Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1251. |
What is meant by problem of double counting? How this problem can be avoided?OR Discuss briefly, the circular flow of income in a two sector economy with the help oi a suitablediagram. (ii)To consideronly the valueadded of theoutputproduced. ORCircular Flowof income in a two Sector economy : Householdareownersof factors of production. Theyprovide factor serviceto thefrms(producingunits ). Fims providefactors payments in exchangeof theirfactor service. So, factor payments flowfrom thefirms (producing units ) to households:Households pruchase good and servicefrom the (producingunits)for whichtheymakepaymentto them. So consumptionexpenditure ( producing units) forwhichthey make paymentto them. So, consumption expenditure (speding on goods and services) flows from housedoldstothefirm |
|
Answer» Solution :The problem of double‘Counting arises when the value of certain goods and services are counted more than once while estimating National Income by Value ADDED Method. This happens when the value: intermediate goods is counted' In the estimation of National Income ALONG with the final value ofgoodservice . Two methodsto avoidthe problem of doublecounting. (i) To consideronlythe finalvalue of outputproduced. (ii) To consider only the value added of the output produced OR Circular Flow of INCOMES in a two SECTOR economy: Household are owners of factors of production. They provide factor services to the FIRMS (producing units). Firms provide factor payment in exchange of their factor services. So, factor payments flow from firms (producing units) to households. Households purchase goods and services from firms (producing units) for which they make payment to them. So, consumption expenditure (spending on goods and services) flows from households to the firms. 
|
|
| 1252. |
An indifference curve slopes down towards rights since more of one commodity and less of another result in - |
|
Answer» Same SATISFACTION. |
|
| 1253. |
How is BOT deficit offset? |
| Answer» Solution :BOT DEFICIT is OFFSET by items in other ACCOUNTS especially by capital account. | |
| 1254. |
Why are financial insitutions like UTI and LIC not considered banks ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because they do not performs bank's ESSENTIAL function of BANKING . | |
| 1255. |
Explain the effects of a price ceiling'. OR Explain the effects of maximum price ceiling' on the market of a good. Use diagram. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) When the government imposed upper limit on the price (maximum price) of a good or service which is lower than equilibrium price is called price ceiling (ii) Price ceiling is generally imposed on necessary items like wheat, rice, kerosene etc. (iii) It can be explained with the help of diagram below: (a) In the given diagram, DD is the MARKET demand curve and SS is the market supply curve of Wheat. SUPPOSE, equilibrium price OP is very high for many individuals andthey are unable to afford at this price. (b) As wheat is necessary product, government has to intervene and impose price ceiling of ` P_(1)` which is below the equilibrium level. (c) SINCE this price is below equilibrium price, there is excess demand in the market. With an shortages, sellers tend to hoard the product. It could also lead to black marketing. ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_021_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 1256. |
It is planned to increase national income by 1000 crore. Calculate, how much increase in investment is required to achieve this goal. Assume that MPC is 0.6. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :400 CRORE | |
| 1257. |
The Government , under Ujjwala Yojana , is providing free LPG kitchen gas connections to the families below the poverty line . What objective the government is trying to fulfil through the government budget and how ? Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :Through Ujjwala Yojana government is TRYING to reduce gap between the rich and the poor. Government sells LPG gas at a higher RATE to those can afford it . Revenue so collected is used by PROVIDE LPG gas connection free of cost and also at subsidized rates to the families below the poverty line . This reduces disposable income of the rich and increases that of the poor , reducing the gap between the TWO. | |
| 1258. |
Calculate net value added at factor cost from the following data : |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1259. |
In an economy, level of income is₹ 2000 crore and MPC= 0.75. Calculate total income if investment is increased by ₹ 200 crore. |
|
Answer» Solution :`""K= (1)/(1-MPC)= (100)/(25)= 4` `""K=4` `""K= (Delta Y)/(Delta I) ""or ""4 = (Delta Y )/(200)` `""K= (DeltY )/(Delta I)""or ""4= (Delta y )/(200)` `""Delta Y= ₹ 800` CRORE `therefore ""` TOTAL income = `Y+Delta Y= 2000+800= ₹ 2800` crores |
|
| 1260. |
Define intermediate goods and final goods . Can milk be an intermediate good ? Give reasons for your answer. Hint for 2^(nd) Part : Milk purchased by a restaurantis intermediate good because it is purchased for reselling. |
| Answer» Solution :Final GOODS refer to those goods which are USED EITHER for CONSUMPTION or for investment. Intermediate goods refer to those goods which are used either for resale or for further production in the same year.Milk PURCHASED by a restaurant is intermediate good because it is purchased for reselling. | |
| 1261. |
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is decrease in supply for this good. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram. Or Explain the chain effects of decrease in supply of a good on its price, supply and demand. |
|
Answer» Solution :As given in the examination problem that market for a good is in equilibrium. So, we ASSUME that initial price is OP as shown in the given figure. In the given figure price is on vertical axis and quantity demanded and supplied is on horizontal axis. But due to decrease in supply the supply curve SHIFTS leftward from SS to `S_(1) S_(1)`. With new supply curve `S_(1)S_(1)` there is excess demand at initial price OP because at price OP, supply is PB and demand is PA, so there is excess demand of AB at price OP. Due to this excess demand competition among the consumer will RISE the price. Due to this rise in price there is upward movement ALONG the supply curve (Expansion in supply) from B to C and similarly, there is upward movement along the demand curve (Contraction in demand) from A to C. So, finally, equilibrium price rises from OP to OP1 and equilibrium quantity falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. Conclusion Due to decrease in supply, (i) Equilibrium price rises from OP to `OP_(1)` (i) Equilibrium quantity falls from OQ to `OQ_(1)`. ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_042_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 1262. |
Which one of the following statements is an example of "explicit cost"? |
|
Answer» The wages a proprietor could have made by working as an employee of a large FIRM. |
|
| 1263. |
If British pound becomes costlier in terms of foreign currency, is it good or bad for growth of Indian economy? Give reasons. |
| Answer» Solution :It is good in one aspect because purchasing power of British pound in Indian MARKET will INCREASE. Britishers will increase IMPORTS from India leading to rise in India's exports which is beneficial for Indian economy. At the same TIME it is bad also because imports of capital goods from UK will become EXPENSIVE. | |
| 1264. |
What is meant by economy? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Economy is a SYSTEM which provides people with the means to WORK and EARN LIVING. | |
| 1265. |
Sustainable development means that the present society passes on the future generation at least as much of the following as we have : |
|
Answer» Man-made capital |
|
| 1266. |
Define intermediate consumption and explain it with an example. How is it different from final consumption ? |
| Answer» Solution :These goods are sold between industries for resale or the production of other goods. ONE example of an intermediate good is salt, a product that is directly CONSUMED but also USED to manufacture food products. Gross domestic product (GDP) is a measurement of the MARKET value of final goods.Final goods refer to those goods which are used EITHER for consumption or for investment. Intermediate goods refer to those goods which are used either for resale or for further production in the same year. | |
| 1267. |
Can Average revenue be negative. |
| Answer» Solution :False : A negative AR implies that the seller does not CHARGE not only any PRICE for the goods but ALSO pays some monetary incentive to the BUYERS, which is irrational. | |
| 1268. |
Calculate investment expenditure from the following data about an economy which is in equiilbirum: National income=1000, MPS=0.25, autonomous consumptionexpenditure=200. |
|
Answer» Solution :`S=bar(C )+(1-b)Y` `I=bar(C )+(1-b)Y [therefore S=I "at EQUILIBRIUM']` `I=-200+(0.5)1000` `=-200+250=50` HENCE, investment epxenditure=50 |
|
| 1269. |
Calculate GNP at Market Price : {:(,,"(Rs. Arab)"),("(i) Mixed income of self-employed",,"80"),("(ii) Goods and services Tax (GST)",,"60"),("(iii) Social securitycontribution by employees ",,"10"),("(iv) Consumption of fixed capital ",,"50"),("(v) Rent",,"40"),("(vi) Compensation of employees ",,"100"),("(vii) Net factor income to abroad ",,"(-) 10"),("(viii) Retained profits",,"5"),("(ix) Interest",,"50"),("(x)Dividends ",,"35"),("(xi) Corporation tax ",,"20"),("(xii) Subsidies",,"5"):} |
|
Answer» Solution :`GNP_(mp)=vi + v + IX + (viii + x + "xi") + i - VII + iv+ ii -" XII"` `100+40+50+(5+35+20)+80-(-10)+50+60-5` = Rs. 445 Arab |
|
| 1270. |
Which of the following conditions satisfy the concept of revenue receipts ? |
|
Answer» Does not CREATE a liability |
|
| 1271. |
Name any one step that the government can take through its budget to check inflation that is causing hardships to the people . |
| Answer» Solution :The GOVERNMENT should reduce UNPRODUCTIVE PUBLIC expenditure to check INFLATION. | |
| 1272. |
In case of indifference curve consumer is in equilibrium if "MRS"_(xy)=P_x/P_y . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TRUE : Here consumer.s BEHAVIOUR and MARKET behaviour MATCH with each other. | |
| 1273. |
Give the meaning of factor income . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1274. |
Whatis full formof N.I.T.I. in NITI Ayog? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :NATIONAL INSTITUTION for TRANSFORMING INDIA . | |
| 1275. |
How does TR change with the output when MR is zero ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Then, TR is MAXIMUM and CONSTANT. | |
| 1276. |
what happens when the credit availability is restricted and credit made costiler? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :AGGREGATE DEMAND will FALL. | |
| 1277. |
Loans taken from world bank are recorded in the: |
|
Answer» CREDIT SIDE of CAPITAL account |
|
| 1278. |
Choose the correct alternative in the following questions. MPC equals : |
|
Answer» `(C)/(Y)` |
|
| 1279. |
The Industrial policy which worked till 1990 was adopted in : |
|
Answer» 1948 |
|
| 1280. |
The price elasticity of supply of a good is 0.8. Its price rises by 50 percent. Calculate the percentage increase in its supply |
|
Answer» Solution :`e_(s) = 0.8` DP = 50% DQ =? `e_(s) = ("Percentage Change in QUANTITY Supplied")/("Percentage Change in PRICE")` or, `0.8 = (DELTA Q)/(50)` or, `Delta Q = 40%` Percentage Change in Quantity Supplied is 40% |
|
| 1281. |
consumption(C )is positivelyrelatedto income( Y)butC in notzerowhenYis also . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1282. |
When does a production function satisfy constant returns to scale? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Out of SYLLABUS. | |
| 1283. |
State any two causes of economic problem. |
|
Answer» Solution :Economic problem arises becauseof scarcity of resources in relation to demand for them. (i) Wants are unlimited: (a) This is a BASIC fact of human life. Human wants are unlimited. (b) They are not only unlimited but also grow and multiplyvery fast. (ii) Resources are limited: (a) The resources to produce goods and SERVICES to satisfy human wants are available in limited quantities. Land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship are the basic scarce resources. (b) These resources are available in limited quantities in every economy, big or small, developed or underdeveloped, rich or poor. Some economies may have more or one or TWO resources but not all the resources. (c ) For example, Indian economy has relatively more labour but less capital and land. The U.S. economy has relatively more land but less labour. No economy in the world is comfortable in all the resources. (iii) Resources have alternative uses: (a) Generally a resource has many alternative uses. (b) A worker can be EMPLOYED in a factory, in a school, in a government OFFICE, self employed and so on. (c ) Like this, nearly all resources have alternative uses. But the problem is that which resource should be put to which use. |
|
| 1284. |
Mention and explain the types of propensity to save. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Average Propensity to Save (APS).It REFERS to the ratio of savings (S) to the corresponding level of income (Y). `APS=(S)/(Y)` (b). Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS). It refers to the ratio of CHANGE in SAVING`(DeltsS)` to change in total income `(DELTAY)`. |
|
| 1285. |
Under oligopoly though firms are free to take decisions about price and quantity to be sold but they do not change the price and hence buyers are deprived of the benefit of fall in price. Comment. |
|
Answer» Solution :Oligopoly firms are MUTUALLY dependent and therefore while FIXING the price and the output they are guided by the reactions of other firms. As such price tends to be RIGID and the consumers SUFFER. Value: CRITICAL thinking |
|
| 1286. |
A consumer consumes two goods X and Y. Explain what will happen if MU_x//P_xis greater than MU_y//P_y ? |
|
Answer» Solution :As, we KNOW conditions for consumer equilibrium is , Necessary Condition Marginal utility of last rupee spent on each commodity is same . Suppose there are TWO commodities, X and Y respectively. So , for commodity X, the condition is, Marginal Utility of MONEY = Price of X Or `(" Marginal in Util Product in Util " [MU_x])/( "Marginal Utility of One Rupee " [MU_R])` = Price of X or `(MU_x)/(P_x) = MU_R "".....(1)` Similarly, for commodity Y , the condition is, `(MU_y)/P_y=MU_R ""....(2)` Putting equation (2) in (1), we get `(MU_x)/(P_y)=(MU_y)/P_y` But as given in the question that the ratio of marginal utility to price in case of X is higher than that in case of Y, i.e., `(MU_x)/P_x gt (MU_y)/P_y` It means marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X is more than marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity Y. So, to attain the equilibrium consumer must increase the quantity of X, which decreases the `MU_x` and decreases the quantity of Y, which will increase the `MU_Y` Increase in quantity of X and DECREASE in quantity of Y CONTINUE till `(MU_x)/P_x = (MU_y)/P_y` . |
|
| 1287. |
What is meant by liquidity of an asset? Which of demand deposits and time deposits are more liquid and why ? |
| Answer» Solution :Liquidity of an asset means the ability to convert an asset into MONEY/cash quickly and without loss of value. An asset is highly liquid if it can be EXCHANGED PROMPTLY and without loss of value. Thus money is the most liquid of all resources. Since TIME ( fixed ) depositsare not chequable deposits and demand deposits are chequable deposits , THEREFORE, demand deposits are more liquid than time deposits. | |
| 1288. |
The price of a commodity is 12rs per unit and its quantity supplied is 500 units. When its price rises to 15rs per unit, its quantity supplied rises to 650 units.Calculate its price elasticity of supply. Is the supply elastic ? |
Answer» Solution : Price Elasticity of Supply (ES) `=(DeltaQ)/(DeltaP)xx(P)/(Q) =(150)/(3)xx(12)/(500)=1.2` ES=1.2(Supply is highly elastic as ES GT 1) ES is always POSITIVE DUE to direct relationship between price and quantity supplied. |
|
| 1289. |
The coefficient of elasticity of supply of a commodity is 3. A seller supplies 20 units of this commodity at a price of 8rs per unit. How much quantity of this commodity will the seller supply if the price rises by 2rs per unit. |
Answer» Solution : PES `=(DeltaQ)/(DELTAP)xx(P)/(Q) 3=(DeltaQ)/(2)xx(8)/(20)` `DeltaQ=(120)/(8)=15` As PRICE increases,quantity suppliedalso increases as per law of SUPPLY NEW Quantity =Initial Quantity+DeltaQ =20+15=35` |
|
| 1290. |
"A day without selling costs is nearly impossible". Comment. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The GIVEN statement is correct. It is the EXPENSES which are incurred for promoting sales or inducing customers to buy a good of a particular BRAND. (II) This includes, the cost of advertisement through newspaper, television and radio and cost on each other sales promotional activities. (iii) As selling costs by the FIRMS in the form of various promotional tools have become a routine activity and the firm generally persuades or lures the customer to avail from one brand to another. |
|
| 1291. |
Export and import of machines are recorded in Capital Account of BOP account. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE because it will be recorded in CURRENT Account of BOP account. | |
| 1292. |
Suppose that a sole proprietorship is earning total revenue of Rs 1,00,000 and is incurring explicit costs of 75,000. If the owner could work for another company for Rs 30,000 a year, would you conclude that the firm is incurring an economic loss or getting profit? |
|
Answer» Solution : ECONOMIC PROFIT = TR – TC (Explicit COST + Implicit cost) = 1,00,000 – 175,000 + 30,000) =-5000 (loss) So the firm is INCURRING an economic loss. |
|
| 1293. |
Define Gross investment . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1294. |
PED =[-]1. A consumer demands 50 units of a commodity when price is Rs. 1 per unit. At what price price will he demands 45 kg of a commodity ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("Elasticity of demand = unity"[-]1),("Original QUANTITY (Q) = 50Original Price (P) = 1"),("New Quantity "(Q_(1))=45 "New Price "(P_(1))=?),("CHANGE in Quantity " (DELTA Q)=[-]5 "Change in Price " (Delta P)=Delta P):}` `PED = (Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q) "or" [-]1=([-]5)/(Delta P)xx(1)/(50)` `Delta P=(1)/(10)=0.1` As quamtity demanded is decreasing, then price must increase by 0.1. New Price = Initial Price `+Delta P=1+0.1=1.1` |
|
| 1295. |
State the three function of foreign exchangemarket. |
| Answer» SOLUTION : (i) Transfer Function , (II)Credit Function , (iii) Hedging FUCNTION | |
| 1296. |
The following table gives the average product schedule of labour. Find the total product and marginal product schedules. It is given that the total product is zero at zero level of labour employment. |
Answer» SOLUTION :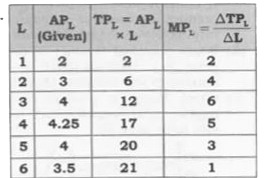
|
|
| 1297. |
AN econimyis in equilibrium ,Calculatenational incomefrom the following:(set 1) {:( "Autonomousconsumption ",=,100),("Marginal propensity to save",=,0.2),("investmentExpenditure ",=,200):} An economyis inequilibrium , find' autonomousconsumption' from following(set 2) : {:("National income ",=,1","000),( "Marginal propensityto consume ",=,0.8),("investmentexpenditure",=,100):} An economyis inequilibrium . findmarginalpropensityto consume fromthe fromthe following : {:("National income ",=,2","000),( "Marginal propensityto consume ",=,400),("investmentexpenditure",=,200):} |
|
Answer» Autonomousconsumption =100 MARGINAL PROPENSITY to consume =0.7 |
|
| 1298. |
The price elasticity of supply of a commodity is 2. When its price falls from 10rs per unit to 8rs per unit, its quantity supplied falls by 500 units. Calculate the quantity supplied at th reduced price. |
Answer» Solution : Price Elasticity of Supply (ES) `=(DeltaQ)/(DeltaP)xx(P)/(Q)=2=(-500)/(-2)xx(10)/(Q)`, i.e., `Q=1,250` As price DECREASES, then quantity supplied will ALSO DECREASE. It MEANS, New Quantity =Original Quantity (Q)+Change in Quantity `(DeltaQ]=1250+(-500)=750` units New Quantity `=750` units |
|
| 1299. |
What is the supply curve of a firm in the short run ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) In the SHORT PERIOD, supply is relatively LESS elastic as firm can change the supply by CHANGING the variable factors only as fixed factors REMAIN fixed during short period. (ii) The supply curve during short period is inelastic i.e., percentage change in quantity supplied is less than percentage change in price as shown below : 
|
|
| 1300. |
A farmer takes a farm on rent and carries on farming with the help of his family members. Identify explicit and implicit costs from this information. Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) For PRODUCING a commodity, a firm REQUIRES factor inputs (like services of land, labour, capital etc.) and NON-factor inputs (like raw material, electricity, fuel etc.). (ii) Actual money spent by a firm on buying and hiring of factor and non- factor inputs is called explicit cost. As per question, a farmer takes a farm on rent. So, the rent he PAYS to landloard is the explicit cost. (iii) Implicit cost is the IMPUTED or estimated value of inputs supplied by the owner of the firm himself. As per question, if a farmer carries on farming with the help of family members, even then the imputed wages will be an implicit cost. |
|