Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 951. |
National income is affected by both factor as well as transfer incomes. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE. It is AFFECTED by FACTOR INCOME only. | |
| 952. |
How will 'Reverse Repo Rate' and 'Open Market Operations' control excess money supply in an economy? |
| Answer» Solution :Reverse Reporate is the rate at which Central Bank borrows money funds COMMERCIAL banks. INCREASE in Reverse Repo Rate INDUCES banks to transfer more funds to Central Bank and reduces banks' ability to create credit. OPEN Market OPERATIONS refers to buying and selling of government securities by Central Bank from/to public and commercial banks. Sale of such securities reduces the reserve of commercial banks and adversely affects bank's ability to create credit and hence decreases the money supply in the economy. | |
| 953. |
After Demonetisation, people deposited the old currency into their bank Accounts.It will decrease the money supply in the economy. Defend or refute. |
| Answer» Solution : The GIVEN statement is refuted. DEPOSIT of old currency by the people REDUCES the ‘Currency held by Public’ (a component of MONEY Supply) and increases the ‘Net Demand Deposits held by COMMERCIAL Banks’ (another component of Money Supply) by the same amount. So, there will be no change in the money supply in the economy. However, Money Supply will decrease permanently to the extent of black money, which does not re-enter the system. | |
| 954. |
What is meantby foreign exchange market ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION : Foreign EXCHANG market I the market where foreign currencies are bought and SOLD | |
| 955. |
Give reasons for the following statements: (i) Every economy has to make the decision relating to what to produce. (ii) Problem of choice arises because available resources have alternative uses. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) As, we know there is no economyin this world which POSSESSES INFINITE resources to produce each and everything in infinite quantities. Therefore, if an economy decides to produce a quantity of one commodity, then they have to SACRIFICE the productionof ANOTHER commodity. (ii) Resources in every economy are always scarce. But the available resources can be put to alternative uses. Therefore, an economy will always prefer to make use of its resources in production of those goods and services that are most required and sacrifice the production of less-required goods and services. |
|
| 956. |
What are the components of Aggregate Demand? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Private CONSUMPTION expenditure(II) Investment expenditure (iii) Government expenditure(iv) Net EXPORTS. While studying two sector mode, AD is the sum total of consumption demand and investment demand, i.e. AD=C+I. |
|
| 957. |
Other things remaining the same, when in a country the market price of foreign current falls, national income is likely: |
|
Answer» to RISE |
|
| 958. |
The price of commodity is Rs. 15 per unit and its quantity demanded is 500 units. Its quantity demanded rises by 80 units as a result of fall in its price by 20 per cent. Calculate its price elasticity of demand. Is its demand inelastic ? Give reason for your answer. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("Original Quantity (Q) = 500 units"," % Change in Price "=-20%),("Change in Quantity "(Delta Q)=80" units"," ELASTICITY of Demand (ED) = ?"),("New Quantity "(Q_(1))=580" units",):}` Percentage change in demand `=(Delta Q)/(Q)xx100=(80)/(500)xx100=16%` Price Elasticity of Demand (ED) `=("% Change in quantity demanded")/("% Change in price")=(16%)/(-20%)` Price Elasticity of Demand (ED) `=(-)0.8` `ED=(-)0.8`, Demand is less elastic because `ED lt 1`. |
|
| 959. |
Are the following statements true or false ? Give reasons. End - use of the goods categorise the goods as intermediate goods and final goods. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 960. |
Measurement of national income suffers from various limitations which leads u to conclude that it is not an overall appropriate measure of welfare of people, still national income accounting is done and national income estimates are prepared. Justify. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) National income accounting helps in IDENTIFYING specific economic ACHIEVEMENTS of a country. (ii) It provides an objective base of evalution and review of policies implemented. (III) It indicates specific contribution of each sector of the economy. Inspite of certain limitations, it is a MEASURE of economic production if not overall welfare. |
|
| 961. |
bothAPC and APSfallwith increase in nationalincome, doyouagree withgivenstatement ? |
| Answer» Solution :NO I donotagree WITHTHE GIVENSTATEMENT, WITHINCREASE in nationalincome, proportion of incomeconsumed (APC) falls,butproportion of incomesaved(APS) RISES. | |
| 962. |
Which one of the following bundles of goods cannot be produced with the resources the economy currently has? |
|
Answer» A |
|
| 963. |
If the value of average propensity to consume is given as 0. 75, the value of average propensity to save would be |
| Answer» SOLUTION :APS=0.25 | |
| 964. |
A monopolist can sell any quantity he likes at a price. Give reasons with true or false. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :False: A monopolist cannot sell any QUANTITY he likes at a price. (i) A monopolist faces a downward sloping DEMAND curve because of price DISCRIMINATION which means that a monopolist can sell more quantity only by lowering the price. (II) A monopolist controls only the supply of the product and not the demand of the product. |
|
| 965. |
When the price of a good rises form Rs 20 per unit to Rs 30 per unit, the revenue of the firm producing this good rises from Rs 100 to Rs 300. Calculate the price elasticity of supply. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Price, `P = Rs 20, TR = Rs 100` `:.` Quantity DEMANDED, `Q = (TR)/(P) = (100)/(20) = 5` Price, `P_(1) = Rs 30, TR = Rs 300` `:.` Quantity demanded, `Q_(1) = (TR)/(P) = (300)/(30) = 10` `DP = P_(1) - P = Rs 30 - Rs 20 = Rs 10` or `DQ = Q_(1) - Q = 10 - 5 = 5` units `:. E_(s) = (Delta Q)/(DeltaP) xx (P)/(Q) = (5)/(10) xx (20)/(5) = 2` |
|
| 966. |
What is difference between intermediate goods and final goods ? |
Answer» SOLUTION :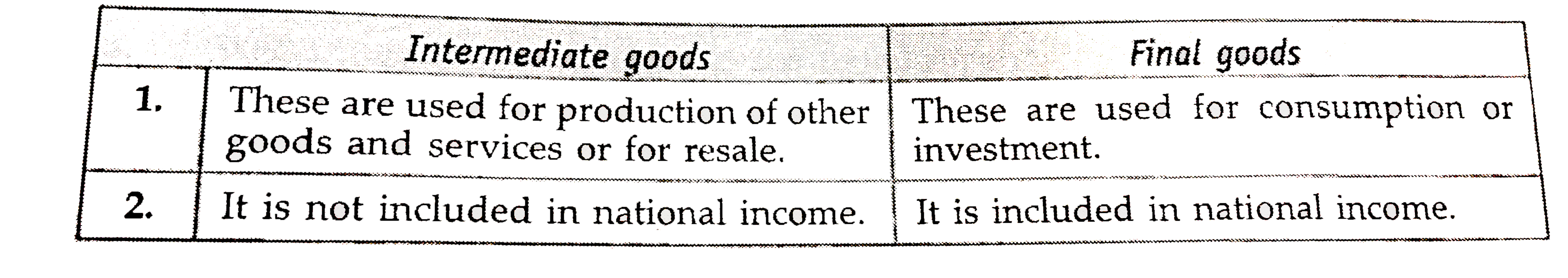
|
|
| 967. |
Scarcity is a situation in which ……….. . |
|
Answer» 1.wants exceed the resources AVAILABLE to SATISFY them |
|
| 968. |
What do you mean by an 'inferior good'? Give some examples. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) A good is called .inferior goods. when its demand falls with a rise in the income of a consumer and vice- versa. (ii)For example, JOWAR or Bajra for a POOR person. (iii) A good is inferior in a RELATIVE terms. It means, a good is inferior or normal is determined by the income level of a consumer. (iv)When a consumer moves to higher income, he/she MAY consider some goods below their income status, and treats them as inferior. |
|
| 969. |
Firm A sells to firm B for Rs. 50 crores and fro Rs. 70 crores to private consumption. Firm B sells fro Rs. 80 crores to firm C. Fim c sells for Rs. 100 crores to private consumption. Calculate value added by Firm A, B and C. |
Answer» 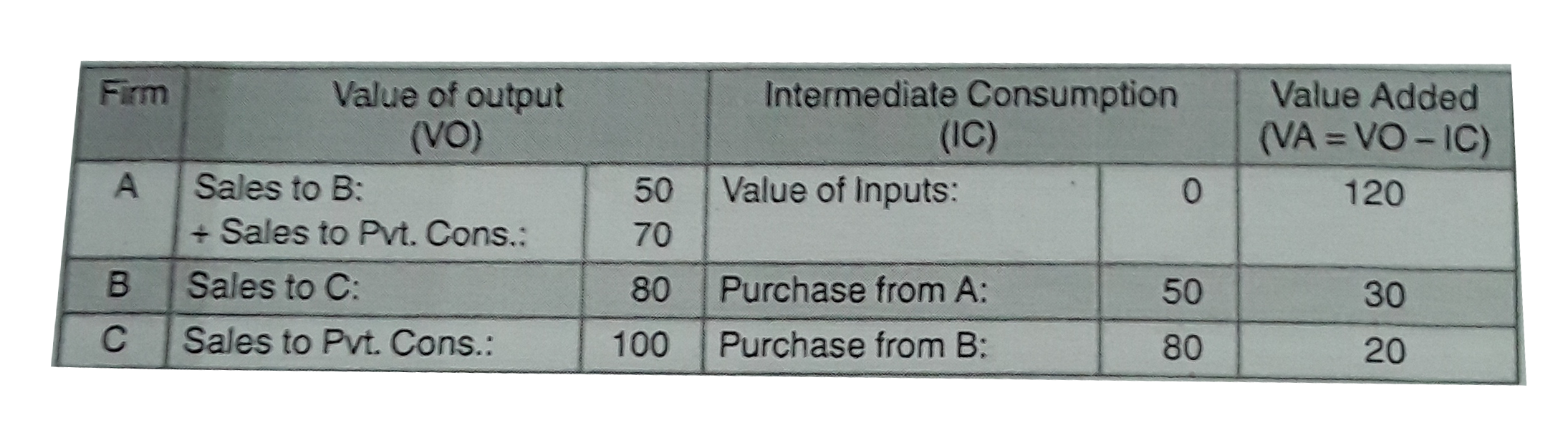 Value added : Firm A= RS. 120 crores, Firm B= Rs. 30 crores Firm C= Rs. 20 crores. |
|
| 970. |
Describe any two functions performed by money. |
| Answer» | |
| 971. |
If the Real GDP is Rs.400 and Nominal GDP is Rs.450, calculate the Price Index (base = 100). |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :We know, Real GDP = `("No MINAL GDP")/("Price INDEX")xx100` `400=(450)/("Price Index")xx100` Price Index `= (450)/(400)xx100=112.50` |
|
| 972. |
Which of the followingwill increasethe moneysupply ? |
|
Answer» FALL in repo rate |
|
| 973. |
Explain the term revenue expenditure of the government . |
| Answer» Solution :Revenue expenditure is the expenditure on items which do not lead to creation of any asset or REDUCTION in liabilities e.g., PAYMENT of SALARIES , maintenance of public PROPERTY , providing FREE services to people etc. | |
| 974. |
What is meant by market period ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Market period REFERS to a very short period in which no adjustment can take place in supply in RESPONSE to a CHANGE in demand/price. | |
| 975. |
It makes possible the maintenance of business accounts |
| Answer» | |
| 976. |
Price elasticity of demand explains qualitative relationship between price and demand. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE : ED explains quantitative RELATIONSHIP between price and demand. | |
| 977. |
What do you understand by ex-post saving and ex-post investment ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Ex-post saving refers to the actual saving in an economy during a YEAR. Ex-post INVESTMENT refers to the actual investment in an economy during a year. | |
| 978. |
Explain the effect of rise inforeignexchangerate on (a) balance of trade and (b) national income. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) RISE in foreignexchange rate makes importscostlier and exports cheaper. This will reduce demand for importsand INCREASE demand for exports. This will have POSITIVE effect on balance of trade. (b) Since rise in foreignexchange rate reduces importsand increase exports, ithas a positive effect on GDP. Through the expenditure method of estimating GDP, rise in exports raises GDP while FALL in importsalso raises GDP. |
|
| 979. |
How should the following be treated in estimating national income of a country ? Give reasons. Payment of corporate tax. |
| Answer» Solution :No, as it is a transfer payment. ALSO it is a part of PROFITS so should not be SEPARATELY ADDED. | |
| 980. |
Export and import of goods is also knows as: |
|
Answer» INDIVISIBLE Trade |
|
| 981. |
Classify the following as factor income or transfer income Salaryreceived by an employee of State Bank of India. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FACTOR INCOME | |
| 982. |
If price elasticity of demand for a product is equal to one, what will be the nature of its demand curve ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Demand curve of a PRODUCT with UNITARY elastic demand is a rectangular HYPERBOLA. | |
| 983. |
"An economy always produces on but not inside PPC. Defend or refute. |
| Answer» Solution :The GIVEN statement is REFUTED. An ECONOMY operates on PPC, only when resources are fully and efficiently utilised. It means, if there is unemployment or inefficient use of resources, the economy may operate inside PPC. So, the economy may operate at point .H., in addition to the points on the curve AB on PPC. | |
| 984. |
Crops raised by using new technology under New Agricultural Strategy were prone to attack by : |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 985. |
Which of the following items is entered on the credit side of BOP account? |
|
Answer» Investment from ABROAD |
|
| 986. |
State geometric or point method of measuring ES (in case of straight line supply curve). |
|
Answer» Solution :Case I : More than Unitary Elastic Supply ES `=("Intercept on X-axis with initial quantity")/("Quantity supplied at that price")=(QR)/(OQ)` Thus, we can get the value of elasticity of supply by dividing QR by OQ. Since, in the FIGURE , `QR GT OQ`, `ES=QR//OQ` will be greater than `1`.  Case II : Less than Unitary Elastic Supply `ES=("Intercept on X-axis with initial quantity")/("Quantity supplied at that price")=(QR)/(OQ)` extended MEETS X-axis to the right ofthe point of origin so that `QR lt OQ`. Therefore, the elasticity of supply `QR//OQ lt 1`  Case III : Unit Elastic Supply `ES=("Intercept on X-axis with initial quantity")/("Quantity supplied at that price")=(QR)/(OQ)` In the GIVEN diagram, supply CURVE when extended meets the X-axis exactly at the point of origin. So that `QR=OQ`. Therefore, there PES will be equal to 1 
|
|
| 987. |
How does the total fixed cost change when output changes? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TOTAL FIXED cost does not change with the change in output. | |
| 988. |
A horizontal supply curve parallel to the quantity axis implies that the elasticity of supply is |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 989. |
Explain the concept of ''real income'' . Explain why, due to the presence of externalities, real national income in itself' cannot be treated as a true index of welfare. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Conceptually, real income means the amount of goods and SERVICES which can be purchased from the money income one has. From the given money income we can find real ICOME by dividing money (or nominal) income by price index. Externalities REFER to the benefits /harms caused by one's activities without any compensation received/paid in return. Real income does not take into account these externalities, good or bad. Due to the presence of these externalities, national income is either underestimated in case of good externalities or OVERESTIMATED, in case of bad externalities. |
|
| 990. |
When planned saving is less than planned investment, then, |
|
Answer» National INCOME is LIKELYTO fall |
|
| 991. |
From the data given below about an economy. Calculate (a) investment expenditure and (b) consumption expenditure (i) Equilibrium level of income 5000 (ii) Autonomous consumption 500 (iii) Marginal propensity to consumer 0.4 |
|
Answer» Solution :Income Y = 5,000, AUTONOMOUS CONSUMPTION, `bar(c) = 5000, MPC, bar(c) = 0.4` Income = Y = Rs 5000 `MPC = c = 0.40` Now `C = bar(c) + cY` `bar(c) = 500 + 0.40 xx 5000` `bar(c) = 500 + 2000` `bar(c) = 2500` `Y = C + I` `5000 = 2500 + I` `I = 2500` `:.` (a) I = Rs 2500 (b) c = Rs 2500 |
|
| 992. |
In an economy, S = -100 + 0.6Y is the saving function, where S is saving and Y is National Income. If investment expenditure is 1100. Calculate. (i) Equilibrium level of National Income (ii) Consumption expenditure of equilibrium level of National Income |
|
Answer» Solution :SAVING function, `S = -100 + 0.6Y` Investment, `I = 1,100 Y`= NATIONAL income (i) We know that `S = I` Given `S = - 100 + 0.6Y` `rArr I = - 100 + 0.6Y rArr 1,100 = - 100 + 0.6Y` `uarr rArr 1,200 = 0,6Y | Y = 1,200 xx (10)/(6) = 2,000` `:.` Equilibrium level of National Income, `Y = 2,000` (ii) `Y = C + I` `2,000 = C + I rArr C = 2,000 - 1,100 = 900` `:.` Consumption expenditure at equilibrium level = 900 |
|
| 993. |
Study the statements given below and state whether demand will be elastic or inelastic citing reasons for your answer : (i) Demand for tea by a habitual cofee.(ii) A consumer postpones the purchase of a refrigerator till the off - season sale. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) INELASTIC. It BECOMES necessity for him. (ii) ELASTIC. Its PURCHASE can be postponed. |
|
| 994. |
Is deficit financing (printing of new currency) always beneficial? Comment. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Deficit FINANCING is beneficial if it promotes ECONOMIC growth by creating new INFRASTRUCTURE and increases productive capacity of the economy. But there is always fear of excess money in the economy than what is required leading to inflationary pressure. So, it is not always beneficial. Value - CRITICAL thinking. |
|
| 995. |
Define direct tax . Give two examples of direct taxes. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :When liability to PAY a tax and the burden of that tax lies on the same PERSON , it is called DIRECT tax , e.g., income tax and CORPORATE tax . | |
| 996. |
When total revenue is maximum and constant marginal revenue is also maximum |
| Answer» Solution :False : It is so because when total revenue is MAXIMUM and constant, MARGINAL revenue is ZERO. | |
| 997. |
Give the meaning of operating surplus. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Operating surplus REFERS to the sum TOTAL of income from property (RENT+ royalty + interest ) and income from entrepreneurship (PROFIT). | |
| 998. |
Given the formula for measuring price elasticity of demand according to percentage method. |
|
Answer» Solution :Elasticity of demand (ED) PERCENTAGE CHANGE in `= ("quantity demanded")/("Percentage change in PRICE")` |
|
| 999. |
What are the functions of a Commercial Bank ? |
| Answer» Solution :MAIN function of a Commerical Bank are : (i) Accepting deposits , (ii) Giving LOANS and advances, (iii) Providing overdraft facility , (IV) Peforming agency functions and (V) Peforming general utility sevices. | |
| 1000. |
Define cost. State the relation between marginal cost and average variable cost. |
|
Answer» Solution :Cost is the sum TOTAL of explicit cost, IMPLICIT cost and certain MINIMUM profit (normal profit). (i) As long as MC is below AVC, AVC curve falls till their intersection at point E. (ii) When MC curve COMES to fall, it falls more RAPIDLY than AVC curve and reaches its minimum point B earlier than the AVC curve reaches its minimum point E. Therefore, MC curve is rising from B to E whereas AVC curve is still falling from A to E. (iii) When MC curve is rising, it cuts the AVC curve at its minimum point E and after that point MC is above than AVC. 
|
|