Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 92701. |
2 g of benzoic acid (C_(6)H_(5)COOH)dissolved in 25 g of benzene shows a depression in freezing point equal to 1.62 K. Molar depression constant for benzene is 4.9 K kg mol^(-1). What is the percentage association of acid if it forms dimer in solution ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The given quantities are : `w_(2)=2g , "" K_(f)=4.9 "K kg mol"^(-1)`, `w_(1)=25 g, "" Delta T_(f)=1.62 K` Substituting these values in equation, `M_(2)=(K_(f)xx w_(2)xx1000)/(Delta T_(f)xx w_(1))` `= (4.9"K kg mol"^(-1)xx 2g xx 1000 g kg^(-1))/(25 g xx 1.62 K)` `= 241.98 g mol^(-1)` Thus, experimental molar mass of benzoic acid in benzene is `= 241.98 g mol^(-1)` Now consider the following equilibrium for the acid : `2C_(6)H_(5)COOH HARR (C_(6)H_(6)COOH)_(2)` If x represents the DEGREE of association of the solute then we would have (1 - x) mol of benzoic acid left in unassociated form and correspondingly `(x)/(2)` as asociated moles of benzoic acid at equilibrium. Therefore, total number of moles of particles at equilibrium is : `1-x+(x)/(2)=1-(x)/(2)` Thus, total number of moles of particles ast equilibrium equals vant.s Hoff factor (i). But `i=("Normal molar mass")/("ABNORMAL molar mass")` `=(122 g mol^(-1))/(241.98 g mol^(-1))` or `(x)/(2)=1-(122)/(241.98)=1-0.504 = 0.496` or `x=2xx0.496=0.992` Therefore, degree of association of benzoic acid in benzene is 99.2 %. |
|
| 92702. |
2 g of benzoic acid (C_(6) H_(5) COOH) dissolved in 25 g of benzene shows a depressionc in freezing point equal to 1.62 K. Molal depression constant for benzene is "4.9 K kg mol"^(-1). What is the percentage association of acid if it forms dinner in solution? How many mL of "0.1 M HCl" are required to react completely with 1 g mixture of Na_(2) CO_(3) and NaHCO_(3) containing equimolar amounts of both? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`"LET MASS of "Na_(2)CO_(3)=xg` `therefore"mass of "NaHCO_(3)=(1-x)g` `therefore"moles of "Na_(2)CO_(3)="moles of "NaHCO_(3)` `(x)/(106)=(1-x)/(84)` `x=0.558g` `"Number of moles of "Na_(2)CO_(3)=(0.558)/(106)="0.00526 mol"` `"Number of moles of "NaHCO_(3)="0.00526 mol"` `Na_(2)CO_(3)+2HCl rarr 2NaCl +H_(2)O +CO_(2)` `NaHCO_(3)+HCl rarr NaCl+H_(2)O+CO_(2)` Total number of moles of HCl required `=(2xx0.00526)+0.00526` `="0.01578 mol"` `therefore"VOLUME 0.1 M HCl"=("Number of moles")/("molarity")` `=(0.01578)/(0.1)=0.1578L` `=157.8mL` |
|
| 92703. |
2 g of a radioactive sample having half life of 15 days was synthesised on 1^(st) Jan 2009. The amount of the sample left behind on 1^(st) March, 2009 (including both the days) |
|
Answer» 0.125 g GIVEN, `t_(1//2) = 15` days Total time, `T = 60` days `:.` No. of half-lives, n = ? Also given, initial AMOUNT of sample, `N_(0) = 2g` `:.` Sample PRESENT after 4 half lives, `N= ?` `N = ((1)/(2))^(n) N_(0)` `rArr N = ((1)/(2))^(4) xx 2 = (2)/(16) = 0.125g` |
|
| 92704. |
2 g of a radioactive sample having half life of 15 days was synthesised on 1st Jan 2009. The amount of the smaple left behind on 1st March, 2009 (including btoh the days) |
|
Answer» 0.125 g `=60` GIVEN `t_(1//2)=15` days total time `T=60` days `:.`no of HALF lives N=? `T=nxxt_(1//2)implies60=nxx10impliesn=4` Also given initial amount of sample `N_(0)=2g ` `:.` sample PRESENT after 4 half lives N=? `N=(1/2)^(n)N_(0)` `impliesN=(1/2)^()xx2=2/16=0.125g` |
|
| 92705. |
2 g of a base whose eq.wt is 40 reacts with 3 g an aid .The eq.wt of the acid is |
|
Answer» 40 |
|
| 92706. |
2 g each of the solutes A and B ( mol mass of A gt B) are dissolved separately in 20 g each of the same solvent C. Which will show gr eater lowering of vapour pressure and why ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`"for dilute solutions, "(p^(@)-p_(s))/(p^(@))=(w_(2)M_(1))/(w_(1)M_(2)) or (DELTAP)/(p^(@))=(w_(2)M_(1))/(w_(1)M_(2))` `"For same SOLVENT, "p^(@)=" constant, "M_(1)="constant. Also, given that "w_(2)=w_(A)=w_(B)=2g, w_(1)=w_(C)=20 g` Hence, `(Deltap_(A))/(Deltap_(B))=(M_(B))/(M_(A))." As "M_(A) gt M_(B)`, therefore, `Deltap_(B) gt Deltap_(A)`, i.e., B will show greater lowering of vapour pressure. |
|
| 92707. |
2 F of electricity will liberate 1 gram atom of the metal from the solution of |
|
Answer» NaCl `therefore 2-=1mol.` of Ba`-=` 1 G of atom of Ba. |
|
| 92708. |
2-ethoxy propane is formed from ethyl bromide and what ? |
|
Answer» SODIUM ETHOXIDE |
|
| 92709. |
2-ethoxy propane is effectively prepared from |
|
Answer» ISOBUTYL IODINE |
|
| 92710. |
Write the relavant chemical equations : 2-chloropropane to l-propanol |
| Answer» Solution :`CH_(3)- overset(overset(Cl)(|))(CH)-CH_(3) overset("ALC KOH")rarr CH_(3)-CH=CH_(2) underset(2. H_(2)O_(2)//OH^(-))overset(1. BH_(3))rarr CH_(3)-CH_(2)-overset(overset(OH)(|))(CH_(2))` | |
| 92711. |
2-Chlorobutane was treated with alc. KOH and the product formed was reacted with dil. KMnO_(4) to give the product B. The structure of B is : |
|
Answer» `CH_(3) - underset(OH)underset(|)(CH) - CH_(2) - CH_(3)` |
|
| 92712. |
2-chlorobutane is heated with alcoholic NaOH, the product formed in larger amount is |
|
Answer» 1-butene |
|
| 92713. |
2-Chloro-2-methylpentane on reaction with sodium methoxide in methanol yields (I). C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)underset(CH_(3))underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)-OCH_(3). (II). C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)=CH_(2) (III). C_(2)H_(5)CH=underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)-CH_(3). |
|
Answer» all these `S_(N^(1))`  . .
|
|
| 92714. |
2-Chloro-2-methylpentane on reaction with sodium methoxide in methanol yields (I) C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)underset(CH_(3))underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)-OCH_(3) (II) C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)=CH_(2) (III) C_(2)H_(5)CH=underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)-CH_(3) |
|
Answer» all of these `underset("2-Chloro-2-methylpentene")(CH_(3)CH_(2)CH_(2)-underset(Cl)underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)-CH_(3))underset(-Cl^(-))overset("Ionization")to underset(3^(@)" carbocation (I)")(CH_(3)CH_(2)CH_(2)-underset(+)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)-CH_(3))` `(I) underset(S_(N)1)overset(CH_(3)ON a)to underset("2-Methoxy-2-methylpentane (Substitution PRODUCT)")(CH_(3)CH_(2)-underset(OCH_(3))underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)-CH_(3))` `(I)underset(-H^(+))overset(E_(1))to underset("2-Methyl-2-pentene (major product)")(CH_(3)CH_(2)CH=overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)=CH_(2))+underset("2-Methyl-1-pentene (minor product)")(CH_(3)CH_(2)CH_(2)-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)=CH_(2))` |
|
| 92715. |
2-chloro-2-methylpentane on reaction with sodium methoxide in methanol yields (A) C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)underset(CH_(3))underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)-OCH_(3) (B) C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)=CH_(2) (C) C_(2)H_(5)CH=underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)-CH_(3) |
|
Answer» (A) and (C) Elimination dominate over substitution in the given REACTION but all the PRODUCTS are possible. |
|
| 92716. |
2-chloro-2-methylpentane on reaction with sodium methoxide in methanol yields- I.CH_2H_5CH_2-overset(CH_3)overset(|)underset(CH_3)underset(|)C-OCH_3 II.C_2H_5CH_2-underset(CH_3)underset(|)C=CH_2 III. C_2H_5CH=underset(CH_3)underset(|)C-CH_3 |
|
Answer» both I and III 
|
|
| 92717. |
2-chloro-2-methylpentane on reaction with sodium methoxide in methanol yields: (a) C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)-OCH_(3) (b) C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)=CH_(2) (c) C_(2)H_(5)CH_(2)=underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)-CH_(3) |
|
Answer» all of these |
|
| 92718. |
2-Chloro -2-methylpentane on reaction with sodium methoxide in methanal yields : |
|
Answer» (a) and (B) 
|
|
| 92719. |
2-cetoxybenzoic acid is an |
|
Answer» antipyratic, analgesic |
|
| 92720. |
2-Butyne undergoes following reactions in steps as indicaed. Identify A to H. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 92721. |
2-Butyne on oxidation with alkaline KMnO_(4) at 298-303 gives : |
|
Answer» Oxalic ACID |
|
| 92722. |
2-butyne is reduced to trans-but-2-ene using |
|
Answer» `H_(2)//Ni` 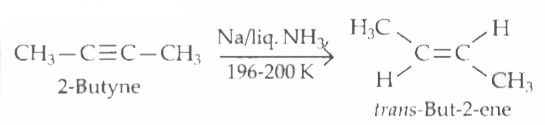
|
|
| 92723. |
2-Butyne can be prepared from which of following compounds? |
|
Answer» `CH_3-UNDERSET(CL)underset(|)OVERSET(Cl)overset(|)C-underset(Cl)underset(|)overset(Cl)overset(|)C-CH_3`<BR>`CH_3-CH_2-underset(Br)underset(|)overset(Br)overset(|)C-CH_3` |
|
| 92724. |
2-butanone can be obtainedheating a mixture of calcium salt of |
|
Answer» FORMIC ACID and BUTYRIC acid |
|
| 92725. |
2-butanol overset("conc. " H_2SO_4)to undersetA"1-butene"+undersetB"2-butene" Which are correct statements ? |
|
Answer» A is Saytzelf PRODUCT B is not |
|
| 92726. |
2-butanol on dehydration mainly gives, |
|
Answer» `CH_3CH_2CH=CH_2` |
|
| 92727. |
2-Bromopentane is heated with potassium ethoxide in ethanol. The major product obtained is |
|
Answer» pent-1-ene |
|
| 92728. |
2-bromopentane is heated with pottasium ethoxide in ethanol the major product is : |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 92729. |
2-bromopentane is treated with alcoholic KOH solution the reaction respectively are : |
|
Answer» `underset("2-Bromopentane")(CH_(3)-overset(Br)overset(|)CH-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-CH_(3) overset(KOH (alc))to(CH_(2) = CH -CH_(2)-CH_(2) - CH_(3) + CH_(3) - CH= CH-CH_(2)CH_(3)` (E & Z) HENCE, 5 products will formed. |
|
| 92730. |
2-Bromobutane (A) is treated with Nal in the presence of dry acetone to give compound 'B'. The compound 'B' is boiled with moist silver oxide to give compound 'C'. Identify compounds 'B' and 'C' . How many optical isomers are possible for compound 'C' / |
|
Answer» 2-iodobutane, Butan-2-ol, 2 isomers |
|
| 92731. |
2-Bromobutane reacts with OH^(-) in H_(2)O to give 2-butanol. The reaction involves |
|
Answer» retention in configuration |
|
| 92732. |
2-Bromo-2, 3-dimethylbutane is treated with alcoholic potash. Write the major product |
|
Answer» Solution :APPLYING ZAITSEV rule, bromine must be lost from C-2 and hydrogen from C-1 or C-3, during DEHYDROBROMINATION REACTION The major PRODUCT is 2, 3-dimethyl-2-butane 
|
|
| 92733. |
2-Acetoxy benzoic acid is used as an |
|
Answer» antimalarial 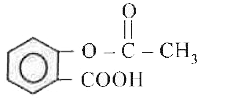
|
|
| 92734. |
2-Acetoxy benzoic acid is used as |
|
Answer» Antimalaria |
|
| 92735. |
2-Acetoxy benzoic acid is |
|
Answer» ANTISEPTIC |
|
| 92736. |
2-Acetoxy benzoic acid can be used as |
|
Answer» ANTISEPTIC |
|
| 92737. |
2 . 76 g of silver carbonate on beingstrongly heated yields a residue weighing . |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 92738. |
2.5 of a mixture of BaO and CaO when heated with H_(2)SO_(4) , produced 4.713 g of the mixed sulphates . Find the percentage of BaO present in the mixture. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 92739. |
2, 4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine test is used for : |
|
Answer» carboxylic ACID GROUP |
|
| 92740. |
2 : 4 Dinitrophenyl hydrazine is an example for |
|
Answer» TRIDENTATE LIGAND  is a monodentate ligand. |
|
| 92741. |
2, 4-Dinitroaniline underset((ii)" Anisole")overset((i) NaNO_(2)//HCl (273 K))(rarr) Z. Compound Z is |
|
Answer»

|
|
| 92742. |
2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid is the important weed killer known as 2,4 - D. Outline its synthesis. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 92743. |
2, 4-dichloro phenoxyacetic acid is used as a |
|
Answer» Insecticide |
|
| 92744. |
2,4- dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is used as a: |
|
Answer» Fungicide |
|
| 92745. |
2, 4, 6 -trinitrochorobenzene is warmed with water gives |
|
Answer» piciric acid |
|
| 92746. |
2-3% solution of iodine in alcohol-water is called _______ |
|
Answer» |
|
| 92747. |
2, 3-dimethyl-2-butene, on reductive ozonolysis gives |
|
Answer» Acetone |
|
| 92748. |
2, 2-dichloro butane on boiling with aq. Potash gives, |
|
Answer» BUTANAL |
|
| 92749. |
1^(st) law of thermodynamics introduces the concept of _______ . |
|
Answer» temperature |
|
| 92750. |
1st law of thermodynamic is represented by the equation. |
|
Answer» `/_\E=Q+W` |
|



