Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 451. |
A small square loop of wire of side y is placed inside a large square loop of side x(xgtgty). The loops are coplanar and their centres coincide. Find the mutual inductance of the system. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let I be the CURRENT flowing through a square loop of SIDE L. Magnetic FIELD at the centre of the loop, `B=4B_(1)` [where `B_(1)` is magnetic field at the centre of the loop due to one of its sides] Now, for the large square loop, L = x `therefore B_(1)=(mu_(0))/(4pi).(I)/((x)/(2))(sin45^(@)+sin45^(@))` [`because` distance of the centre from each side of the large loop = `(x)/(2)`] `=(mu_(0))/(2pi).(I)/(x)((1)/(sqrt(2))+(1)/(sqrt(2)))=(mu_(0)I)/(sqrt(2)pix)` `therefore B=(4mu_(0)I)/(sqrt(2)pix)=(2sqrt(2)mu_(0)I)/(pix)` Now, magnetic flux linked with the small square loop, `phi=Bxx` area of the small square loop `=Bxxy^(2)=(2sqrt(2)mu_(0)Iy^(2))/(pix)"... (1)"` If M be the mutual inductance between the two loops,then `phi=MI"... (2)"` From equations (1) and (2), `M=(2sqrt(2)mu_(0)y^(2))/(pix)` |
|
| 452. |
A ball is dropped from rest at the top of a 6.10-m-tall building, falls straight downward, collides inelastically with the ground, and bounces back. The ball loses 10.0% of its kinetic energy every time it collides with the ground. How many bounces can the ball make and still reach a windowsill that is 2.44 m above the ground? |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 453. |
Two plane mirrors are inclined at 70^(@). A ray incident on one mirror at angle theta. After reflection falls on the second mirror and after reflected from there it moves parallel to the first mirror. Then theta is: |
|
Answer» `50^(@)` |
|
| 454. |
Three large conducting plates A, B and C having charges +q,-2q and +q asshown in fig. The gaps l_(1) and l_2are small and gtl_(2)The plates A and C are fixed and B is free to move. Neglest gravity. If switch S is closed, the plate B will start moving towards |
|
Answer» LEFT |
|
| 455. |
Whatdoes the term LOS communication mean? Name the types of waves that are used for this communication. Which of the two height of tansmittingantenna and height of receivingantenna can effect the range over which this mode of communication remains effective? |
|
Answer» Solution : LOS means LINE-of-sight communication space WAVES. These are used for line of sight (LOS) communication. If `h_(T) and h_(R)` be the heights of transmitting antenna and the receiving antenna respectively, then the maximum Line-of-sight distance `d_(M)` between the two antennas is GIVEN by `d_(M)=sqrt(2Rh_(T))+sqrt(2Rh_(R))` where `R rarr` radius of the EARTH. The height of transmitting antenna can effect the communication system but the height of receiving antenna cannot effect the communication system. |
|
| 456. |
When earth is at one end of the major axis of the elliptical orbit having major and minor axes 2A and 2B , respectively, its velocity (with magnitude V_0 ) makes an angle theta with the major axis. What is the value of theta and what may be the areal velocity of the earth ? |
|
Answer» `0^@ and 0.5 V_0 [A+sqrt(A^2-B^2)]` |
|
| 457. |
If in an hydrogen atom electron is excited to n=4 state then we can have six different spectral lines in all. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 458. |
If force (F), velocity (V) and time (T) are chosen as fundamental units, the dimensions of mass in this system will be represented as |
|
Answer» `ML^0T^0` |
|
| 459. |
Is there any relation between M and H ? |
|
Answer» Solution :YES . The RATIO of intensity of magnetising FIELD strength is defined as the susceptibility (X) i.e., `M/H=X` |
|
| 460. |
Explain cell, emf and internal resistance. Derive relation between potential difference emf and internal resistance. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :`rArr` As shown in figure in a glass vessel electrolyte is field in. `rArr` In this electrolyte tw" electrode are partially DIPPED. One electrode is positive electrode (P) and second electrolyte is negative (N) . `rArr` Electrodes dipped in electronde exchange electric charge in form of positive and negative ion produced asresult of positive and negative ion produced as a result of chaemical reaction. `rArr ` Potential difference between electrode A and electrolyte is`(V_(+) V_(+) gt0) ` and potential difference between electrolyte and negative electrode is `V_(-)V_(-)LT 0. ` `rArr` When current is not flowing in the circuit potential drift between two point P and N. ` V_(+) - (V_(-))` = `V_(+)+ V_(-)` `rArr` Potential difference between `V_(+) and V_(-) ` is called electromotive force (emf) of the cell, it is denoted by `epsilon`. `epsilon = V_(+) + V_(-) gt 0 `.... (1) `rArr ` Definition of emf of cell : " When unit positive charge moves from negative to positive terminal of cell due to non electric force then energy gained by charge is called emf of cell. " `. epsilon. ` is not force force but it is potential difference. `rArr`Consider resistor R connected to cell as shown in figure. `rArr `In resistor R, current I flows from C to D. `rArr ` In electrolyte steady current flows from negative terminal (N) to positive tenninal (P) and in resistance current Hows from P to N. `rArr` If resistance R is infinite then, `I = (V)/(R) = (V)/("infinite" ) = 0 ` where, V is potential difference between P and N. `therefore V = `[p.d. between p and N [ + [ p.d. between A and B ] + [ p.d. between B and N] = `V_(+) + (-Ir) + V_(-)` `= V_(+) + V_(-) - Ir` `epsilon = V_(+) + V_(-)` In open circuit condition, I = 0 `therefore V = epsilon` `rArr"" ` Thus, `epsilon` is potential difference between positive and negative electrode. `rArr` If R be finite resistance of the circuit then potential difference betweenP and N , V = `epsilon - 1r"" ` ...(2) `rArr` Practically If `epsilon gt `Ir then internal resistance of cell can be neglected. `rArr ` For different cell internal resistance is of different value . `rArr` Internal resistance of dry cell is large compared to internal resistance of electrolytic cell. `rArr` When current I flows through R, then p.d. between two END of resistance, V = IR `""` ... (3) from equation (2) and (3) IR = `epsilon`- Ir or I = `(epsilon)/(r + R)` when R = 0 MAXIMUM current tlow through cell. `therefore I_("max") = (epsilon)/(R)` Remember : (1) When cell is not in use then, V = `epsilon ` (2) In case of open circuit condition, ` V = epsilon ` (3)When cell is in use , ` ( V lt epsilon)` (4) When cell is being charged, `(V gt epsilon)` `therefore V = epsilon + Ir ` |
|
| 461. |
Depict the behaviour of magneticfield lines near(i) diamagnetic and (ii) paramagnetic substances. Justify, giving reasons. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) When paramagnetic substances are placed in a MAGNETIC field most of the magnetic filed lines prefer to PASS through them. It SHOWS `mu` is more than 1 i.e. `B//H gt 1 or B gt H.` [B inside the material is larger than air.] (ii) In ferromagnetic material the magnetic field lines prefer to pass through them. It shows `mu gt gt 1 or B//H gt gt 1 RARR B gt gt ` H and B magnetic field density inside material is much larger than air.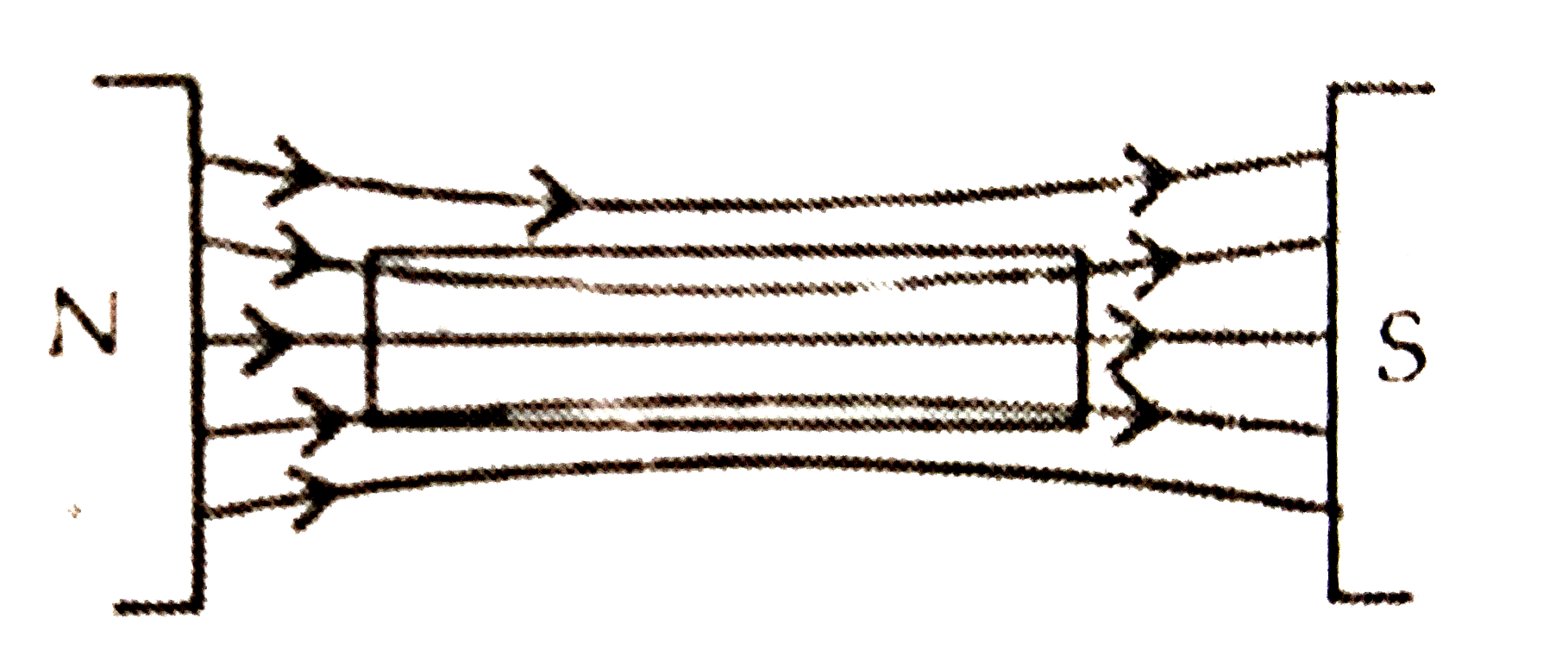  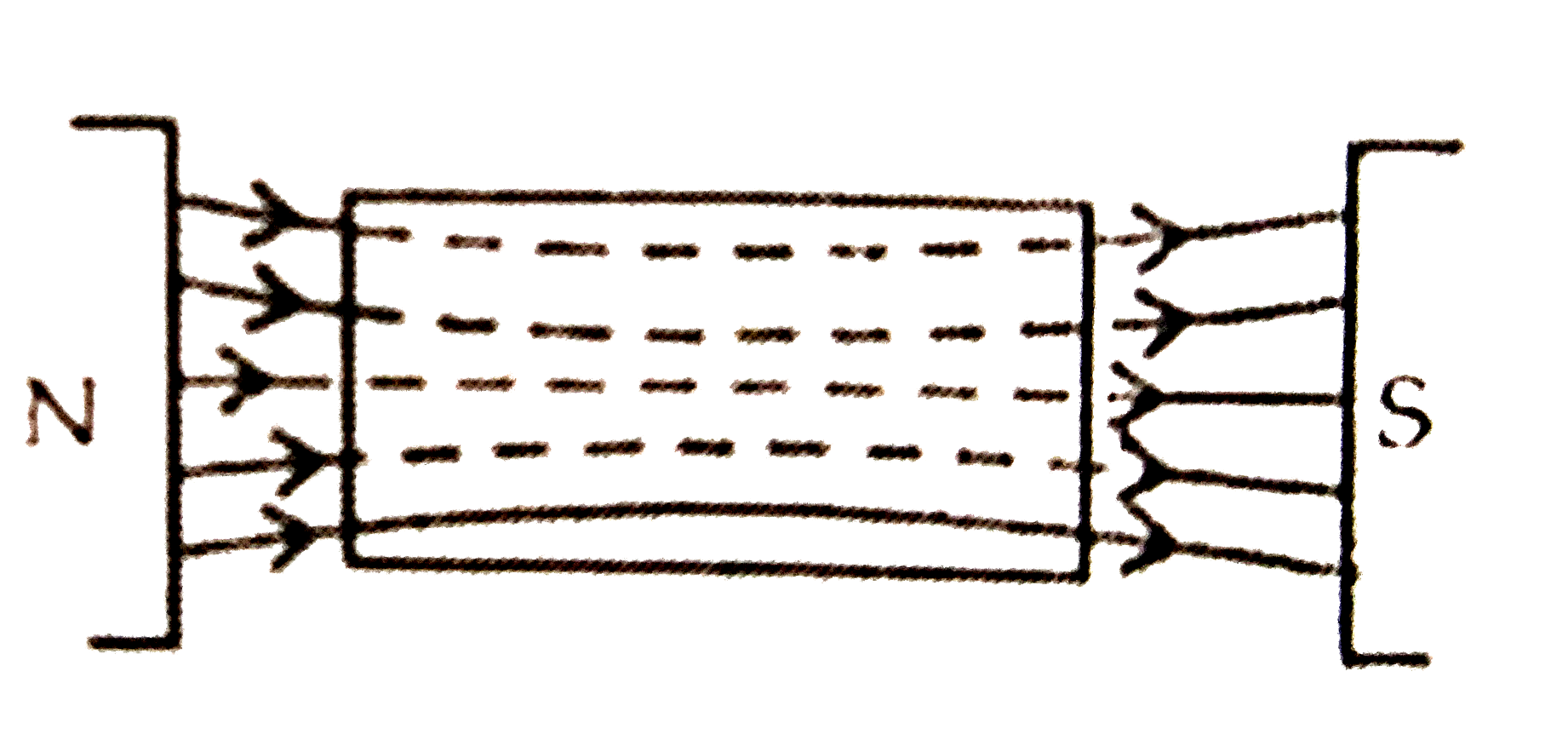
|
|
| 462. |
The no. of possible overtones of air column in closed pipe of length 83.2 cm and of diameter 6cm whose frequencies lie below 1000Hz will be (velocity of sound=340m/s) |
|
Answer» 5 |
|
| 463. |
Calculate the mean zero-point energy per one oscillator of a crystal in terms of Debye theory if the Debye temperaute of the crystel is equal to Theta. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The total zero POINT energy of 1 mole of the solid is `(9)/(8)R Theta`. Dividing this by the NUMBER of modes `3N` we get the average zero point energy per mode. It is `(3)/(8)k Theta` |
|
| 464. |
which of the following collection is a set ? |
|
Answer» the COLLECTION of all GIRLS in your class. |
|
| 465. |
The critical angular for a particular medium is sin^(-1)((3)/(5)) , then how much is the angle of polarisation in that medium ? |
|
Answer» `sin^(-1)((4)/(5))` `:.sin theta=(3)/(5)` `:. (1)/(n)=(3)/(5)`(From total internal reflection) `:.n=(5)/(3)` Now from Brewster.s LAW, `n=tan theta_(p)` `:. theta_(p)=tan^(-1)(n)` `:. theta_(p)=tan^(-1)((5)/(3))` |
|
| 466. |
A constant force acts on a body of mass 0.9 kg at rest for 10s. If the body moves a distance of 250m, the magnitude on the force is : |
|
Answer» 8N |
|
| 467. |
Calculate the orbital period of the electron in the first excited state of hydrogen atom. |
|
Answer» Solution :`becauser_(n) =( in_(0) n^(2) h^(2))/( PI m e^(2)) ` and`v_(n) = (e^(2))/(2 in_(0) n h)` <BR> `therefore `Orbital period `T_(n) =(2 pi r_(n))/(v_(n)) = (4 in_(0)^(2) n^(3) h^(3))/( me^(4))` In firstexcitedstate of hydrogenatom n = 2 . ,br>`therefore"" T_(n) = ( 4 xx (8.85 xx 10^(-12))^(2) xx (2)^(3) xx (6.63 xx 10^(-34))^(3))/((9.1 xx 10^(-31)) xx (1.6 xx 10^(-19))^(4)) = 3.14 xx 10^(-15) s` |
|
| 468. |
Potential difference of 100 V is applied to the ends of a copper wire one metre long. Calculate the average drift velocity of the electrons ? Compare it with thermal velocity at 27^(@)C. Consider there is one conduction electron per atom. The density of copper is 9.0xx10^(3), Atomic mass of copper is 63.5g. Avogadro's number =6.0xx10^(23) per gram - mole. Conductivity of copper is 5.81xx10^(7)Omega^(-1). Boltzmann constant =1.38xx10^(-23)KJ^(-1). |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Since `6XX10^(23)` copper atoms have a MASS of 63.5 g, and there is one conduction electron per atom, so number of electrons per unit volume is `n=(6.0xx10^(23))/(63.5xx10^(-3))xx9.0xx10^(3)kg//m^(3)=8.5xx10^(28)m^(-3)` `"Electric field "E=(V)/(l)=(100)/(1)=100Vm^(-1)` As `J=sigma E=n ev_(d)` `therefore v_(d)=(sigmaE)/(n e)=((5.81xx10^(7))xx(100))/((8.5xx10^(28))xx1.61xx10^(-19))=0.43 ms^(-1)` `"Thermal velocity "v_("rms")=sqrt((3k_(B)T)/(m_(e)))` `=sqrt((3xx1.38xx10^(-23)xx300)/(9.1xx10^(-31))=1.17xx10^(5)m//s` `(upsilon_(d))/(upsilon_("rms"))=(0.43)/(1.17xx10^(5))=3.67xx10^(-6)` |
|
| 469. |
In the figure shown ABC is a circle of radius a. Arc AB and AC each have resistance R. Arc BC has resistance 2R. A current I enters at point A and leaves the circle at B and C. All straight wires are radial. Calculate the magnetic field at the centre of the circle. Each arc AB, BC and AC subtends 120^(@) at the centre of the circle. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 470. |
Abullet is fired horizontal from the top of a tower of height H. The time of flightT varies as |
|
Answer» `sqrtH` |
|
| 471. |
A capacitor is made of two circular plates of radius R each, separated by a dJstance d lt ltR. The capacitor is connected to a constant voltage. A th.in conducting disc of radius r ltlt R and thickness t lt lt R is placed at a centre of the bottom plate. Find the minimum voltage required to lift the disc if the mass of the disc is m. |
|
Answer» Solution :Initially the thin conducting ruse is placed at the centre of the BOTTOM plate. Whole plate is equipotential surface. If electric field applied to disc is E, then the electric field between the plates of capacitor ` E =(V)/(d)` Let charge q. is transferred to the disc during the process. HENCE, by Gaussu.s law, `ointEds =(q)/(in_0)` `:. q = in_(0)(V)/(d)pir^(2)"" [becauseE= (V)/(d) ds=pir^(2)]` The repulsive force acting on the disc is in upward direction, so F= qE =` E_(0). (V)/(d).pi R^(2) . (V)/(d) [ because E= (V)/(d)]` `= (V^(2))/(d^(2)).pir^(2) in_(0)` This repulsive force will be balanced by weight (mg) of disc, `:. (V^(2))/(d^(2))pi r^(2) in_(0)` = mg If the disc is to be lifted then minimum voltage, `V= sqrt((mgd^(2))/(piin_(0)r^(2)))` is required equation . |
|
| 472. |
For a certain gas the ratio of specific heat is 1.5, for thisg gas : |
|
Answer» `C_(p)=(5R)/(J)` or `C_(p) =(3)/(2) C_(v)` `C1_(v)=(2)/(3) C_(p)` Now `C_(p) -C_(v) =(R )/(J)` `therefore C_(p) -(2)/(3) C_(p) =(R )/(J)` `therefore C_(p) =(3R)/(J)` `therefore` Correct choice is (B). |
|
| 473. |
A trnsistor is a current operated device. Comment. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :In a transistor, the collector current is centrolled- by the base current which is a part of EMITTER current. The changes in the emitter current are proportional to the charges in the base current and not to the input (base) voltage. THUS, a transistor is a current OPERATED device. | |
| 474. |
Two identical positive charges are fixed on the y-axis, at equal distances from the origin O. A particle with a negative charge starts on the negative x-axis at a large distance from O, moves along the x-axis, passed through O and moves far away from O. Ita acceleration a is taken as positive along its direction of motion. The particle's acceleration ais plotter against its x-co-ordinate. Which of the following best represents the plot ? |
|
Answer» Solution :When the particle is to the left of the origin O, the net force F on it is towards and HENCE, cause acceleration a `F = 2F_0 COS theta` `= 2k (qQ)/((x^2 + 1^2)) cdot x/(SQRT(x^2 + 1^2))` `2kQ q (x)/((x^2 + 1^2)^3//2)` F is zero for large values of x and also for x=0.  Thus, it must increase to a maximum and fall to zero at O. The acceleration a=F/m, must have the same nature. To the right of O, the net force is to the left while motion is to the right. Thus, the direction of a is opposite to the particle.s direction of motion and is TAKEN as negative. The variation of a with x will follow the same pattern. Hence, 2nd graph represents the pattern. |
|
| 475. |
An electron does not suffer any deflection while passing through a region of uniform magnetic field. What is the direction of the magnetic field? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Either there is no MAGNETIC FIELD or electron is moving PARALLEL or antiparallel to the magnetic field DIRECTION. | |
| 476. |
A radioactive element X with a half life of 2 hours decays giving a satble element Y. After a time t, the ratio of X to Y atoms is 1 : 7, then time t is : |
|
Answer» 6 hours x+y=1+7=8 so, if x =N=1 then x+y `=N_(0)=8` `N/N_(0)=(1/2)^(n)` or `1/8=(1/2)^(n) or (1/2)^(3)=(1/2)^n` n=3 half LIFE PERIOD `=3 xx 2=6"hours"`. |
|
| 477. |
The equation of a wave travelling along the positive x-axis, as shown in figure at t = 0 is given by |
|
Answer» `1 SIN(kx - OMEGAT + pi/6)` |
|
| 478. |
One end of a rod of length 20 cm is maintained at 800 K. The temperature of the other end of the rod is 750 K in steady state and this end is blackened to radiate thermal radiations like a black body. If temperature of the surrounding is 300 K, find the thermal conductivity of the rod. Assume no energy loss takes place through the lateral surface of the rod during conduction through its length. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 479. |
In Mosley's equation , sqrtv = a(Z-b) which was derived from the observations made during the bombardment of the metal target with X - rays |
|
Answer» a is INDEPENDENT but B DEPENDS on the METAL |
|
| 480. |
A message signal of frequency 10 kHz and peak voltage of 10 volts is used to modulate a carrier of frequency 1 MHz and peak voltage of 20 volts. Then modullation index, the side bands produced are. |
|
Answer» `0.5` , 1010 KHZ and 990 kHz |
|
| 481. |
Which of the following is the unit of electric charge? |
|
Answer» ampere |
|
| 482. |
Focal length of concave mirror is f and ratio of heights of object to image for an object at x distance from mirror is ..... |
|
Answer» `sqrt(f/x)` `(f)/(f-u)=(h.)/h` Here,u=f+x `THEREFORE(f)/(f-(f+x))=(h.)/h` `therefore(f)/(-x)-(h.)/h` `therefore |(h.)/h|=f/x` |
|
| 483. |
Write the unit of intensity of magnetisation. |
| Answer» Solution :Net MAGNETIC moment per UNIT VOLUME or Pole strength ACQUIRED per unit area of a sample is CALLED magnetisation of the sample. | |
| 484. |
Show that the normal component of electrostatic field has a discontinuity from one side of a charged surface to another given by (vecE_2 - vecE_1). Htan = sigma/(epsi_0) where hatn is a unit vector normal to the surface at a point and o is the surface charge density at that point. (The direction of în is from side 1 to side 2). Hence, show that just outside a conductor, the electric field is sigma/(epsi_0) hatn. |
|
Answer» Solution : Consider a charged surface having surface CHARGE density o. Normal electric field is PRESENT oneither side of surface but directions of electric fields `vecE_1 and vecE_2`are mutually opposite as shown in Fig. Thus field has a DISCONTINUITY from one side of charged surface to ANOTHER, As `vecE_2 = SIGMA(2epsi_0)hatn and vecE_1 = (-sigma)/(2epsi_0).hatn` Thus, `(vecE_2 - vecE_1)hatn = sigma/epsi_0` This shows that the electric field just outside the conductor is ` sigma//epsi_0`. 
|
|
| 485. |
The time period of a simple pendulum on a freely revolving artificial satellite is |
|
Answer» Infinite |
|
| 486. |
Two rails of a railway track insulated from each other and the ground are connected to a voltmeter. What is the reading of voltmeter, when a train travels with a speed of 180 km/hr along the track. Given that the vertical component of earth.s magnetic field is 0.2 Xx 10^(-4) weber//m^2and the rails are separated by 1 metre. |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 487. |
Which spectral series of hydrogen atom lie in the ultraviolet region ? |
|
Answer» Lyman |
|
| 488. |
A current of 2 A flows through a 2Omegaresistor when connected across a battery. The same batterysupplies a current of 0.5 A when connected across a 9 Omegaresistor. The internal resistance of the battery is |
|
Answer» `1Omega` ` therefore 2 = (epsi)/(2 + r) " and " 0.5 = (epsi)/(9 + r) rArr r = 1/3 Omega` |
|
| 489. |
When a rubber sheet is rubbed with woolen carpet, the carpet is found to acquire a positive charge of 8 x 10^7C In the above process charging is by |
|
Answer» conduction |
|
| 490. |
When a rubber sheet is rubbed with woolen carpet, the carpet is found to acquire a positive charge of 8 x 10^7C br Among Rubber shoe and woolen carpet which one acquire both mass and charge during rubbing? Explain. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :CARPET is FOUND to be positive body which means that electrons are lost from carpet to rubber shoe. Hence rubber shoe acquires CHARGE and mass. | |
| 491. |
Which of the following frequencies will be suitable for beyond the horizon communication using sky waves ? |
|
Answer» 10 kHz |
|
| 492. |
Total internal reflection takes place when.(i) Light travles from_____to_____medium. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :DENSER,RARER | |
| 493. |
Seven indetical plates each of area A and successive separation d are arranged as shown in figures, the effective capacitance of the system between |
|
Answer» `(7 epsilon_(0)A)/(d )` |
|
| 494. |
A natural magnet has…………and………….properties. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 496. |
Force between two magnetic poles varies as _____ and _____ |
| Answer» SOLUTION :DIRECTLY, POLE STRENGTH INVERSELY `r^2` | |
| 497. |
A ray of light travels from air to glass, It is found that the angle of refraction is half the angle of incidence. Then the angle of refraction is given by: |
|
Answer» `R = cos^-1(n/2)` |
|
| 498. |
Potential of a conductor changes on charging. a. How is charge related to the potential? b. What is the ratio called? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :a. On charging a body its POTENTIAL rises. The potential of the body is proportional to the QUANTITY of charge. b. `V ALPHA Q or V=Q/C therefore C=Q/V` It is called capacity. |
|
| 499. |
Modulation used to _____. |
|
Answer» Reduce the BANDWIDTH used |
|
| 500. |
Light with an energy flux of 18 W//cm^(2) falls on a non reflecting surface at normal incidence. If the surface has an area of 20 cm^(2) . Find the average force exerted on the surface during a 30 minute time span. |
|
Answer» Solution :The TOTAL energy falling on the SURFACE is `U=(18 W//cm^(2))xx(20 cm^(2))xx(30xx60)` `=6.48 xx 10^(5) J` Therefore, the total momentum delivered (for complete absorption) is `P=(U)/(C)=(6.48xx10^(5) J)/(3xx10^(8) m//s) =2.16xx10^(-3) kg m//s` The average force exerted on the surface is `F=(P)/(t)=(2.16xx10^(-3))/(0.18xx10^(4))=1.2xx10^(-6) N` |
|