Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 44901. |
A parallel beam of light (lambda =500) is incident at an angle alpha = 30^(@) with the normal to the slit plane in Young's double-slit experiment. Assume that the intensity due to each slit at any point on the screen is I_(0). Point O is equidistant from S_(1) and S_(2). The distance between slits is 1 mm. Then |
|
Answer» the INTENSITY at O is `4 I_(0)` CORRESPONDING PHASE difference, `Delta phi = (2pi)/(lambda) XX Delta x` `= (2 pi (0.5 xx 10^(-3)))/(5000 xx 10^(-10)) = 2000 pi = 2 pi xx 1000` O is point corresponding to a maxima with the point at 1m below O corresponding to central maixma. |
|
| 44902. |
Even though the average current in the circuit is zero, how does an electric bulb glow? |
| Answer» Solution :The direction of CURRENT is changing for every half a CYCLE. So if we TAKE the simple addition it gives zero value. But here we have to CONSIDER SQUARE value of emf and current and their mean square value which will give you a non-zero value | |
| 44903. |
Statement-I : The time period of a simple pendulum on a setellite orbiting the earth is infinite. Statement-II : The time period of a satellite T prop(1)/(g) |
|
Answer» STATEMENT-I is true, Statement-II is true and |
|
| 44904. |
In the above Wustration, if rectangle ABCO along with the particle at Pis rotated by an angle of 180^(@) about the x-axis, find the position of the particle w .r.t point O. |
Answer» SOLUTION :`vecr=xhati+yhatj=2.5hati-2hatj`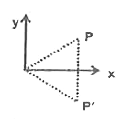
|
|
| 44905. |
Which physical quantity in a nuclear reaction is considered equivalent to the Q - value of the reaction? |
| Answer» Solution :Q-value of REACTION is the DIFFERENCE in total MASS ENERGY of reactants and total mass energy of products. | |
| 44906. |
Two cells each of 5V are connectedin series across a 8 Omega resistor and three parallel resistors of 4Omega, 6 Omega and 12 Omega. Draw a circuit diagram for the above arrangement. Calculate (i) the current drawn fron the cell (ii) current through each resistor. |
|
Answer» Solution :`V_1=5V , V_2=5V` `R_1=8Omega, R_2=4Omega , R_3=6Omega , R_4=12Omega` THREE resistors `R_2,R_3` and `R_4` are connected PARALLEL combination `1/R_p=1/R_2+1/R_3+1/R_4` `=1/4+1/6+1/12=3/12+2/12+1/12=6/12` `R_p=2Omega` 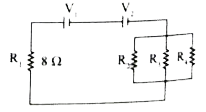 Resistors `R_1` and `R_p` are connectedin series combination `R_s=R_1+R_p` =8+2=10 `R_s=10Omega` TOTAL voltage connected series to the circuit `V=V_1+V_2` =5+5=10 V=10 V (i) Current through the circuit , `I=V/R_s=10/10` I=1 A Potential drop across the parallel combination , `V.=1 R_p=1xx2` V.=2V (ii) Current in `4Omega` resistor , `I=(V.)/R_2=2/4`=0.5 A Current in `6Omega` resistor , `I=(V.)/R_3=2/6`=0.33 A Current in `12Omega` resistor , `I=(V.)/R_4 =2/12` = 0.17A |
|
| 44907. |
In transition from the state n = 4 to n = 3 in a hydrogen like atom results in ultraviolet region, then what should be the transition for the infrared region ? |
|
Answer» `2to1` |
|
| 44908. |
उत्तल लेंस में जब वस्तु (बिंब) फोकस एवं लेंस के बीच रखी जाती है तब कैसा प्रतिबिंब बनता है |
|
Answer» काल्पनिक और सीधा |
|
| 44909. |
SI unit of inductance is henry, where 1 H = 1omegas^(-1). |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44910. |
Two balls each of mass 2kg (one at rest) undergo oblique collision is perfectly elastic, then the angle between their velocities after collision is |
|
Answer» 30° |
|
| 44911. |
Give the direction of current passing through an open surface. |
Answer» Solution :If the FINGERS of the right hand be CURLED in the sense the boundary is traversed in the loop intergral, then the DIRECTION of the thumb gives the sense in which the current is REGARDED as POSITIVE. 
|
|
| 44912. |
In the above problem , now a liquid is poured into the vessel and filled up to OQ. The central bright fringe is found to be at Q . The refractive index of the liquid is . |
|
Answer» `1.0016` |
|
| 44913. |
A cycle is fitted with small brakes and another is fitted with very brakes. The one which is more effective is |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 44914. |
What is a hole ? |
| Answer» Solution :A HOLE is a seat of POSITIVE CHARGE which is produced when an electron breaks AWAY from a covalent bond in a senuconductor. | |
| 44915. |
Two particles are projected from the same point with the same speed at different angles theta_(1)and theta_(2)to the horizontal. If their respective times of flights are T_(1), and T_2 and horizontal ranges are same then |
|
Answer» a, B, d are CORRECT |
|
| 44916. |
In an interference experiment, the ratio of the intensities of the bright and dark fringes is 16. The ratio of the amplitudes due to the two slits is |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 44917. |
For sky wave, the critical frequency gamma_c for reflection from a layer of atmosphere is gamma_c=-. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`9(N_max)^(1/2)` | |
| 44918. |
Oxygen is ionized by gamma-radiation, the ion concentration being 10^(15)m^(-3). Find the conductivity of the gas in these conditions. The ion mobilities are: b_(+)=1.32xx10^(-4)m^(2)//(V.s),b_(-)=1.81xx10^(-4)m^(2)//(V.s). |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44919. |
For hydrogen atom transition from n=2ton=3 represent which of the following line ? |
|
Answer» Absorption line of Paschen series. `(1)/(lamda)=R[(1)/(m^(2))-(1)/(N^(2))]` Here m = 2 and n = 3 is given. `(1)/(lamda)=R[(1)/(2^(2))-(1)/(3^(2))]` which REPRESENT Balmer series |
|
| 44920. |
The distance between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor is d. A metal plate of thickness d/2 is placed between the plates, without touching either of the two plates. What will be the new capacity ? |
| Answer» Solution :NEW CAPACITANCE will be double of its INITIAL VALUE. | |
| 44921. |
The wavelength of first line of Balmer series in hydrogen atom is 2, the wavelength of first of corresponding double ionized lithium atom is ………… |
|
Answer» `(LAMDA)/(3)` Here for first line in Balmer series of hydrogen atom `(1)/(lamda_(H))=Z_(H)^(2)R[(1)/(n_(f)^(2))-(1)/(3^(2))]` For `L_(i),(1)/(lamda_(Li))=Z_(Li)^(2)R[(1)/(2^(2))-(1)/(3^(2))]` `:.(lamda_(Li))/(lamda_(H))=(Z_(H)^(2))/(Z_(Li)^(2))=(1)/(9)""(Z_(Li)=3,Z_(H)=1)` `:.lamda_(Li)=(lamda_(H))/(9)` but `lamda_(H)=lamda:.lamda_(Li)=(lamda)/(9)` |
|
| 44922. |
Consider the neutron capture reaction ""^(109)Ag+nto""^(110)Agto""^(110)Ag+gamma (40-34) in which a compound nucleus (""^(110)Ag) is formed. Figure 40-18 shows the relative rate at which such events take place, plotted against the energy of the incoming neutron. Find the mean lifetime of this compound nucleus by using the uncertainty principle in the form DeltaE.Deltat~~hath. (40-35) here DeltaE is a mesure of the uncertainty with which the energyof a state can be defined. The quantity Deltat is ameasure of the time available of measure this energy. In fact here Deltat is just t_("avg"), the average life of the compound nucleus befoe it decays to its ground state. Reasoning: We see that the relative reaction rate peaks sharply at a neutron energy of about 5.2 eV.This suggests that we are dealing with a single excited energy level of the compund nucleus ""^(110)Ag. When the availabel energy(of the incoming neutron) just matches the energy of this level above the neutron) just matches the energy of this level above the ""^(110)Ag ground state, we have resonance and the reaction of Eq. 40 -34 really goes. However, the resonance peak is not infinitely sharp but has an approximate half peak is not infinitely shart but has an approximate half width (DeltaE in the figue) of about 0.20 eV. We can account for this resonance peak width by saying that the excited level is not sharply definedin energy but has an energy uncertainty DeltaE of about 0.20 eV. Calculation : Subsitiuting that uncertainty of 0.20 2V into Eq.given us Delta= t_(avg) ~~ h/(DeltaE) ~~ ((4.14 xx 10^(-15) eV.s)//2pi)/(0.20 eV) ~~ 3 xx 10^(-15) s.This is several hundraed times greater than the time a 5.2 eV neutron takes to cross the diameter ofa ""^(109)Agnucleus . Therefore , the neutron is spending this time of 3xx 10^(-15) s as part of the nucleus. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Reasoning: We see that the relative reaction rate peaks sharply at a neutron energy of about 5.2 eV.This suggests that we are dealing with a single excited energy level of the compund nucleus `""^(110)Ag`. When the available energy(of the incoming neutron) just matches the energy of this level above the neutron) just matches the energy of this level above the `""^(110)Ag` ground state, we have resonance and the reaction of Eq. 40 -34 really goes. HOWEVER, the resonance peak is not infinitely sharp but has an approximate half peak is not infinitely shart but has an approximate half width (`DeltaE` in the figue) of about 0.20 eV. We can account for this resonance peak width by saying that the excited level is not sharply definedin energy but has an energy uncertainty `DeltaE` of about 0.20 eV. Calculations: Substituting that uncertainty of 0.20 eV into Eq. 40-35 gives us `Deltat=t_("avg")~~(hath)/(DeltAE)~~((4.14xx10^(15)eV.s)//2pi)/(0.20eV)` `~~3xx10^(-15)s` this is several HUNDRED times GREATER than the TIME a 5.2 eV neutron takes to cross the diameter of a `""^(109)Ag` nucleus. Therefore, the neutron is spending this time of `3xx10^(-15)` as a part of the nucleus. 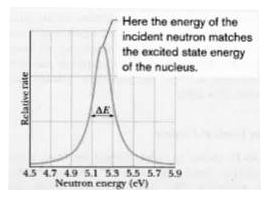
|
|
| 44923. |
A particlemoves in the x-y palnewitha constantaccelerationof 1.5m//s^(2) in the direction makingan angleof 37^(@) with the x-axis. At t=0 the particleis the origin and itsvelocity is 8.0m/s alongthe x- aixs . Findthe velocityand the position of the particleat t = 4.0s. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`13.3 m//s (41.6m, 7.2m)` | |
| 44924. |
At the moment t=0 a particle of mass m starts moving due to a force F=F_0 sin omega t, where F_0 and omega are constants. Find the distance covered by the particle as a function of t. Draw the approximate plot of this function. |
|
Answer» Solution :We have `F=F_0sin omegat` or `m(dvecv)/(dt)=vecF_0sin omegat` or `md vecv=vecF_0sin omegat dt` On INTEGRATING, `vecmv=(-vecF_0)/(omega)cos omegat+C`, (where C is integration CONSTANT) When `t=0`, `v=0`, so `C=(vecF_0)/(momega)` Hence, `vecv=(-vecF_0)/(momega)cos omegat+(vecF_0)/(momega)` As `|cos omegatle1` so, `v=(F_0)/(momega)(1-cos omegat)` THUS `s=underset(0)overset(t)int v dt` `=(F_0t)/(momega)-(F_0sin omegat)/(momega^2)=(F_0)/(momega^2)(omegat-sinomegat)` |
|
| 44925. |
A point positive charge is brought near an isolated conducting sphere as shown in figures. The electric field is best given by: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) |
|
Answer»
Electric field lines from positive charge is PERPENDICULAR to surface and outwards and from negative charge is perpendicular to surface and inwards. This PROPERTY is SHOWN in (A). |
|
| 44926. |
How mean value and peak value are related mathematically |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`I_m=2/pi I/0` | |
| 44927. |
How can a galvanometer be converted into a voltmeter to read a maximum potential difference of V ? Support your answer with related mathematical expression. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :To convert a GALVANOMETER into a voltmeter, we JOIN a suitable high resistance in series of galvanometer. If the galvanometer gives full scale deflection for a current `I_g` and has a resistance `R_G`, then to measure a potential difference up to V volt we MUST join a resistance R in series, so that `V = I_g (R_G+ R)` `:. "" R = V/(I_g) - R_G`. |
|
| 44928. |
In Young's double slit experiment, fringes of certain width are produced on the screen kept at a certain distance from the slits. When the screen is moved away from the slits by 0.1m, fringe width increases by 6xx10^(-5)m. The separation between the slits is 1 mm. calculate the wavelength of the light used. |
|
Answer» Solution :`beta=(lamdaD)/(d)`. .(i) `{beta+6xx10^(-5)}=beta.=(lamdaD.)/(d)=(lamda(D+0.1))/(d)`. . (II) EQUATION (ii)-equation (i) gives `6xx10^(-5)=(0.1lamda)/(d)` } As d=1mm `=1xx10^(-3)m`, `lamda=(6xx10^(-5)xxd)/(0.1)=(6xx10^(-5)xx1xx10^(-3))/(10^(-1))}` Arriving `lamda=6xx10^(-7)m=600nm=6000` Å Detailed Answer: `D=0.1m`, `beta=6xx10^(-5)m` `d=1xx10^(-3)m` `beta=(lamdaD)/(d)` `lamda=(betad)/(D)=(6xx10^(-5)xx1xx10^(-3))/(0.1)=(6xx10^(-8))/(0.1)` `=6xx10^(-7)m` |
|
| 44929. |
Four identical monochromatic sources A,B,C,D as shown in the (figure) produce waves of the same wavelength lambda and are coherent. Two receiver R_(1) and R_(2) are at great but equal distances from B. (i) Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when B is turned off? (iii) Which of the two receivers picks up the larger singnal when D is turned off ? (iv) Which of the two receivers can distinguish which of the sources B or D has been turned off ? |
|
Answer» `R_(1)` THUS, the wave at `R_(1)` because of B is `y_(B)=a" cos"(wt-pi)= -a" cos"wt.` The path difference fo the signal from C with that from A is `lambda` adn hence, the phase difference is `2 pi`. Thus, the wave at `R_(1)` because of C is `y_(c)=a" cos"wt.` The path difference between the signals from D with that of A is `P=R_(1)D-R_(1)A=sqrt((R_(1)B)^(2)+(BD)^(2))-(R_(1)B-AB)` 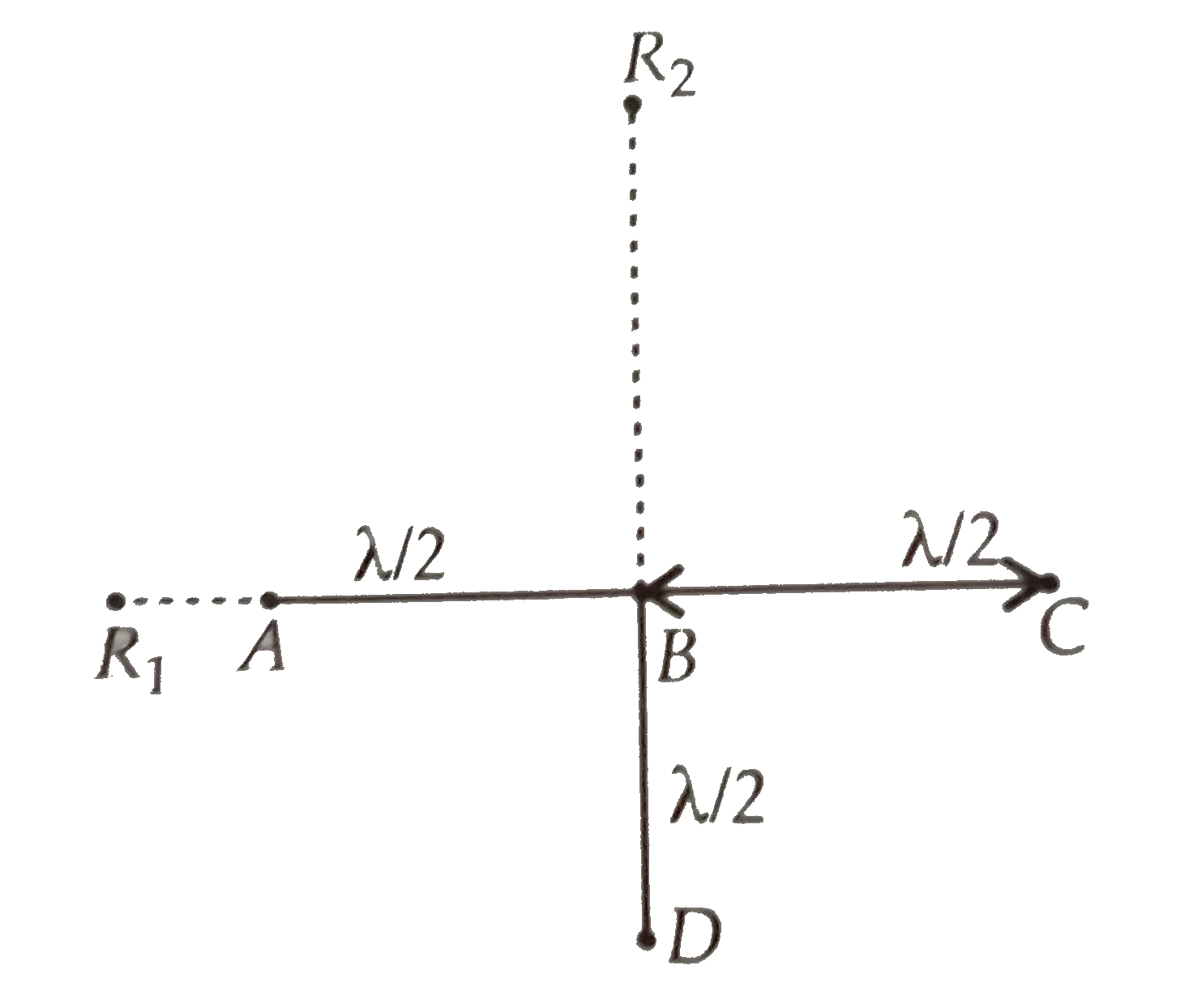 `=sqrt(d^(2)+((lambda)/(2))^(2))-(d-lambda//2)=d(1+(lambda^(2))/(4d^(2)))^(1//2)-d+(lambda)/(2)` `=d(1+(lambda^(2))/(8d^(2)))-d+(lambda)/(2)=(lambda^(2))/(8d)+(lambda)/(2)` If `d gt gt lambda,` the path difference `~(lambda)/(2)` and hence the phase difference is `pi`. ` :. y_(D)= -a" cos"wt.` Thus, the signal picked up at `R_(1)` is ` "y"="y"_(A)+"y"_(B)+"y"_(C)+"y"_(D)=0` Let the signal picked up at `R_(2)` from B be ` "y"_(B)^(')=a_(1)" cos"wt.` The path difference between signal at D and that at B is `lambda//2.` ` :. "y"_(D)^(')= -a_(1)" cos"wt` The path difference between signal at A and B is `sqrt((d)^(2)+((lambda)/(2))^(2))-d=d(1+(lambda^(2))/(4d^(2)))^(1//2)-d=(lambda^(2))/(8d)` ` :. ` The phase difference is `(2pi)/(lambda)*(lambda^(2))/(8d)=(pi lambda)/(4d)=phi~0.` Hence, ` "y"_(A)^(')=a_(1)" cos"(wt-phi)` Similarly, ` "y"_(C)^(')=a_(1)" cos"(wt-phi)` ` :.`Signal picked up by `R_(2)` is ` "y"_(A)^(')+"y"_(B)^(')+"y"_(C)^(')+"y"_(D)^(')="y"^(')=2a" cos"(wt-phi)` ` "" [ :' "y"_(B)^(')+"y"_(D)^(')=0]` ` |"y"|^(2)=4a_(1)^(2)" cos"^(2)(wt-phi)` ` :. lt I gt =2a_(1)^(2)` Thus `R_(2)` picks up the LARGE signal. |
|
| 44930. |
A ball is projected from a point in a horizontal plane with a velocity of 20 m/s at 30^(@) with the horizontal. Coefficient of restitution is 0.8, then |
|
Answer» duration for which BALL will rebound is 20 s |
|
| 44931. |
Wave length of light in denser mediumis 4000Å, it is grazing into a rarer medium. If critical angle for the pairof mediam is sin^(-1)(2/3) then the wave length of light in rarer medium is |
|
Answer» `4000Å` |
|
| 44932. |
A bar made of iron for which alpha =11xx10^(-6)""^(@)C^(-1) is 10.000 cm at 20^(@)C. At 19^(@)C the length is : |
|
Answer» `11xx10^(-6) cm` longer `Delta l =-11+10^(-5) cm` -ve sign show that length decreases. Thus, CORRECT choice is (C ). |
|
| 44933. |
The potential difference between the cathode and the target in a coolidge tube is 120 kV. What can be the minimum wavelength (in Å) of the X-rays emitted by this tube ? |
|
Answer» 0.4 `Å` |
|
| 44934. |
The variation of current and voltage in a conductor has been shown in figure. The resistance of the conductor is |
|
Answer» `4 Omega ` |
|
| 44935. |
The source is at some distance from an obstacle. Distance between obstacle and the point of observation is .b. and wavelength of light is .lambda.. Then the distance of nth Fresnel Zone will be at a distance……….from the point of observation. |
|
Answer» `(b N L)/(2)` |
|
| 44936. |
For a carnot engine the source and the sink temperatures are 527^@C and 47^@C respectively and the engine extracts 800J of heat in each cycle. What is the area enclosed by the P-V diagram in terms of energy units |
|
Answer» 480 J |
|
| 44937. |
Give some properties of a semiconductor. |
|
Answer» Solution :i. It has COVALENT bonding ii. It is CRYSTALLINE in nature . iii. It has a negative temperature COEFFICIENT of resistance . iv. Its conductivity increases with ADDITION of impurities. |
|
| 44938. |
A point charge q_(1)=+6e fixed at the origin of a conducting system, and another point charge q_(2) = -10e is fixed at x=8 nm, y=0. The locus of all points in the xy plane for which potential V=0 (other than infinity) is a circle contered on the x-axis, as shown x-coordinate of the centre of the circle is |
|
Answer» `-2` NM |
|
| 44939. |
A container is filled with a liquid that cools from 100 ""^(@)C to 70 ""^(@)C. The times that it must have taken to cool down to 80 ""^(@)C from its initial temperature approximately is |
|
Answer» 1.7 min In first case, `{:(T_1=100^@C),(T_2=70^@C):}""|""{:(T_0=30^@C),("time,"t_1=5min=300s):}` According to Newton. s law of cooling, `mc((T_(1)-T_(2))/(t))=K ((T_(1)+T_(2))/(2)-T_(0))` `mc[(100-70)/(300)] = k [(100+70)/(2)-30]` `mc[(30)/(300)] =k[(170)/(2)-30]` `mc[(1)/(10)] = k [85-30]` `rArr mc ((1)/(10)) = k(55)` For, second case, `{:(T_1=100^@C),(T_2=80^@C):}""|""{:(T_0=30^@C),("time,"t_2=t.min=t.s):}` According to Newton. s law of cooling , `mc[(100-80)/(t.)]=k [(100+80)/(2)-30]` `mc[(20)/(t.)]=k[90-30]` `rArr mc[(20)/(t.)]=k[60]` After, solving Eqs: (i) and (ii), we get t. = 3. 05 min (NEAREST answer isb) |
|
| 44940. |
ग्राम - धनात्मक (Gram -positive) जीवाणु की कशाभिका के आधार काय (basal body) में घेरो (rings) की सांख्य होती है : |
|
Answer» चार |
|
| 44941. |
The space wave propagation is utilised in |
|
Answer» only TELEVISION communication |
|
| 44942. |
What our parents do by their instinct? |
|
Answer» CARE for child |
|
| 44943. |
Suppose there are two points A and B that are having equal potential V. Can we move a charged particle between these two points without doing any work on it? By this can we assert that without applying any force the charged particle can be moved between points A and B? |
| Answer» Solution :Yes, the work done to MOVE a charged particle between points A and B is zero. But we cannot conclude that the charged particle was moved WITHOUT exerting any force on it. To understand this, let us suppose we take an object and LIFT it up from one point and finally bring it to another point that is at a same height as the previous one. In this case, the work done on the object is zero, but certainly the force exerted on the object against gravity. Similarly, force may be exerted on the charged particle in order to overcome electric fields between points A and B, but the net work done is zero (as the net work in a CONSERVATIVE field depends only on INITIAL and final positions). | |
| 44944. |
A series LCR circuit with L = 0.12 H, C = 480 nF, R = 23 Omega is connected to a 230 V variable frequency supply. What is the source frequency for which current amplitude is maximum. Obtain this maximum vlaue. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `omega_(0)=4167 "rad s"^(-1), v_(0)=663Hz` `I_(0)^("max")=14.1A` (b) `barP=(1//2)I_(0)^(2)R` which is maximum at the same frequency (663 Hz) for which `I_(0)` is maximum `barP_("max")=(1//2)(I_("max"))^(2)R=2300W`. (c ) At `omega=omega_(0)pm Deltaw` [Approximation good if `(R//2L) lt lt omega_(0)`]. `Delta omega=R//2L=95.8"rad s"^(-1), Deltav=Delta omega//2pi =15.2Hz.` POWER ABSORBED is half the peak power at n = 648 Hz and 678 Hz. At these frequencies, current AMPLITUDE is`(1//sqrt(2))` times `I_(0)^("max")`, i.e., current amplitude(at half the peak power points) is 10 A. (d) Q = 21.7 |
|
| 44945. |
Two parallel plate capacitors of capacitances C_1 and C_2 such that C_2 = 2 C_1 are connected across battery of V volts as shown in the Fig . Initially the key K is kept closed to fully charge the capacitors . The key K is now thrown open and dielectric slabs of dielectric constant K_0 are inserted in the two capacitors to completely fill the gap between the plates . Find the ratio of the energies stored in the combination before and after the introduction of dielectric slabs . |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Total initial energy of the combination `U_i = 1/2 C_i V^(2)` As the KEY K is then thrown OPEN , net charge Q remains constant but voltage V changes to `V_(f) = (V)/(K_(0))` `therefore` Total final energy of the combination `U_(f) = 1/2 C_f V_f^2 = 1/2 (K_(0) . C_(f)) ((V)/(K_(0)))^(2) = (C_(1) * V^(2))/(2 K_(0)) implies (U_(i))/(U_(f)) = K_(0)` |
|
| 44946. |
Two parallel plate capacitors of capacitances C_1 and C_2 such that C_2 = 2 C_1 are connected across battery of V volts as shown in the Fig . Initially the key K is kept closed to fully charge the capacitors . The key K is now thrown open and dielectric slabs of dielectric constant K_0 are inserted in the two capacitors to completely fill the gap between the plates . Find the ratio of the net capacitance |
|
Answer» Solution :As two capacitors are joined in PARALLEL , the net initial capacitance `C_1 = C_1 + C_2 = C_1 + 2 C_1 = 3 C_1` On introduction of dielectric slabs of dielectric constant `K_0` , new capacitances BECOME `C._1 = K_0 C_1` and `C._2 = K_0 C_2 = 2 K_0 C_1` `therefore` Net final capacitance `C_(f) = C_(1) + C_(2) = K_(0) C_(1) + 2 K_(0) C_(1) = 3K_(0) C_(1) implies (C_(i))/(C_(f)) = (3C_(1))/(3 K_(0) C_(1)) = (1)/(K_0)` |
|
| 44947. |
In the above problem, the work performed by the engine will be |
|
Answer» Solution :Work performed by the engine `W =eta Q_(1) =2/3 XX 10^(6) xx 4.2` or `W=2.8 xx 10^(6) ` JOULE |
|
| 44948. |
What is mathematical statement of Faradays laws of electromagnetic induction? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :E = `-dphi_B/dt` | |
| 44949. |
State the law of radioactivity and hence, show thatN=N_(0)e^(-lambda t). |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) `(dN)/( DT) = - lambda N` `int_(N_0)^(N) (dN)/( N) = int_(0)^(t) -lambda dt` `[log_(E)^(N) ]_(N_0)^(N) = - lambda [t]_(0)^(t)` `log_(e) (N)/(N_0)=- lambda t` `N=N_(0) e^(- lambda t)` (b) (i) `""{:(22),(11):} Na to {:(22),(11):} Ne + e^(+) +v` or, `{:(22),(11):} Na to {:(22),(11):} Xe + e^(+) + v` Basic PROCESS `p to n + e^(+) + v` (II) Isobar. |
|
| 44950. |
Which of the following from a virtual and erect image for all positions of a real object ? |
|
Answer» Convex |
|