Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2051. |
At the time of independence private sector did not come forward to start capital goods industries due to : |
|
Answer» LACK of capital |
|
| 2052. |
Compare where India, Pakistanand China relativelystand with respect to (a) growth rate population, and (b) sex ratio. Also give reason. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Growth rate of population It is lowest in China DUE to state policy of limiting population growth. It is highest in Pakistan due toabsence of any state policy on family planning. India is in between because India has some state policy on family planning bu not as strict as China has. Sex Ratio `*` It refers to number of femalesper1000 of males. `*` It is nearly the same on the LOWER SIDE in all the three countrieswith lowest in India. `*` It is mainly due to PREFERENCE for son and adoptingillegalmeansto stop birth of female child by many . |
|
| 2053. |
The fiscal deficit gives the borrowing requirement of the government. Elucidate. |
|
Answer» Solution :We know , Fiscal Deficit = Total Expenditure- Revenue RECEIPTS - Non-dept creating capital receipts . It means , fiscal deficit is financed by debt-creating capital receipts , i.e., fiscal deficit is met through borrowings. So , it is RIGHTLY SAID that fiscal deficit gives the borrowing REQUIREMENT of the government . |
|
| 2054. |
Why is Goods and Services Tax (GST), an indirect tax ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The burden of GST can be SHIFTED to other persons (ULTIMATE consumers). | |
| 2055. |
PPC is concave shaped as production of one good can be increased only by reducing quantity of another good. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False: PPC is concave shaped DUE to INCREASING marginal opportunity cost. | |
| 2056. |
Outline the steps taken in deriving Consumption Curve from Saving Curve. Use diagram. |
Answer» Solution :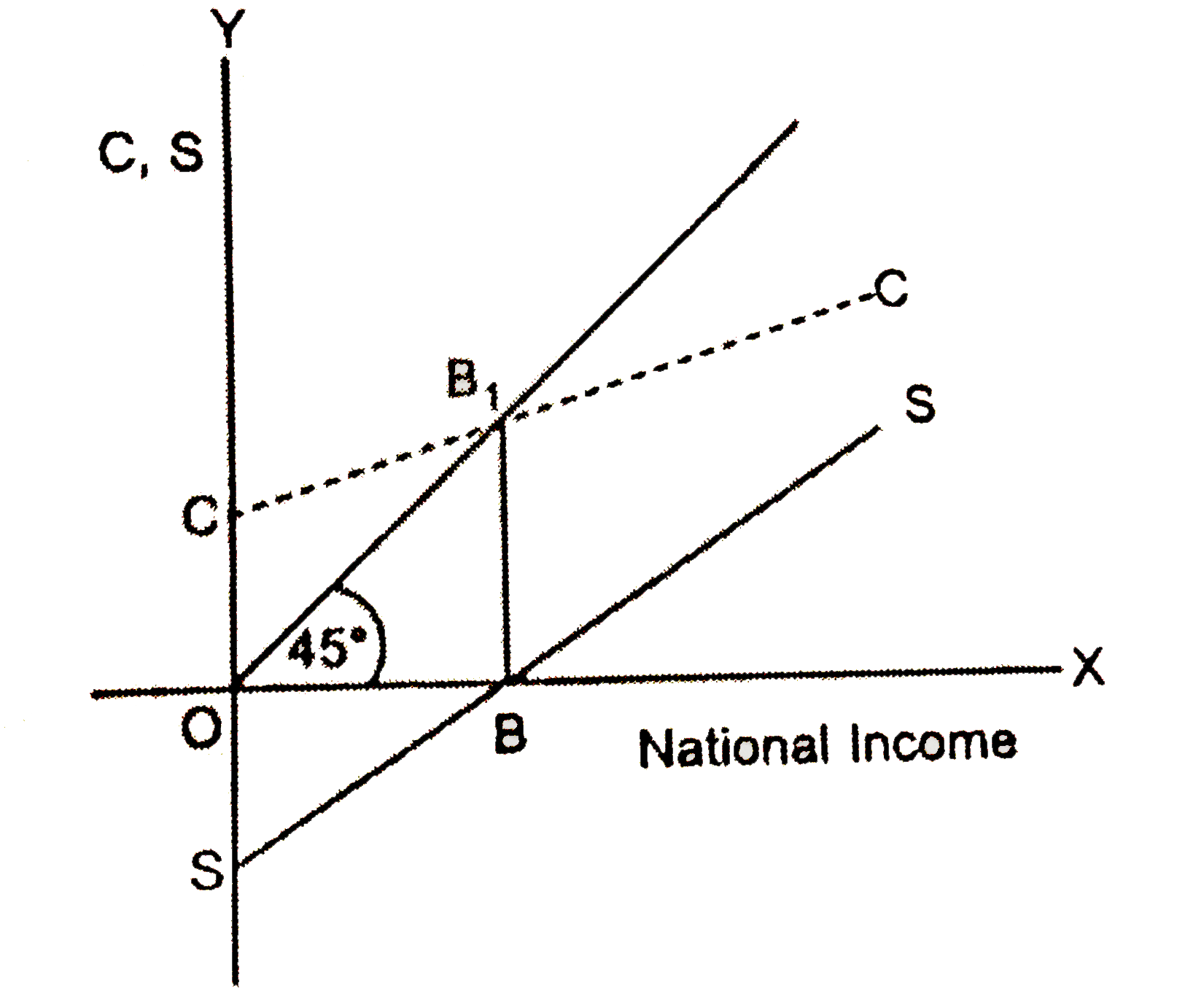 Step 1. GIVES S CURVE, take OC as EQUAL to OS Step 2. Take a POINT `B_(1)` on the `45^(@)` line exactly above point B Step 3. Join C and `B_(1)` and extend |
|
| 2057. |
Define money supply |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Money SUPPLY refers to the total VOLUME of money held by public at a PARTICULAR POINT of time in economy. | |
| 2058. |
How can the productivity of Human resources be increased? |
|
Answer» Solution :The productivity of human resource can be increased with the help of human capital formation by providing training and SKILL to available LABOUR FORCE. Value: Creative THINKING. |
|
| 2059. |
What is the behaviour of Total Variable Cost, as output increases? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TVC first INCREASES at a diminishing rate and then increases at an INCREASING rate. | |
| 2060. |
Calculate the elasticity of demand by total expenditure method.{:("Price (Rs.)Total Expenditure (Rs.)"),("440"),("650"):} |
|
Answer» Solution :Demand is LESS elastic `(ED lt 1)` as the total expenditure increases from Rs. 40 to Rs. 50 with the rise in price from Rs. 4 to Rs. 6. Demand is less elastic `(ED lt 1)`. |
|
| 2061. |
The consumer is in equilibrium when the following condition is satisfied : |
|
Answer» `(MUX)/(MU_y)GT(P_x)/(P_y)` |
|
| 2062. |
What is the relationship between marginal cost and fixed cost? |
| Answer» Solution :There is no relationship between marginal cost and FIXED cost. Marginal cost examines the change in TOTAL cost from a change in output. Fixed cost REMAINS the same even when output CHANGES. | |
| 2063. |
Define 'depreciation'. OR What is meant by 'Consumption of fixed capital '? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2064. |
A teacher is getting Rs. 6,000 per month as salary. If he leaves the job and starts tuition work, he is expected to earn Rs. 5,000 per month. What would be his opportunity cost? |
| Answer» Solution :The opportunity COST of school job is Rs. 5,000 p.m., that the TEACHER COULD have earned in the ALTERNATIVE USE, by doing tuition work. | |
| 2065. |
Deficit or Disequilibrium in BOP may occur either due to autonomous transactions or due to accommodating transactions.' Defend or refute. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2066. |
Growthof resources shifts PPC towards left. |
| Answer» Solution :FALSE: Growth of resources INCREASES the CAPACITY of ECONOMY to produce more. It shifts PPC TOWARDS right and not left. | |
| 2067. |
What is full employment |
| Answer» Solution :FULL EMPLOYMENT REFERS to a situation in which all those people, who are willing to work at the existing wage rate GET work | |
| 2068. |
Calculate autonomous consumption expenditure from the following data about in an economy which is in equilibiru: National income=500, MPS=0.3, Investment expenditure=100. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`S=-bar(C )+(1-b)Y` `100=-bar(C )+(0.3)500` `100=-bar(C )+150` `-50=-bar(C ) or bar(C )=50` Hence, Autonomous Consumption EXPENDITURE =50 |
|
| 2069. |
On the basis of given diagram, answer the following questions: (i) What is the value of autonomous consumption ? What is the break-even level of income or at what level of income saving is zero ? (iii) How much is APC corresponding to point E ? (iv) If MPC = 0.6, determine the consumption and saving function. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Consumption curve makes an itercept of ₹ 40 crores on the Y-axis. So, Autonomous Consumption (`barc`) = ₹ 40 crores. (II) Break-even point occurs when Consumption = Income (or Saving = 0) So, Break-even LEVEL of income = ₹ 100 crores. (iii) At point E, C = Y = ₹ 100 crores. So, APC = `("Consumption(C)")/("Income(Y)")=(100)/(100)` = 1 Consumption FUNCTION is given as: C= `barc` +b(Y) Autonomous Consumption (`barc`)= ₹ 40 crores and b or MPC = 0.6 Putting value of b and (`barc`) in consumption function, we get: C= 40+0.6Y Saving Function in given as: S= -`barc`+(1-b)Y (1-b) or MPS = 1-MPC=1-0.6=0.4 Putting values of (1-b) or MPS and -(`barc`), we get: S=-40+0.4Y |
|
| 2070. |
Full employment implies absence of involuntary unemployment. |
| Answer» Solution :True. : During full employment, all WILLING and capable people get WORK WITHOUT any undue DIFFICULTY and there is no INVOLUNTARY unempolyment. | |
| 2071. |
National income includes : |
|
Answer» TRANSFER INCOME |
|
| 2072. |
Explainthe concept of human capitalformation . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Expenditure on education, HEALTH, on -the -JOB training,migrationand seeking information is INVESTMENT in human capital or human capital FORMATION. | |
| 2073. |
Explain the concept of normal residents. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :A resident is said to be a person (or INSTITUTION) who ordinarily resides in a COUNTRY and whose centre of economic interest lies in that country. He is called a normal resident since he NORMALLY lives in the country of his economic interest. The period of stay should be at least ONE year or more. | |
| 2074. |
Discuss the various steps of expenditure method for calculating national income. |
| Answer» Solution :The steps involved in calculating National Income by Expenditure METHOD are:Step 1: Identify the Economic Units incurring Final Expenditure:Step 2: Classification of Final Expenditure:Final expenditures incurred by the above mentioned economic units are estimated and classified under the following heads:1. Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE)2. Government Final Consumption Expenditure (GFCE)3.Gross Domestic CAPITAL Formation (GDCF)4. Net .EXPORTS (X-M).The sum total of four components of final expenditure gives Gross Domestic Product at Market Price (GDPMP), i.e. GDPMP = PFCE + GFCE + GDCF + (X-M)Step 3: Calculate Domestic Income (NDPFC)By subtracting the amount of depreciation and net indirect TAXES from GDPMP, we get domestic income, i.e. NDPFC = GDPMP – Depreciation – Net Indirect Taxes.Step 4: Estimate net factor income from ABROAD (NFIA) to arrive at National Income:In the final step, NFIA is added to domestic income to arrive at National Income.National Income (NNPFC) = NDPFC+ NFIA | |
| 2075. |
From the data given below about ·an economy calculate: (a) Investment-expenditure (b) Consumption expenditure (i) Equilibrium level of income 5000 (ii) Autonomous consumption 500 (iii) Marginal propensity to consume 0.4 |
| Answer» SOLUTION :25002500 | |
| 2076. |
Suppose output increases in the short run, than the Total cost will: |
|
Answer» increase DUE to an increase in FIXED costs only. |
|
| 2077. |
Explain the behaviour of average fixed cost using numerical example. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) The PER unit cost INCURRED on fixed factors of production is KNOWN as average fixed cost. `AFC= (TFC)/("Output")` AFC falls as output increases because `AFC= (TFC)/("Output")`and TFC REMAINS Output constant. So, as output increases, TFC remains constant, AFC falls. 
|
|
| 2078. |
Will the following be included in the domestic product of India? Give reasons for your answer. (a) Profits earned by foreign companies in India (b) Salaries of Indians working in the Russian Embassy in India (c) Profits earned by a branch of State Bank of India in Japan |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) YES, it will be included in domestic product because it is a FACTOR income earned within domestic territory of India. (B) No, it will not be included in domestic product because Russian EMBASSY is not a part of domestic territory of India. (c) No, it will not be included in domestic product as profits are not earned within domestic territory of India. |
|
| 2079. |
Identify the following as revenue expenditureand capital expenditure . Givereasons. (i) Salary paid to Army officers. (ii) Purchase of Metro coaches from Japan. (iii) Repaymentof loans. (iv) Grants given by central government to state Government . (v) Loan given to Union Territories. (vi) Interest paid on National Debt. (vii) Expenditure on construction of Metro. Pension paid to retired Government employees. (ix) 10 % shares purchased by the Government in a private company. (x) Subsidies . (xi) Expenditure on collection of taxes. (xii) Expenditure on building a bridge . |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) It is a REVENUE expenditure as it neither creates any asset nor reduces any liability of the government . (ii) It is a capital expenditure as it increases asset of the government . (iii)ITIS a capital expenditure as it reduces the liability of the government. (IV) It isa revenue expenditure as it neither creates any asset nor reducesany liabilityof the government . (v) It is a capital expenditure as it increases asset of the government . (vi) It is a revenue expenditure as it neither creates any asset nor reduces any liability of the government . (VII) It is a capital expenditure as it increases asset of the government. (viii) It is a revenue expenditure as it neither creates any asset norreduces any liability of the government . (ix) It is a capital expenditure as it increases asset of the government . (x)It is a revenue expenditureas it neither creates any asset nor reduces any liability of the government . (xi) It is a revenue expenditure as it neither creates any asset nor reduces any liability of the government (xii) It is a capital expenditure as it increases asset of the government . |
|
| 2080. |
Name any one step the government can take through its budget to reduce the gap between the rich and thepoor. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Government can reduce the gap between the rich and the poor by imposingtaxes on the rich and SPENDING more on the WELFARE of the poor. | |
| 2081. |
If price of a commodity falls from 50rs per unit to 45rs per unit, its supply falls from 1000 units to 800 units. Find out its elasticity of supply. |
Answer» Solution : Price ELASTICITY of Supply (ES) `=(DeltaQ)/(DeltaP)xx(P)/(Q) =(200)/(5)xx(50)/(1000)=2` ES=2(Supply is highly elastic as ES gt 1) ES is always positive due to direct relationship between price and QUANTITY SUPPLIED. |
|
| 2082. |
Explain education as a source of human capitalformation in India. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Expenditure incurredon acquiringeducation is investment in human capital . The objective is to enhance future prospects of earnings.It increases learning capacity,SOCIAL standing and knowledge. Itstimulates innovations,FACILITATES inventions and quickadoption of new technologies,and thus INCREASE productivity. | |
| 2083. |
Briefly discussthe concept of over full employment. Use diagram. |
| Answer» Solution :Above full-employment EQUILIBRIUM is a macroeconomic term used to describe a SITUATION in which an ECONOMY’s real gross DOMESTIC product (GDP) is in EXCESS of its long-run potential level. | |
| 2084. |
What is the value of MPC when MPS= 0 ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :We know thatMPC+ MPS =1, Then ifMPS=0 , VALUE of MPS WOULD be 1 | |
| 2085. |
Expenditure by a firm on buyinga bus for use of employeesis : (Choose the correct alternative ) |
|
Answer» COMPENSATION of employees |
|
| 2086. |
What is high Powered Money ? |
| Answer» Solution :High Powered MONEY REFERS to the moneyproduced by RBI and GOVERNMENT of INDIA. | |
| 2087. |
Goods purchased for the following purpose are final goods : (choose the correct alternative ) |
|
Answer» For satisfaction of WANTS |
|
| 2088. |
Give equation of Budget Line . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`P_1X_1 +P_2X_2=M` | |
| 2089. |
To the right of middle point of a line AB touching X and Y - axes, E_(d) would be more than one. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False : It WOULD be less than one. Lower PORTION is smaller than upper portion, `E_(d)=("Lower portion")/("Upper portion")`. | |
| 2090. |
What would be an effect on equilibrium price and quantity when demand and supply both increase at the same rate? Or Explain with the help of a diagram a situation when demand and supply curves shift to the right but equilibrium price remains the same. Or Market for a good is in equilibrium. What is the effect on equilibriumn price and quantity if both the market demand and the market supply of the goods increase in the same proportion? Use diagram. |
|
Answer» Solution :When demand and supply both increase at the same RATE, equilibrium price remains constant and equilibrium quantity RISES. It can be SHOWN with the help of the following diagram. In the above diagram price is measured on vertical axis and quantity DEMANDED and SUPPLIED is measured on horizontal axis. Initially, the equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. But as given in the examination problem, "demand and supply both increase at the same rate", then, (i) Equilibrium price remains constant OP and (ii) Equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_048_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 2091. |
Equilibrium price of an essential1 medicineis too high. Explain what possible steps can be taken to bringdown the equilibrium price but only through the market forces. Also explain the series of changes that will occur in the market. |
|
Answer» Solution :Following are the POSSIBLE steps that can be taken to bring down the equilibrium price: (i) The government should provide subsidy on the production of such medicines. (ii) The government should cut down or abolish all the taxes on such medicine. (iii) The government should offer various facilities to industrialists to motivate them for the production of such medicine. These facilities will REDUCE the cost of inputs used in the production of medicines. The effect of above steps will be that SUPPLY of such medicines will increase and as the result of, the equilibrium price of medicines will reduce as shown in the given figure. In the given figure price is on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied is on horizontal axis. But due to increase in supply the supply curve shifts rightward from SS to `S_(1)S_(1)` . With new supply curve `S_(1)S_(1)`, there is exces_ supply at initial price OP because at price OP, supply is PB and demand is PA, so there is excess supply of AB at price OP. Due to this excess supply competition among the producer will make the price fall. Due to this fall in price there is downward movement alongg the supply curve (Contraction in supply) from B to C and similarly, there is downward movement along the demand curve (Expansion in demand) from A to C. So, finally, equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)` and equilibrium quantity RISES from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. Conclusion Duw to increase in supply (i) Equilibrium price falls from OP to `OP_(1)`. (ii) Equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to `OQ_(1)` Value : Analytic ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_061_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 2092. |
Which of the following is not a revenue receipt? |
|
Answer» RECOVERY of loans |
|
| 2093. |
Define the term 'multiplier'. How do we measure it? |
| Answer» Solution :The INVESTMENT multiplier (K) tells US how much increase in income occurs when autonomous investment increases by 1.Thus the investment multiplier may be defined as the ratio of the change in national income to the initial change in planned investment expenditure that brings it about. We can measure it USING the following FORMULA:K = deltaY / DELTA I | |
| 2094. |
Define a Central Bank . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :A Central BANK is the apexinstitution of the monetaryand banking SYSTEM that controls and regulates the MONETARY and financial system of the COUNTRY. | |
| 2095. |
A phase of circular flow of income : |
|
Answer» production |
|
| 2096. |
How is primary deficit calculated ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :PRIMARY Deficit = FISCAL Deficit - INTEREST Payments | |
| 2097. |
Currencyis issuedby thecentral bank, yetwe saythat commercialbankscreate money. Explain. How is this moneycreationby commercialbankslikelyto affectthe national income ? Explain. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Money supply has two components: CURRENCY and demand deposits with commercial banks . Currencypeople . In thisway, commercial banks also create money Commercial banks LEND money mainly to investors. The riseinthe economyleadsto RISEIN national income throughthe multipliereffect. |
|
| 2098. |
Besides the sun rays global warming is also caused by |
|
Answer» BURING of coal |
|
| 2099. |
Which of the three countries has the highest growth rate of GDP? |
|
Answer» INDIA |
|
| 2100. |
What are (i) Spot Market and (ii) Forward Market in foreign exchange? |
| Answer» Solution :(i) If operation is of daily nature, it is called SPOT market or current market. The exchange rate which prevails in the spot market is called Spot rate. (ii) A market for FOREIGN exchange for future delivery is known as FORWARD market. It deals with forward transactions (SALE and purchase of foreign exchange) which are contracted today but implemented on a specified future date at a rate agreed upon today. | |