Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39701. |
Two bodies whose masses are in the ratio 2:1 are dropped simultaneously at two places A and B where the accelerations due to gravity are g_(A)andg_(B) respectively. If they reach the ground simultaneously, the ratio of the heights from which they are dropped is |
|
Answer» `g_(A):g_(B)` |
|
| 39702. |
In an aluminium sheet there is a hole of diameter 1 m and is horizontally mounted on a stand. Onto this hole an iron sphere of diameter 1.004 m is resting. Initial temperature of this system is 25^(@)C. Find at what temperature, the iron sphere will fall down through the hole in sheet. The coefficients of linear expansion for aluminium and iron are 2.4xx10^(-5)and1.2xx10^(-5) respectively. |
|
Answer» Solution :As value of coefficient of linear EXPANSION for aluminium is more thant that for iron, it expands faster than iron. So at some higher temperature when DIAMETER of hole will exactly become EQUAL to that of iron sphere, the sphere will pass through the hole. Let it happen at some higher temperature T. Thus we have at this temperature T, `("diameter of hole" )_(Al)` = `("diameterof sphere")_("ion")` ` 1 [ 1 + alpha_(Al) (T - 25) ] = 1.004 [ 1 + alpha_("iron") ( T - 25) ]` `alpha_(Al) ( T - 25) = 0.004 + 1.004 alpha_("iron") (T - 25)` or `T = ((0.004)/(alpha_(A L) - 1.004 alpha_("iron")) + 25 ) ""^(@)C ` or T = `(0.004)/(1 xx 2.4 xx 10^(-5) - 1.004 xx 1.2 xx 10^(-5)) + 25 ` or T = `359.7^(@)` C |
|
| 39703. |
State two basic characterstic ofan oscillating system |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The BASIC CHARACTERISTICS are ELASTICITY and INERTIA. | |
| 39704. |
When a body is projected vertically up from ground, the ratio of its potential to kinetic energies at a height 'h' above the ground is 3: 4. The height above ground at which the ratio of potential to kinetic energies becomes 4:3 is |
|
Answer» `(4)/(3)H` |
|
| 39705. |
Velocity -time graph of a particle of mass 2 kg moving in a straight line is as shown in figure. Work done by all the forces on the particle is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 39706. |
three pieces of wire of the same intererinal and radius but of different length are tied to three -colliner , , equispesd pege in the ceiling of a room knotted together at their other ends so that the side wirs subtend the same angle alpha with the middaone .If a load P is attached to the knot ,calculate the tension in the wires. |
|
Answer» <P> |
|
| 39707. |
The displacement of a particle of mass 3 gm executing S.H.M is given by y = 3 sin(0.2 t) in S.I units. The K.E of a particle at a point which is at a distance equal to 1/3 of its amplitude from its mean position |
|
Answer» `12 XX 10^(3)J` |
|
| 39708. |
Estimate the average mass density of a sodium atom assuming its size to be about 2.5Å. (Use the known values of Avagardo's number and the atomic mass of sodium). Compare it with the mass density of sodium in its crystalline phase : 970 kg m^(-3). Are the two densities of the same order of magnitude ? If so, why ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Radius of sodium atom `r=2.5Å` `=2.5xx10^(-10)m` Volume of sodium atom `V.=(4)/(3)pir^(3)` `=(4)/(3)xx3.14xx(2.5xx10^(-10))^(3)` `65.416xx10^(-30)` `~~65.42xx10^(-30)m^(3)` No. of atoms in 1 mole `N=6.023xx10^(23)` volume of 1 mole of sodium V=NV. `=65.42xx10^(-30)xx6.023xx10^(23)` `=394.02xx10^(-7)` `~~3.94xx10^(-5)m^(3)` Mass of 1 mole of sodium = sodium mass `M=23g=23xx10^(-3)kg` Average density of 1 mole atoms of sodium `rho=(M)/(V)` `:.rho=(23xx10^(-3))/(3.94xx10^(-5))` `=5.8375xx10^(2)` `:.rho~~584kgm^(-3)` Density of sodium in crystalline FORM `rho~~970kgm^(-3)` Ratio `(rho)/(rho.)=(584)/(970)` =0.6020 0.6 Yes, both densities are in same no. of power. Because atoms are BOUND strongly in solid form. Therefore, ATOMIC density is close to density of solid. |
|
| 39709. |
What is the temperature of the aluminium junction in the steady state of the system shown in Fig. Length of the load =15.0 cm, length of the aluminium rod =10.0 cm temperature of the furnace = 400" "^(@)C, temperature of the other end =0" "^(@)C. The area of cross section of the lead rod is twice that of the aluminium rod. (Thermal conductivity of steel =34.9" J s"^(-1)m^(-1)K^(-1), and copper =205" J s"^(-1)m-1" "K^(-1)) |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`T=56.24^(@)C` | |
| 39710. |
A particle in a certain conservative force field has a potential energy given by V=(20xy)/(z). The force exerted on it is |
|
Answer» `((20y)/(z))HAT(i)+((20x)/(z))hat(J)+((20XY)/(z^(2)))hat(K)` |
|
| 39711. |
A vessel is filled with mercury to a hiegt of 0.9 m . Could the vessul be completely empited with the aid of a siphon ? If not , to what extent can it be empited ? (Barometer reading is 0.7 mmercury) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39712. |
Calculate the force required to move a train of 2000 quintal up on an incline plane of 1 in 50 with an acceleration of 2 ms^(-2). The force of friction per quintal is 0.5 N. |
|
Answer» Solution :Force of friction = 0.5 N per QUINTAL `f = 0.5 xx 2000= 1000`per quintal m = 2000 quintals =` 2000 xx 100` kg ` sin theta = 1/50 , a=2m//s^2` In MOVING up an inclined PLANE, force REQUIRED against gravity `= mg sin theta= 39200N` And force required to produce acceleration = ma. ` = 2000 xx 100 xx 2 = 40,0000 N` Total force required = 1000+ 39,200 + 40,0000 = 440200 N. |
|
| 39713. |
A 2 kg mass moving with a velocity of 10 mS^(-1)collides with another 6 kg mass moving in opposite direction with a velocity of 20 ms^(-1)During collision, they stick together. Find the magnitudes of their common velocity and the momentum. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39714. |
Three rods A, B and C form an equilateral triangle at 0°C. Rods AB and BC have same coefficient of expansion alpha_(1) and rod AC has alpha_2. If change in angle between AB and BC isd theta then temperature through which system is heated. |
|
Answer» `( sqrt(2) d THETA)/( 3 ( alpha_(2) - alpha_(1) ))` |
|
| 39715. |
The radius of gyration of a body about an axis at a distance of 12 cm from its centre of mass is 13 cm. Find its radius of gyration about a parallel axis through its centre of mass. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :By PARALLEL axes theorem, `M(13)^(2)=I_(0)+M(12)^(2)` `I_(0)=M(13^(2)-12^(2))=M(25)` Its radius of gyration about a parallel AXIS through its centre of mass `K = sqrt((I_(0))/(M))=sqrt(25) = 5cm` |
|
| 39716. |
A physical quantity P is related to four observables a, b, c and d as follows: P= (a^(3)b^(2))/(sqrt(c)d)The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c and d are 1%, 3%, 4% and 2%, respectively. What is the percentage error in the quantity P? |
|
Answer» `12%` The percentage error in P is `(DELTAP)/(P)xx100= [3((Deltaa)/(a))+ 2((Deltab)/(b))+ (1)/(2)((Deltac)/(c))+ (DELTAD)/(d)] xx 100` `[ 3 xx 1%+ 2 xx 3%+ (1)/(2) xx 4%+ 2%]= 13%` |
|
| 39717. |
A sphere rolls down in an inclined plane without slipping. The percentage of translational energy in its total energy is |
|
Answer» `29.6%` Translational K.E `(E_("TRANS"))=(1)/(2)Mv^(2)=(1)/(2)MR^(2)omega^(2)` `E_("rot")=E_("rot")+E_("trans") =(1)/(5) MR^(2)+(1)/(2) MR^(2) omega^(2)=(7)/(10) MR^(2) omega^(2)` `%"of" E_("trans")=(E_("trans"))/(E_("Tot"))xx100%=(5)/(7)%=71.4%` |
|
| 39718. |
If a simple pendulum of length 1 is about to start to make SHM, when it is brought a position so that its length has a maximum angular displacement q. If the mass of the bob is m, then the maximum K.E at its mean position is |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 39719. |
What is the difference between radiation and thermal radiation? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The total energy emitted by a body including heat, light. X-rays, y-rays etc. is CALLED radiation. The radiation emitted by a body due to its TEMPERATURE is called THERMAL radiation. | |
| 39720. |
A wire is bent in the formof a U. shape and a sider of negligible mass is connecting the two verticalslides of the U-shape. This arrangement is dipped in to soap solutiona and lifted, a thin soap film is formed in the frame. It supports a weight of 2.0xx10^(-3)N. If the length of the slider is 40 cm, what is the surface tension of the film? |
|
Answer» Solution :`W=2.0xx10^(-2)N,l=40cm=0.4m` Upward FORCE DUE to surface tesion `=Sxx2l` In equilibrium `W=Sxx2l` `S=W/(2l)=(2xx10^(-2))/(2xx0.4)=2.5xx10^(-2)Nm^(-1)` |
|
| 39721. |
Precision of measurement depends on |
|
Answer» Least count of measuring INSTRUMENT |
|
| 39722. |
Though the statement quoted above may be disputed, most physicists do have a feeling that the great laws of physics are at once simple and beautiful. Some of the notable physicists, besides Dirac, who have articulated this feeling, are Einstein, Bohr, Heisenberg, Chandrasekhar and Feynman. You are urged to make special efforts to get access to the general books and writings by these and other great masters of physics. (See the Bibliography at the end of this book.) Their writings are truly inspiring! |
|
Answer» Solution :`to` (1) Dialogue concerning the two CHIEF WORLD System By Galileo in 1632. (2) DE Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium. By NICOLAS Copernicus in 1543. (3) PHYSICA by Aristotle By Aristotle. |
|
| 39723. |
In perfect elastic collision, the relative velocity of the body before impact is: |
|
Answer» before impact is ZERO |
|
| 39724. |
Doppler's effect will not be applicable when the velocity of sound source is |
|
Answer» Equal to that of the SOUND VELOCITY |
|
| 39725. |
The molecular weight of a gas is 2. Find the root mean square velocity of its molecules at 100°C (R=8.3 "J mol"^(-1) "K"^(-1) ) |
|
Answer» `2.155 XX 10^(3) "m/s"` |
|
| 39726. |
A bar magnet of length 5.0 cm and breadth 1.2 cm is rotated about an axis passing through its center and perpendicular to its plane. Find its moment of inertia if the mass of the magnet is 200 g. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :MOMENT of inertia `I=(M(l^(2)+b^(2)))/(12)` `=200xx10^(-3)(((5xx10^(-2))^(2)+(1.2xx10^(-2))^(2))/(12))` `= 4.407xx10^(-5)kgm^(2)` |
|
| 39727. |
A bag of mass M hangs by a long thread and a bullet (mass m) comes horizontally with velocity v and gets caught in the bag. Then for the combined system (bag + bullet) |
|
Answer» momentum is m `Mv"/"(M+m)` |
|
| 39728. |
Two identical heavy spheres are separated by a distance 10 times their radius. Will an object placed at the mid-point of the line joining their centres be in stable equilibrium or unstable equilibrium ? Give reason for your answer. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :`implies` Let the MASS and radius of each identical heavy sphere be M and R respectively. An object of mass m be placed at the mid-point P of the line joining their centres. Force acting on the object placed at the midpointdue to each sphere `F_1 =F_2 =(GMM)/((5R)^2)`The direction of forces are opposite, therefore net force acting on the object is zero. This is equilibrium. If we move object towards A by distance X,  `F._1=(GMm)/((5R-x)^2)` `F._2=(GMm)/((5R+x)^2)` As `F._1 gt F_2,`therefore a resultant force `(F_1 - F_2.)` acts on the object towards sphere A, therefore object start to move towards sphere A and hence equilibrium is unstable. |
|
| 39729. |
In the Ingenhausz's methodto comparethe thermalconductivityof differentof different substance , the lengthupto whichwax meltedin copper and zinc rods are 9.3 cm and 5 cm respectively . Compare theirthermalconductivites . |
|
Answer» Solution :GIVEN and `l_(2) = 5CM` `therefore (k_(c))/(k_(z)) = (l_(c)^(2))/(l_(z)^(2)) = ((9.3 cm)/(5cm))^(2) = 3.46` Thus , the thermal conductivityof copperis 3.46 times THATOF ZINC. |
|
| 39730. |
a wooden block is floating in a liquid. About 50% of its volume is inside the liquid when the vessel is stationary. Percentage volume immersed when the vessel moves upwards with acceleration a=g.2 is |
|
Answer» 0.75 |
|
| 39731. |
The breaking strength of the cable used to pull a body is 40 N. A body of mass 8 kg is resting on a table of coefficient of friction mu=0.20. The maximum acceleration which can be produced by the cable is ( take , g=ms^(-2) ) |
|
Answer» `6 MS^(-2)` |
|
| 39732. |
In the above problem, the time taken by the displacement vectors of the two fragments to become perpendicular to each other is |
|
Answer» 1s |
|
| 39733. |
What is the temperature of the triple - point of water on an absolute scale whose unit interval size is equal to that of the Fahrenheit scale ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Rotation between Fahrenheit and kelvin scale. `(T_(F)-32)/(180)=(T_(K)-273)/(100)`. . . (1) FO different TEMPERATURE, `(T_(F)^(.)-32)/(180)=(T_(K)^(.)-273)/(100)`. . . (2) By subtracting equating (2) from equation (1) `(T_(F)^(.)-T_(F))/(180)=(T_(K)^(.)-T_(K))=(T_(K)^(.)-T_(K))/(100)` `:.T_(F)^(.)-T_(F)=(180)/(100)(T_(K)^(.)-T_(K))` But `T_(K)^(.)-T_(K)=1K` `:.T_(F)^(.)-T_(F)=(180)/(100)` Now new temperature at triple point is `273.16K`, Tmeprature `=273.16xx(180)/(100)` `=491.688" "^(@)F~~491.69^(@)F` |
|
| 39734. |
A metre stick is balanced on a knife edge at its centre. When two coins, each of mass 5 g are put one on top of the other at the 12.0 cm mark, the stick is found to be balanced at 45.0 cm. What is the mass of the metre stick? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`66.0 G` | |
| 39735. |
A metal piece of mass 120 g is stretched to form a plane rectangular sheet of area of cross section 0.54m^(2). If length and breadth of this sheet are in the ratio 1:6, find its moment of inertia about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane. |
|
Answer» Solution :Mass `M=120g=120xx10^(-3)KG` area `lb=0.54m^(2)` `(l)/(b)=(1)/(6),"":.l=(b)/(6)` `lb=0.54,""(b)/(6).b=0.54` `b^(2)=0.54xx6impliesb=sqrt3.24=1.8m` Similarly `l=(0.54)/(1.8)=0.3m`. Moment of INERTIA `I=(M(l^(2)+b^(2)))/(12)=(120xx10^(-3)[(0.3)^(2)+(1.8)^(2)])/(12)` `I=33.3xx10^(-3)KGM^(2)` |
|
| 39736. |
A ballet dancer spins about a vertical axis at 120 rpm with arms outstretched. With her arms folded, the moment of inertia about the axis of rotation decreases by 4%. Calculate the new rate of rotation. |
|
Answer» Solution :`n_(1)=120` rpm, `n_(2)=?` `I_(1(omega_(1)=I_(2)omega_(2)` LET `I_(1)=100` units , then `I_(2)=60` units `100xx120=60xxomega_(2)` `omega_(2)=200`rpm |
|
| 39737. |
In the question number 46, if the mass M is hung the free end of the wire, then the extension produc in the wire is |
|
Answer» `(mugL^(2) + MgL)/(2YA)` TENSIONIN the wire at a distance x from THELOWER end is`T(x) = mugx + Mg` Let dl be increase in lengthof the elemenet 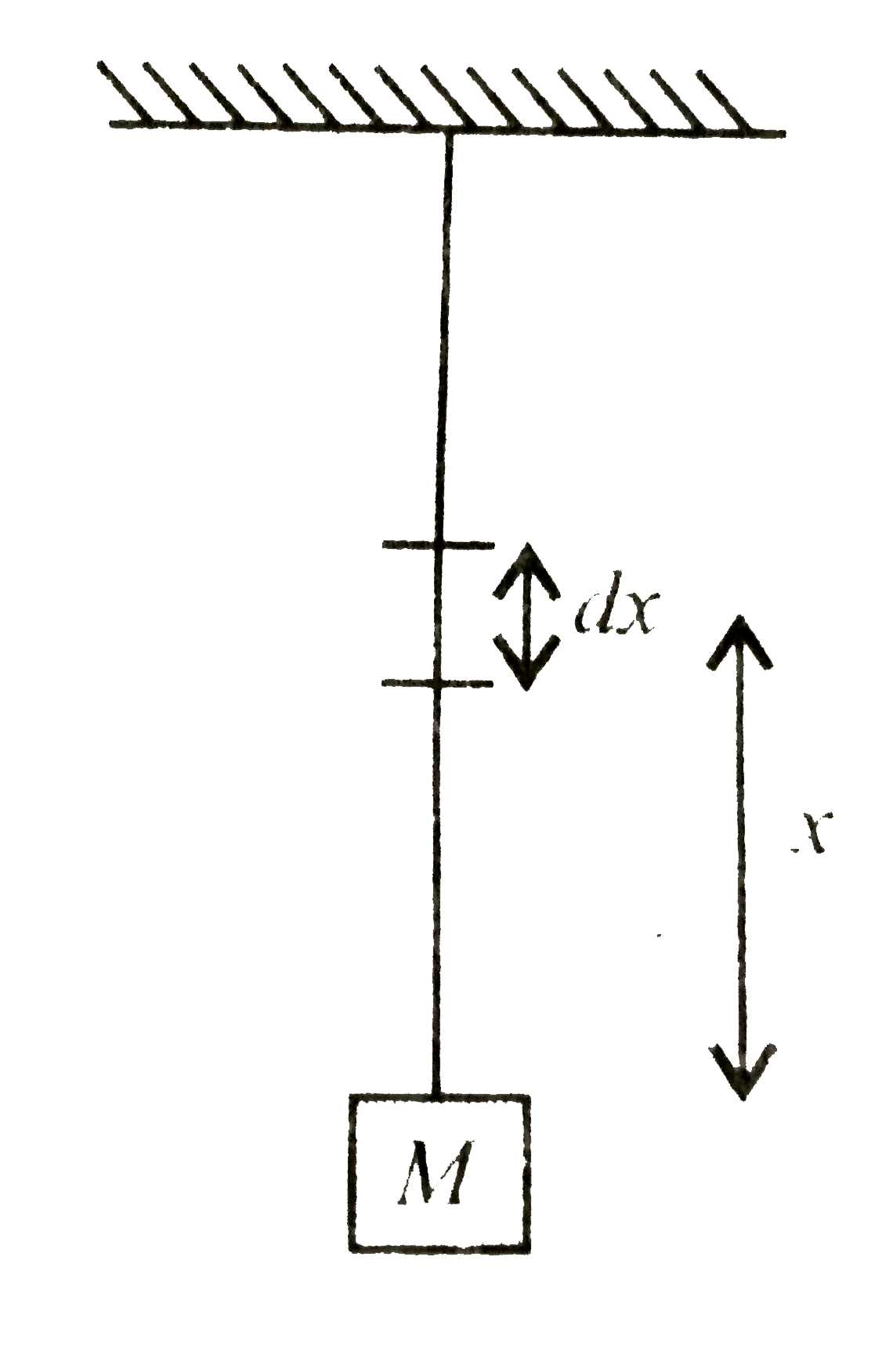 Then `Y= (T(x)//A)/(dl//dx)` `dl =(T(x)dx)/(YA) = ((mugx+Mg)/(YA))dx ""("USING (i)")` `therefore` Totalextensionproduced in thewire is `l = underset(0)overset(L)int ((mugx+Mg)/(YA))dx = (1)/(Y) [(mugx)/(2) +Mgx]_(0)^(L) = (1)/(YA) [(mugL^(2))/(L)+Mgl] =(mugx^(2)+2MgL)/(2YA)` |
|
| 39738. |
Statement I : A cylinder fitted with a movable piston contains a certain amount of liquid in equilibrium with its vapour. The temperature of the system is kept constant with the help of a thermostat. When the volume of the vapour is decreased by moving the piston inwards, the vapour pressure does not increase. Statement II : Vapour in equilibrium with its liquid, at a constant temperature, does not obey Boyle's law. |
|
Answer» STATEMENT I is TRUE, statement II is true , statement II is a correct explanation for statement I. |
|
| 39739. |
It is common observation that rain clouds can be at about a kilometre altitude above the grond. (a) If a rain drop falls from such a height freely under gravity, what will be its speed ? Also calculate in km //h. (g=10 m//s^2) (b) A typical rain drop is about4 mm diameter. Vomentum is mass xxspeed in vagnitude . Estimate its momentum when it hits ground. (c ) Estimate the time required to flatten the drop. (d) Rete of change of momentum id force. Fstmate how much forece such a drop would exert you. (e) Estiate the order of magitude force of magnitude force on umbrella.Typical lateral separation between tao rain drops is5 cm. (Assume that umbrella is circular and has a diameter of1 m and cloth is not prierced through it) |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, ` H= 1000 m, g=10 m//s^2` (a) Velcoity of rain drop after fallin height (h) si ` v = sqrt (2 gh) = sqrt (2 xx 10 xx 1000) = 100 sqrt 2 m//s = ( 100 sqer 2 xx 60 xx 60)/(1000) km// h = 36 0 sqrt 2~~ 510 km //h` (B) Diameter of drop, ` d = 2 =4 mm or r= 2 mm = 2 xxx 10^(-3)m` Mass of rain drop, ` m= 4/3/ pi r^3 roh = 4/3 xx (220/7 xx ( 2 xx 10^3)^3 xx 10^(-3)^3 xx 10^3 ~~ 3.4 xx 10 ^(-5) kg` Mumentum of rain drop when it hits the ground, ` P = mu = ( 3.4 xx 10 ^(-5) xx 100 sqrt 2 ~~ 4.7 xx 10^(-3) kg m//s` (c ) Timerequired to flatten the frop is ` DELTA t = d/v = (4 xx 10^(-3))/(100 sqrt 2) = 0/028 xx 10^(-3) = 28 xx 10^(-6) s` (d) Force, ` F= (change in momentum )/(time) = ( P-0)/(Delta t) = ( 4. 7 xx 10^(-3))/(28 xx 10^(-6)) ~~ 16 8 N` (e) Given , rakies of umbrella, ` R = 1//2 m` Area of umbrella ` =pi R^2 = 922) /7 9 1/2 )^2 = (22)/(28) = (11)/(14) ~~ 0.8 m^@` with average separaion of ` 5 cm (= 5 xx 10^(-2) m), number of drops those will hit nubrella simultanceously ` = (0.8)/((5 xx 10^(-2))^2` Net force on umbrella`= 320 xx 168 = 53760 N ~~ 54000 N`. |
|
| 39740. |
A ball is thrown at a speed of 20 m/s at an angle of 30^(@) with the horizontal. The maximum height reached by the ball is (use g = 10m//s^(2)) |
|
Answer» 2m |
|
| 39741. |
transverse waves: |
|
Answer» both in a GAS and in a METAL |
|
| 39742. |
Pendulum clock shows correct time at O^(@)C. At a higher temperature the clock |
|
Answer» Loses time |
|
| 39743. |
Calculate the difference between the two principal specific heat capacities for hydrogen, Given density of hydrogen at a temperature of 270 K and pressure 10 Nm ^(-2) is 0.090 kgm ^(-3). |
| Answer» Solution :`C _(P) -C_(V)=r, P //rho = r T, r = P //rho T = 10^(5) //0.09 xx 270 = 4115.22 J kg ^(-1) K ^(-1).` | |
| 39744. |
The displacement of an elastic wave is given by the function y = 3 sin omega t + 4 cos omega t.where y is in cm and t is in second. Calculate the resultant amplitude. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `y =3 sin (OMEGA t ) + 4 cos (omega t) ""…(1)` But for a harmonic wave, `y = sin (omega t + phi)` `therefore y = a [sin (omega t) cos phi+ cos (omega t ) sin phi]` `therefore y = (a cos phi ) sin (omega t ) + (a sin phi) cos (omega t ) ...(2)` Comparing equations (1) and (2), we get, `a cos phi =3""...(3)` `a sin phi =4""...(4)` Squaringand adding `a ^(2) cos ^(2) phi + a ^(2) sin ^(2) phi = 9 + 16 ` `therefore a ^(2) (sin ^(2) phi + cos ^(2) phi ) = 25` `thereofre a ^(2) (1) = 25` `therefore a ^(2) = 25` `therefore a = 5 cm (because a gt 0)` Taking ratio of EQUATION (4) to equation (3), `(a sin phi)/( a cos phi) = 4/3` `therefore tan phi = (4)/(3) implies phi = tan^(-1) ((4)/(3))` |
|
| 39745. |
Assertion: A combination of two simple harmonic motions with a arbitrary amplitudes and phases is not necessarily periodic. Reason: A periodic motion can always be expressed as a sum of infinite number of harmonic motions with appropriate amplitudes. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and reson are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion |
|
| 39746. |
A satellite is in a circular polar orbit of altitude 300 km. Determine the sparation d at the equator between the ground tracks associated with two successive overhead passes of the satellite. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39747. |
Assertion :Water in a U-tube executes S.H.M when water is replaced by mercury filled up to the same height , the time period of S.H.Mwill increases. Reasion :Time period of liquid oscillating in a U-tube increases with density of liquid . |
|
Answer» If the assertion and reason are CORRECT and reason is a correct explanation of the assertion |
|
| 39748. |
Calculatethe force .F. needed to punch a 1.46cm diameter hole in a steel plate 1.27 cm thick (as shown in fig). The ultimate shear strength of steel is 345 M N//m^(2) |
Answer» Solution : As in punching, shearelasticity is involved, the hole will be punched it `((F_(11))/(A)) gt` ultimateshear stress `F_(11) gt ` (SHEAR stress ) X Area `F_(11)` min `=(3.45xx10^(8))(2pi RL)(A=2pirL)` `=(3.45xx10^(8)) (2xx3.14)xx0.73xx10^(-2) xx 1.27 xx 10^(-2)` `=200KN` |
|
| 39749. |
The Ratio of the numerical values of the average velocity and average speed of a body is always |
|
Answer» UNITY |
|
| 39750. |
A wall OP is inclined to the horizontal ground at an angle alpha. Two particles are projected from points A and B on the ground with same speed (u) in directions making an angle theta to the horizontal (see figure). Distance between points A and B is x_(0) = 24 m. Both particles hit the wall elastically and fall back on the ground. Time of flight (time required to hit the wall and then fall back on to the ground) for particles projected from A and B are 4 s and 2 s respectively. Both the particles strike the wall perpendicularly and at the same location. [In elastic collision, the velocity component of the particle that is perpendicular to the wall gets reversed without change in magnitude] (a) Calculate maximum height attained by the particle projected fromA. (b)Calculate the inclination of the wall to the horizontal (alpha) [g =10 m//s^(2)] |
|
Answer» |
|