
|
| 506. |
Calculate the work done by electric field in moving an electron from point A(0, 2 cm) to point B(5cm, 9cm) in a region of electric field vecE=10^(4) hatj V m^(-1) |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`-11.2xx10^(-7)J` | |
| 507. |
An observer stand on the bank of lake finds fish at the depth 12 cm in water. At what height is the image of fish found raised ? |
|
Answer» 9 cm  Shift in IMAGE of FISH, d=H-h.=h-`(h)/(MU)` `h(1-1/mu)` `=h(1-3/4)` `=12(1/4)` =3 xm |
|
| 508. |
Three charges 'q' each are vertices of an equilateraltriangle of side 'r'. How much charge shouldbe placedat the centroid so that the system remains in equilibrium. |
|
Answer» Solution :Force on the charge .q. is `SQRT(3) (1)/(4pi in_(0)) .(q^(2))/(r^(2)) =F_(1)` A charge .Q. is placed at its centroid. Force APPLIED by this charge on .q. is `(1)/(4pi in_(0)) .(3Qq)/(r^(2)) =F_(2)`. If `F_(1)=F_(2)` the systemremains in EQUILIBRIUM.  `sqrt(3) (1)/(4pi in_(0)) (q^(2))/(r^(2)) =(1)/(4pi in_(0)) (3Qq)/( r^(2)) ` `Q= -(q)/(sqrt(3))` |
|
| 509. |
If Bohr 's quantisation postulate (angular momentum =nh//2pi) isa basic law of nature, it should be equally valid for the case of planetary motion also. Why then do we never speak ofquantisation of planets around the sun? |
| Answer» Solution :In CASE of planetarymotion, the value of angular momentum is much larger than the value of h ( in case of earth its value is `10^(70)h`). As a result the value of N BECOMES NEARLY `10^(70)` , making the difference betweenthe successive ENERGY levelsinfinitesimally small and the levels may be consideredcontinuous. | |
| 510. |
The total power content of an AM wave is 2.64 KW at a modulation factor of 80%. The power content of each side band is |
|
Answer» 160 w |
|
| 511. |
For a transistor, the current gain of common base configuration is 0.8. If the transistor is in common-emitter configuration and the base current changes by 5mA, then the change in collector current is |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 512. |
A fork of unkown frequency when sounded with another fork of frequency 256 produces 4 beats/s. he first fork is loaded with wax. It again produces 4 beats/s. when sounded together with fork of 256 Hz frequency then the frequency of first tunning fork is : |
|
Answer» 260 Hz `v_(2) = v_(1) + B = 256 + 4 ` = 260 Hz. HENCE the correct choice is (a). |
|
| 513. |
(A) : The ammeter and voltmeters used for measuring alternating current and volta- ges have uniform divisions on their scales. (R) : The instruments used for measuring alternating current and voltage are based on heating effect of current. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the correct EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 514. |
A tube 1.0 m long is closed at one end. A stretched wire is placed near the open end. The wire is 0.3 m long and a mass of 0.01 kg . It is held fixed at both ends and vibrates in its fundamental mode. It sets the air column in the tube into vibration at its fundamental frequency by resonance. Find (a) the frequency of oscillation of the air column and (b) the tension in the wire. Speed of sound in air = 330 m//s . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`(a) 286 HZ, (b) 1.04 xx 10^3 N` | |
| 515. |
In previous question, if both conductors carry equal currents in the same direction |
|
Answer» `B_(1)ne0,B_(2)ne0` `RGTC, B_(2)=(mu_(0).2I)/(2pir)=(mu_(0)I)/(pir)` |
|
| 516. |
Two metal wires of identical dimensions are connected in series. If sigma_(1) and sigma_(2) are the conductivities of the metal wires respectively, the effective conductivity of the combination is |
|
Answer» `(sigma_(1)sigma_(2))/(sigma_(1)+sigma_(2))` |
|
| 517. |
Alnico is an alloy of........ |
|
Answer» `AI, Ni, CU, P` |
|
| 518. |
For the given capacitor configuration (a) Find the charges on each capacitor (b) potential difference across them ( c) energy stored in each capacitor . |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Capacitor b and c in parallel combination`C_(p) =C_(b) + C_(c) = (6+2) mu F = 8 muF ` 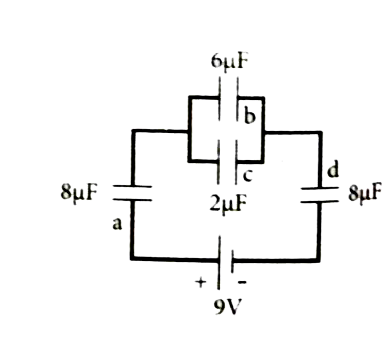 Capacitor a, `c_(p)` and d are in series combination , so the resulatant copacitance `(1)/(C_(s))=(1)/(C_(a))+(1)/(C_(cp))+(1)/(C_(d))=(1)/(8) +(1)/(8) +(1)/(8) = (3)/(8)` `C_(s)= (8)/(3) muF ` 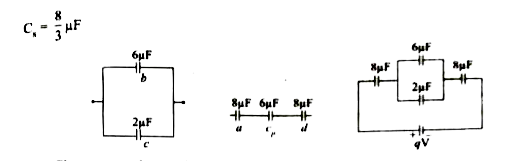 (a) CHARGE on each capacitor , Charge on capacitor a `Q_(a) =C_(s) V= (8)/(3) xx9` `Q_(a)= 24muC` Capacitor b and c in parallel Charge on capacitor `b , Q_(b) =(6)/(3)xx9=18` `Q_(b) = 18muC` Charge on capacitor` c , Q_(c) = (2)/(3)xx9=6 ` `Q_(c) = 6 muC` (b) Potential difference across each capacitor `V= (q)/(C)` Capacitor `C_(a), V_(a) =(q_(a))/(C_(a))= (24xx10^(-6))/(8xx10^(-6))=3V` Capacitor `C_(b), V_(b)= (qb)/(C_(b))= (18xx10^(-6))/(6xx10^(-6))=3V` Capacitor `C_(c), V_(c) = (q_(c))/(C_(c))= (6xx10^(-6))/(2xx10^(-6))= 3 V ` Capacitor `C_(d), V_(d)= (q_(d))_/(C_(d))= (24xx10^(-6))/(8xx10^(-6))=3V ` (c) Energy stores in a capacitor `U=(1)/(2) CV^(2)` Energy in capacitor `C_(a), U_(a)=(1)/(2) C_(a)V_(a)^(2)=(1)/(2)xx8xx10^(-6) xx(3)^(2)` `U_(a)= 36 muj` Capacitor `C_(b), U_(b)= (1)/(2)C_(b)V_(b)^(2)=(1)/(2)xx6xx10^(-6)xx(3)^(2)` `U_(a)=27 muj` Capacitor `C_(c) , U_(c)=(1)/(2)C_(c)V_(c)^(2)=(1)/(2)xx2xx10^(-6)xx(3)^(2)` `U_(a)=9muJ ` Capacitor `C_(d), U_(d)=(1)/(2)C_(d)V_(d)^(2)=(1)/(2)xx8xx10^(-6)xx(3)^(2)` `U_(a)36 muJ` |
|
| 519. |
If A={1,2,3} and B={2,3,4} then which of the function from A to B? |
|
Answer» {(1,2),(2,3),(3,4),(2,2)} |
|
| 520. |
In previous problem, if the current is I and the magnetic field at D has magnitude B, then |
|
Answer» `B=(mu_0I)/(2sqrt2pi)` from the x-axis. Point A and C are at distance of 1 unit each from the x-axis. Points B and D are at distance of `sqrt2` unit each from the x-axis. Magnetic field at point D, `B=(mu_0I)/(1sqrt2pi)` It is obvious that B is INCLINED at an angle of `45^@` with the x-y plane. |
|
| 521. |
A : In a movie ordinary 24 frames are projected per second from one end to the other of the complete film. R : The image formed on the retina of the eye is sustained upto (1"/"10)s after the removed of the stimulus. |
|
Answer» Both A and R are true and R is the correct EXPLANATION of A |
|
| 522. |
In an experiment to measure the speed of light by Fizeau's apparatus, following data are used : Distance between the mirrors = 12.0 km, Number of teeth in the wheel = 180. Find the minimum angular speed of the wheel for which the image is not seen. |
|
Answer» `D=12 km=12xx10^-3m` n=180 `c=3xx10^8m/sec` We KNOW c=(2Dnomega)/PI` `rarr w=(pc)/(2Dm)rad/sec` `=(pc)/(2Dm)xx180/pdeg/s` `rarr w=180xx3xx10^8/(24xx10^3)xx180` `=1.25xx10^4deg/sec` |
|
| 523. |
A magnet is moved in the direction indicated by an arrow between two coils AB and CD as shown in the Fig. 6.19. Suggest the direction of current in each coil. |
| Answer» Solution :In coil AB induced current flows in clockwise direction when seen from right SIDE of B. Again in coil CD, the current appears to flow in clockwise direction when seen from LEFT hand side (or anticlockwise when seen from right side of end D of coil CD). | |
| 524. |
Two equal charges q of opposite sign separated by a distance 2a constitute an electric dipole of dipole moment p. If P is a point at a distance r from the centre of the dipole and the line joining the centre of the dipole to this point makes an angle theta with the axis of the dipole, then then potential at P is given by (f gt gt 2a) where (p = 2 qa) |
|
Answer» <P>`V=(p cos theta)/(4 piepsilon_(0)R^(2))` |
|
| 525. |
The electric field at (30, 30) cm due to a charge of -8 nC at the origin in NC^(-1)is |
|
Answer» `-400 (bari + BARJ)` |
|
| 526. |
A short bar magnet placed with its axis at 30^@ to a uniform magnetic field of 0.2 T experiences a torque of 0.060 Nm. i. Calculate magnetic moment of the magnet ii. Find out what orientation of the magnet corresponds to its stable equilibrium in the magnetic field. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `TAU =0.060 Nm, theta = 30^@ , B = 0.2 T` As `tau =m B sin theta "" 0.060 = mxx 0.2 XX sin 30^@` `therefore m = (0.060)/(0.2 xx 0.5) = 0.06JT^(-1)` ii PE of MAGNET in field `vec B` is GIVEN by U=-m cos `theta` When magnet is paced parallel to `vec B , theta = 0^@` and `U = mB cos 0^(@)`=- mB i.e , the PE of the dipole is minimum. This is the STATE of stable equilibrium. |
|
| 527. |
In a YDSE experiment if a slab whoserefractiveindex can be varied is placed in front of one of the slits then the variation of resultant intensity at mid - pointof screen with mu will be best represented by [Assumeslits of equalwidth and there is no absortion by slab ] |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 528. |
The constituents of atomic nuclei are believed to be |
|
Answer» NEUTRONS and PROTONS |
|
| 529. |
Five charges q_1 q_2, q_3, q_4, and q_5 are fixed at their positions as shown in figure. S is a Gaussian surface. The Gauss's law is given by int_(S)vecE.vec(ds) = q/epsilon_(0). Which of the following statements is correct? |
|
Answer» `vecE` on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from `q_(1),q_(5)`and `q_3` while q on the RHS will have a contribution from `q_2` and `q_4` only. But, `q_1` is the charge enclosed by the closed surface, the charges outside the surface are not taken into CONSIDERATION. |
|
| 530. |
(a) Draw the circuit diagrma of an 1-p-transistor with emitter-base junction forward biased and collector-base junction reverse biased. Describe briefly how the motion of charge carriers in the transistor constitutes the emitter current (I_E), the base current (I_B) and the collector current (I_C). Hence deduce the relation l_E= I_B + I_C |
Answer» Solution :Thecircuitdiagramis showshere:  The emitter-BASE junction, being forward biased, the majority charge CARRIERS (electrons), from the emitter, flow into the base region CONSTITUTING the emitter current (`l_E`). The base region, being very thin, only a (very) SMALL fraction, of these small base current (`I_B`) The majority of these charge carriers, are ATTRACTED by the (reverse biased) collector. These make up the collector current (`I_C`). `I_E=I_C +I_B` |
|
| 531. |
Show that the magnetic moment of an atom is M = 1/2 eomegar^2 , where e the charge of an electron , omega - angular speed of electron and r - the radius of electron orbit. |
|
Answer» Solution :The electrons are revolving round of nucleus of an atom. If .e. is the charge of an electron and T its period of revolution , then Current `I=e/T=(eomega)/(2PI)`. Since `T=(2pi)/OMEGA, omega` is the angular VELOCITY . If `A = pir^2` , is the area of the orbit of radius .R. , then MAGNETIC moment of the atom, `M=IA=(eomega)/(2pi).pir^2=1/2eomegar^2` |
|
| 532. |
A cricketer can throw a ball to a maximum horizontal distance of 100m. How much high above the ground can the cricketer throw the same ball? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`R_max=100m=v^2/G`As` v^2-u^2=2as` Here `v=0, a=-g s=R_max=100m` `THEREFORE(0^2)-u^2=2(-g)s or S=1/2u^2/g` SINCE u=v, S=1/2 v^2/g = 1/2xx100m=50m` |
|
| 533. |
A positive charge .Q. is fixed at a point, A negatively charged of mass .m. and charge .q. is revolving in a circular path of radius radius r_(1) with .Q. as the centre. The change in potential energy to change the radius of the circular path from r_(1) and r_(2) in joule is |
|
Answer» zero |
|
| 535. |
Figure shows electrons 1 and 2 on an x axis and charged ions 3 and 4 of identical charge -q and at identical angles theta. Electron 2 is free to move, the other three particles are fixed in place at horizontal distances R from electron 2 and are intended to hold electron 2 in place. For physically possible values of q le 5e, what are the (a) largest, (b) second largest , and (c ) third largest values of theta for which electron 2 is held in place ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `62.3^(@)`, (B) `60^(@)`, (C ) `56.6^(@)` | |
| 536. |
The density of a newly discovered planet is twice that of earth. The acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the planet is equal to that at the surface of the earth. If the radius of the earth R_(e ), the radius of the planet would be |
|
Answer» `2R_(E )` `g_(e )=(GM_(e ))/(R_(e )^(2))=(G(4//3)piR_(e )^(3))/(R_(e )^(2))rho_(e )` `g_(e )prop R_(e )rho_(e )` Acceleration due to gravity of planet `g_(p) prop R_(p)rho_(p)` `:. R_(e )rho_(p) rArr R_(e )rho_(e )=R_(p)2rho_(e ) rArr R_(p)=(1)/(2)r_(e )` |
|
| 537. |
Match the statements in Column I labelled as a,b,c, and d with those in Column II labelled as p,q,r, and s. Any given statement in column I can have correct matching with one or more statementsin Column II |
|
Answer» |
|
| 538. |
A Carnot engine, whose efficiency is 40%, takes in heat from a source maintained at a temperature of 500 K. It is desired to have an engine of efficiency 60%. Then, the intake temperature for the same exhaust (sink) temperature must be : |
|
Answer» 600 K `(400)/(100) =1-(T_(2))/(T_(1))=1-(T_(2))/(500)` `rArr (T_(2))/(500) =1-(40)/(100)=(60)/(100)` `rArr T_(2) =(60)/(100xx500=300 K` Case II: `eta =(1-(T_(2))/(T_(1))) rArr (60)/(100)=1-(300)/(T_(1))` `rArr (300)/(T_(1)) =1-(60)/(100)=(40)/(100)` `rArr T_(1)=(300xx100)/(40)=(3000)/(4)=750 K` Correct CHOICE : (d). |
|
| 540. |
If a carrier wave of 100kHz is used to carry the signal, the length of transmitting antenna will be equal to |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 541. |
A stationary positive pion disintergrated into a muon and n nertrino. Find the kinetic energy of the moun and the energy of the neutrino. |
|
Answer» Solution :Energy-momentum conservation implies `O=vec(P)_(mu)+vec(pv)` `m_(pi)c^(2)=E_(mu)+E_(v) or m_(pi)c^(2)-E_(v)=E_(mu)` But `E_(v)=c|vec(p_(v))|=c|P_(mu)|`. THUS `m_(pi)^(2)c^(4)-2m_(pi)c^(2).c|vec(p)_(mu)|+c^(2)p_(mu)^(2)=E_(mu)^(2)=c^(2)P_(mu)^(2)c^(4)` Hence `c|vec(p_(mu))|=(m_(pi)^(2)-m_(mu)^(2))/(2m_(pi)).c^(2)` Substituting `m_(pi)c^(2)= 139.6MeV` `m_(mu)c^(2)= 105.7MeV` we GET `T_(mu)= 4.12 MeV` Also `E_(v)=(m_(pi)^(2)-m_(mu)^(2))/(2m_(pi))c^(2)= 29.8MeV` |
|
| 542. |
In double slit experiment, when a glass plate of mu = 1.5 ans thickness t is introduced in path of one of the interfering beams of wavelengths lambda, the intensity at position of central maxima remains unchanged. Minimum thickness of glass plate is : |
|
Answer» `2 lambda` `Deltax = (mu - 1) t = N lambda ,n = 1,2,3`......... `t = (n lambda)/(mu -1)` For minimum VALUE of t , n = 1 `therefore t = (1 lambda)/(1.5 -1) = (lambda)/(0.5) = 2 lambda` |
|
| 543. |
Two solenoid of the cross-section area have their length and number of turns in the ratio of 1:2. The ratio of the self-inductance of the two solenoid is: |
|
Answer» 0.043055555555556 |
|
| 544. |
(A): Faraday's laws are consequences of conservation of energy. (R) : In a purely resistive A.C. circuit, the current lags behind the e.m.f in phase. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 546. |
The displacement of a particle in S.H.M. varies according to the relationx = 4(cos pi t + sin pit) . The amplitude of the particle is |
|
Answer» `-4` `= 4sqrt(2) (1/sqrt(2) cos pit + 1/sqrt(2) sin pit)` `=4sqrt(2) [sin pi/4 cos pi t + cos pi/4 sin pit]` `=4sqrt(2) [sin pit cos pi/4 + cos pi t sin pi/4]` `=4sqrt(2) sin (pi t + pi/4)` HENCE, the AMPLITUDE of particle is `4sqrt(2)`. |
|
| 547. |
Two Carnot engines A and B are operated in series. The first one, A, receives heat at T_(1) (=600 K) and rejects to a reservoir at temperature T_2.The second engine and, in turn, rejects to a heat reservoir at T_(3) (=400 K)Calculate the temperature T_(2)(in K) if the work outputs of the two engines are equal. |
Answer» 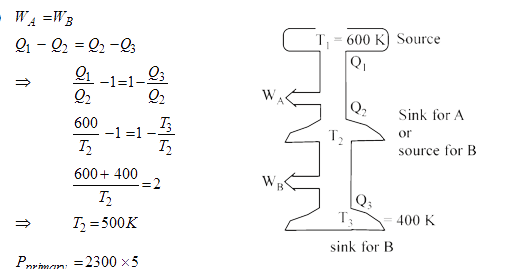
|
|
| 548. |
Two wires of equal length, one of aluminium and the other of copper have the same resistance. Which of the two wires is lighter ? Hence explain why aluminium wires are preferred for overhead power cables. (rho_(Al) = 2.63xx10^(-8)Omega m), rho_(Cu)= 1.72xx10^(-8)Omega m, relative density of Al= 2.7, Cu = 8.9.) |
| Answer» Solution :The mass RATIO of COPPER to ALUMINIUM WIRE is (1.72763)`xx` (8.9/2.7) = 2.2. Since aluminium is LIGHTER, it is preferred for long suspensions of cables | |
| 549. |
The wavelength of the first line of Lyman series for hydrogen atom is equal to that ofthe second line of Balmer series for a hydrogen like ion. The atomic number Z of hydrogen like ion is ......... |
|
Answer» 3 `(HC)/(lambda_(1))=Rhc((1)/(1^(2))-(1)/(2^(2)))` For the second line of Balmer series for a hydrogen like ion `(hc)/(lambda_(2))=Z^(2)Rhc((1)/(2^(2))-(1)/(4^(2)))` according to question `lambda_(1)=lambda_(2)` `rArr ((1)/(1)-(1)/(2))=Z^(2)((1)/(4)-(1)/(16))` `:.Z=2` |
|
| 550. |
The young.s double slit experiment is performed with four different sources. The number of fringes observed in a given region for that sources are n_(1)= 100, n_(2)= 60, n_(3)= 150, n_(4)= 120. The descending order of wave lengths of sources is |
|
Answer» `n_(4), n_(2), n_(3), n_(1)` |
|



