Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39651. |
Which of the following statements is correct for a bulb thermometer |
|
Answer» The bulb of the thermometer is MADE of a conducting material |
|
| 39652. |
Associative law is obeyed by |
|
Answer» ADDITION of vectors |
|
| 39654. |
The study of production and propagation of sound waves…….. |
|
Answer» Astrophysics |
|
| 39655. |
What are the maximum number of rectangular components of a vector can be split in space and in plane respectively. |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 39656. |
A block is placed on a smooth inclined plane at an angle thetato the horizontal. The acceleration must the plane be moved horizontally so that the block to fall freely is |
|
Answer» `G tan q` |
|
| 39657. |
If for hydrogen C_p-C_v = m and for nitrogen C_p -C_v= n , where C_p and C_v refer to specific heats perunit mass respectively at constant pressure and constant volume, the relation between m and n is : (Molecular weight of hydrogen = 2 molecular weight or nitrogen= 14 ) |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 39658. |
Out of the following the correct order of dimensions of mass increases is (A) Velocity (B) Power (C ) Gravitational Constant |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 39659. |
On a P-V diagram starting from an initial state (P_0 V_0) plot an adiabatic expansion to 2V_0 an isothermal expansion to 2V_0 and an isobaric expansion to 2V_0 Use this graph to determine in which process the least work is done by the system |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ADIABATIC | |
| 39660. |
A car of mass 1000 kg is moving with a velocity 20m /s on a horizontal straight road. If the driver applies brakes to produce a constant breaking force of 5000 Newton, the acceleration of the car i s ..... m /s^(2). |
|
Answer» `-5` F= ma HereF=breakingforce `=-500 N` ACCELERATION`a= (F )/( m ) = (5000)/( 1000) =0 5 MS^(2)` |
|
| 39661. |
A simple pendulum is vibrating with an angular amplitude of 90^(@) as shown in the figure. For what value of a is the acceleration directed i) vertically upwards ii) horizontally iii) vertically downward |
|
Answer» `0^(@), cos^(-1)(1/sqrt3), 90^(@)` 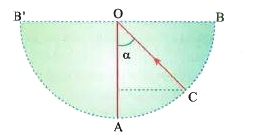 At "C", `T cos alpha = MG .......(i)` `P.E_(B) = K.E_(A) Rightarrow mgr = 1/2(mv_(A)^(2))` hence at "C" , `v = SQRT (v_(A)^(2) - 2gr(1-cos alpha))` `T -Mg cos alpha = (Mv)^(2)/(r) = (M.2 GR cos alpha)/(r)` |
|
| 39662. |
Which body will emit more radiation under the similar condition, a black body or polished body ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :BLACK BODY | |
| 39663. |
When the distance between the two atoms becomes gamma_(0), then the inter atomic force will be, |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 39664. |
Two forces equal to P and 2P newton act on a particle . If the first be doubled and the second be increased by 20 newton, the direction of the resultant is unaltered . Find the value of P . |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Let the resultant make angle `beta`with the force P .`:.`In FIRST case, `tan beta = (2 P sin theta)/( P + 2 P cos theta)` In second case, `tan beta = ((2P + 20) sin theta)/(2P + (2P + 20) cos theta)` HENCE, `((2P + 20) sin theta)/( 2 P + (2P + 20) cos theta) = (2P sin theta)/(P + 2 P cos theta)` (or)`(2P sin theta)/( P +2 P cos theta) = (2 0 sin theta)/( P + 2 0 cos theta)`[`:' (a)/(b) = (c)/(d) = (a-c)/(b-d)` ] From the above EQUATION , 2P = 20 (or) P = 10 N |
|
| 39665. |
Why angular diameter of the sun and the moon in the sky same? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :ANGULAR diameter of any object in the SKY can be measured as : `alpha=(d)/(D)` Here d is the diameter of object and D is the distance object and the earth. In case of the moon and sun, by coincidence, the RATIO d : D is same for both and HENCE their angular diameter is same in the sky. |
|
| 39666. |
A stone is dropped from a height of 10cm above the top of a window 80 cm high. The time taken by the stone to cross the window is |
|
Answer» `1/7 s ` |
|
| 39667. |
Which of the following will make the volume of an ideal gas four times ? |
|
Answer» double the ABSOLUTE temperature and double the pressure. |
|
| 39668. |
A cannon and a target are 5.10 km apart and located at the same level. How soon will the shell launched with the initial velocity 240 m/s reach the target in the absence of air drag ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, `v_(0) = 240 ms^(-1), R = 5.10 km = 5100 m`, `g = 9.8 ms^(-2), ALPHA = ? ""R = (v_(0)^(2) sin 2 alpha)/(g)` `sin 2 alpha = (Rg)/(v_(0)^(2)) ""rArr alpha = 30^(@)` or `60^(@)` using `= T = (2v_(0)sin alpha)/(g)` when, `alpha = 30^(@) , T_(1) = (2 xx 240 xx 0.5)/(9.8) = 24.5 s` When, `alpha = 60^(@), T_(2) = (2 xx 240 xx 0.867)/(9.8) = 42.41s` |
|
| 39669. |
(A) : Centripetal force does no work in circular motion. (R ) : Force and displacement are perpendicular to each other in circular motion |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' and true and 'R' is the correct EXPLANTATION of 'A' |
|
| 39670. |
A door of moment of inertia 4 kg m^(2) is at rest. When a torque of 2 pi Nm acts on it find its angular acceleration. Find also its angular velocity after 1 s. |
|
Answer» Solution :`alpha=(TAU)/(I)=(2pi)/(4)=(PI)/(2)rad//s^(2)` `omega_(2)-omega_(1)=alphat""omega_(2)=(pi)/(2)XX1` `omega_(2)=1.57` rad/sec. |
|
| 39671. |
"Speed of a particle can be negative ". Is this statement correct ? If not why? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :NO, SPEED cannot be NEGATIVE .it is a SCALAR QUANTITY. | |
| 39672. |
If the inertial mass and gravitational mass of the simple pendulum of length 1 are not equal, then the time period of the simple pendulum is |
|
Answer» `T=2pisqrt((m_(i)L)/(m_(G)g))` |
|
| 39673. |
100 g cms^(-1)=x Ns then x=.... |
|
Answer» `3.6xx10^(-3)` `=x(1xx10^(3)g)XX(10^(2)cm)xx1 (s^(-1))` `=x xx10^(5) g cms^(-1)` `=10^(-3)=x` `:.x=1xx10^(-3)` |
|
| 39674. |
If 'g' on the surface of the earth is 9.8ms^(-2), find its value at a depth of 3200 km (radius of the earth = 6400 km) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :with d = 3200 km `g_(d) = g[1-(d)/(R)]RARR g_(d) = 4.9 ms^(-2)` |
|
| 39675. |
A train runs along an unbanked circular track of radius 30 m at a speed of 54 km/h. The mass of the train is 10^(6) kg. What provides the centripetal force required for this purpose - The engine or the rails ? What is the angle of banking required to prevent wearing out of the rail ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The centripetal force is provided by the lateral thrust by the RAIL on the flanges of the wheels.By the THIRD Law, the train exerts an equal and opposite thrust on the rail causing its wear and tear. Angle of banking ` = tan^(-1)( (v^2)/(R G)) = tan^(-1) ( (15 xx 15)/(30 xx 10)) = 37^@` |
|
| 39676. |
A force can change the velocity of a particle in three different ways explain with example |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) themagnitude of thevelocitycan bechangedwithoutchangingthe directionof THEVELOCITY . EG. Particlefallingdownverticallybikemovingin astraightroadwithaccelerationetc. (ii) the directionof motionalonecan bechangedwithoutchangingthe MAGNITUDE. ifthishappenscontinusouslythen it iscalledasuniformciruclarmotion. (iii)Both thedirectionand magnitudeof velocitycan bechanged. if thishappens then non-ciruclarmotionoccurs. Forexampleoscillation of aswingor asimplependulum ellipticalmotionof planeltsaroundthe sun. |
|
| 39677. |
A large vessel with a small hole at the bottom is filled with water and kerosene. The height of he water column is 20 cm and that of the kerosene is 25 cm. The velocity with which water flows out of the hole is (density of kerosene = 0.8 gm/cc) (Neglect viscous forced) |
|
Answer» `2MS^(-1)` |
|
| 39678. |
Figure shows a cylindrical tank of cross sectional are A having a small pipe at its bottom with a cross sectional area a, containing a liquid of density rho and specific heat capacity s, filled to an initial height H. The initial temperature is T_(0). The liquid is heated by means of a heater at t = 0, emitting heat at the rate of P Simultaneously the lower tap is opened. Find the temperature of the liquid (contained in the tank) as a function time t where t ltA/a sqrt((2H)/g) |
|
Answer» <P> |
|
| 39679. |
A string with one end fixed on a rigid wall, passing over a fixed frictionless pulley at a distance of 2 m from the wall, has a point mass M of 2 kg attached to it at a distance of 1 m from the wall. A mass in of 0.5 kg is attached to the free end. The system is initially held at rest so that the string is horizontal between wall and pulley and vertical beyond the pulley as shown in Fig. The system is released from the rest from the position as shown. The ratio of velocity of M and m when M strikes the wall is |
|
Answer» `(sqrt(5))/2` `C'B=sqrt(1^(2)+2^(2))=sqrt(5)m` When its INITIAL distance from the pulley was `CB=1m`. It means vertically upward displacement of mass `m` is `(sqrt(5)-1)m`. 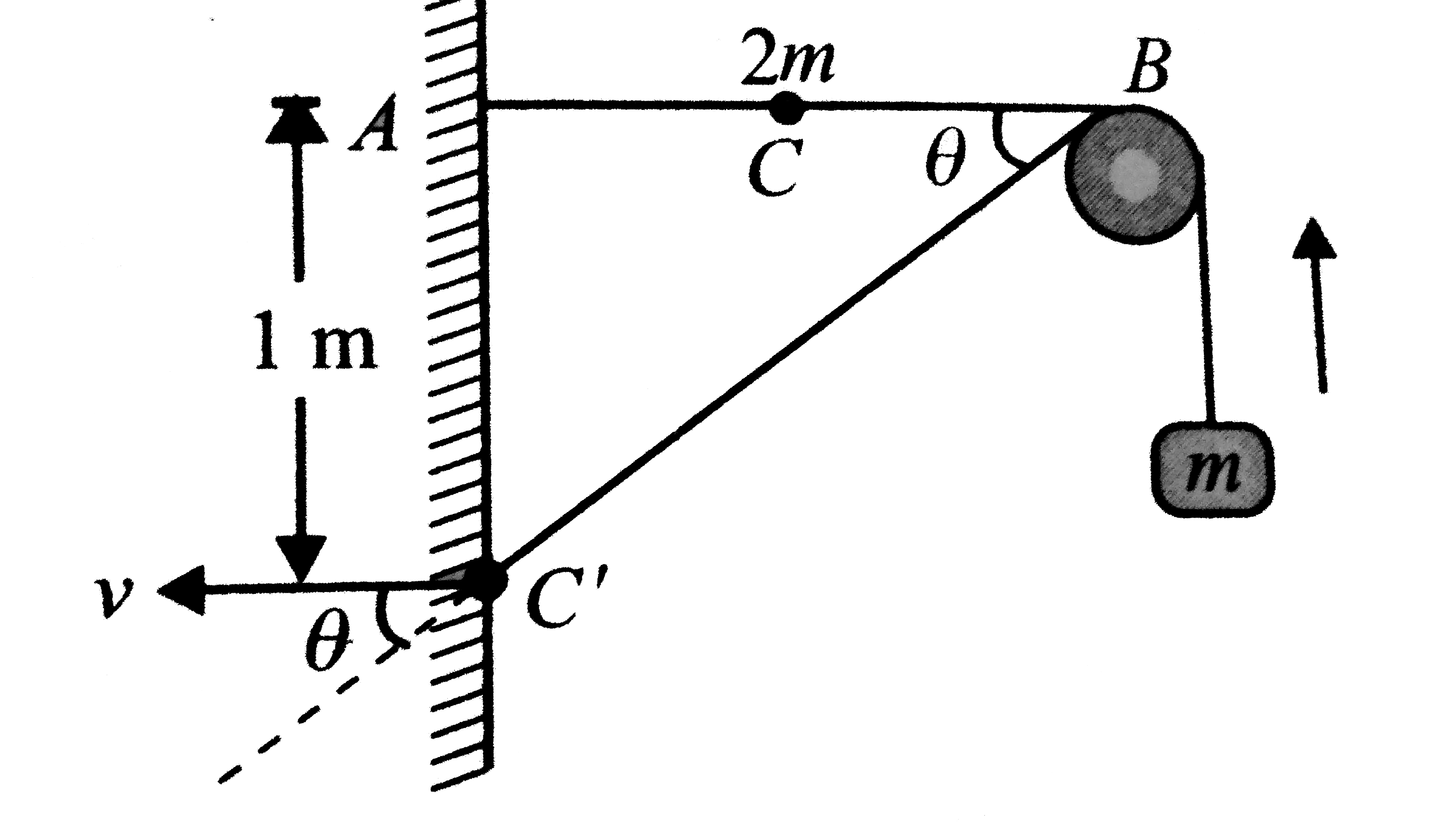 Let `M` strike the wall velocity `v`. Since the string between the two blocks always REMAINS taut, therefore at any instant speed of `m` is EQUAL to that component of velocity of `M` which which is along the string `C'B`. Hence , velocity of `m` when `M` strikes the wall is `vcostheta`, where `costheta=2/sqrt(5)` `:. (v_(M))/(v_(m))=v/(vcostheta)=(sqrt(5))/2` According to law of energy, LOSS of potential energy of `M=`increase in `PE` of `m+KE` of `M+KE` of `m` `Mgxx1=mg(sqrt(5)-1)+1/2Mv^(2)+1/2m(vcostheta)^(2)` `v=5sqrt((5-sqrt(5))/6)m//s` |
|
| 39680. |
Two block of masses 1 kg 2 are connected by a metal wire going over a smooth pulley. The breaking stress of metal is 40/(3pi) xx10^(6)Mm^(-2) . What should be the minimum radius of wire used if it should not break?(g=10ms^-2) |
|
Answer» 0.5mm |
|
| 39681. |
Work of 3.0xx10^(-4) Joule is required to be done in increasing the size of a soap film from 10cmxx6cm to 10cmxx11cm. The surface tension of the film is …… |
|
Answer» `5xx10^(-2)N//m` Soap film has two free surface , `thereforeT=(3.0xx10^(-4)J)/(2XX(10xx11-10xx6)xx10^(-4))` `=3xx10^(-2)(N)/(m)` |
|
| 39682. |
A dancer spins about a vertical axis at 60 rpm with her arms folded. If she strectes her hands so that M.I. about the vertical axis increases by 25% the new rate of revolvution is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 39683. |
How much is the empty space in 1 mole of Helium gas at STP if the radius of helium molecule is about 0.98 dot(A)? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`=99.98%` | |
| 39684. |
At a given temperature the r.m.s velocity will be greater for |
|
Answer» HYDROGEN |
|
| 39685. |
Select the alternatatives. (a) A diverging beam of light form a point source S having divergence angle alpha ,falls symmetrically on a glass slabas shown .the angles of incidence of the two extreme rays are equal .Fi the thickness of the glass slab is tand the refractive index nthe n the divergence angle of the emergent beam is (A) zero,(B) alpha(C ) sin^(-1)(1//n)(D) 2 sin^(-1)(1//n) (b) Arectangular glass slabABCDof refractive index n_(1) is immersed in water of refractive indexn_(2)(n_(1)gtn_(2)) A ray of light is incident at the surface ABof the slab as shown .The maximum value of the angle of incidenc ealpha_(max)such that the ray comes out only from the other surface CD is given by (A) "sin"^(-1)[(n_(1))/(n_(2))cos("sin"^(-1)n_(2)/n_(1))] (B)sin^(-1)[(n_(1))/(n_(2))cos("sin"^(-1)(1)/n_(2))] (C)sin^(-1)((n_(1))/(n_(2)))(D)sin^(-1)((n_(2))/n_(1)) (c) A point source of lightB is placed at a distance L inother of the centre of a mirror of width hung vertically onawall A man walks is front of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror at a distance 2L from it as shown .the greatest distance over which he can see the image of the light source in the mirror is (A)d//2 (B) d,(c )2d,(d)3d, a hollow double concave lens is made of very thin transparents meterial .It can be filledwith air or either of two liquids L_(1)andL_(2)having refractive indicesn_(1)and n_(2)respectively(n_(2)gtn_(!)gt1) the lens will diverge a parallel beam of light of it is filled with (A)air and placed in air.(B) air and immersed inL_(1)(C ),L_(1) and immersed inL_(2) (D),L_(2) ans immersed in L_(1) |
Answer» 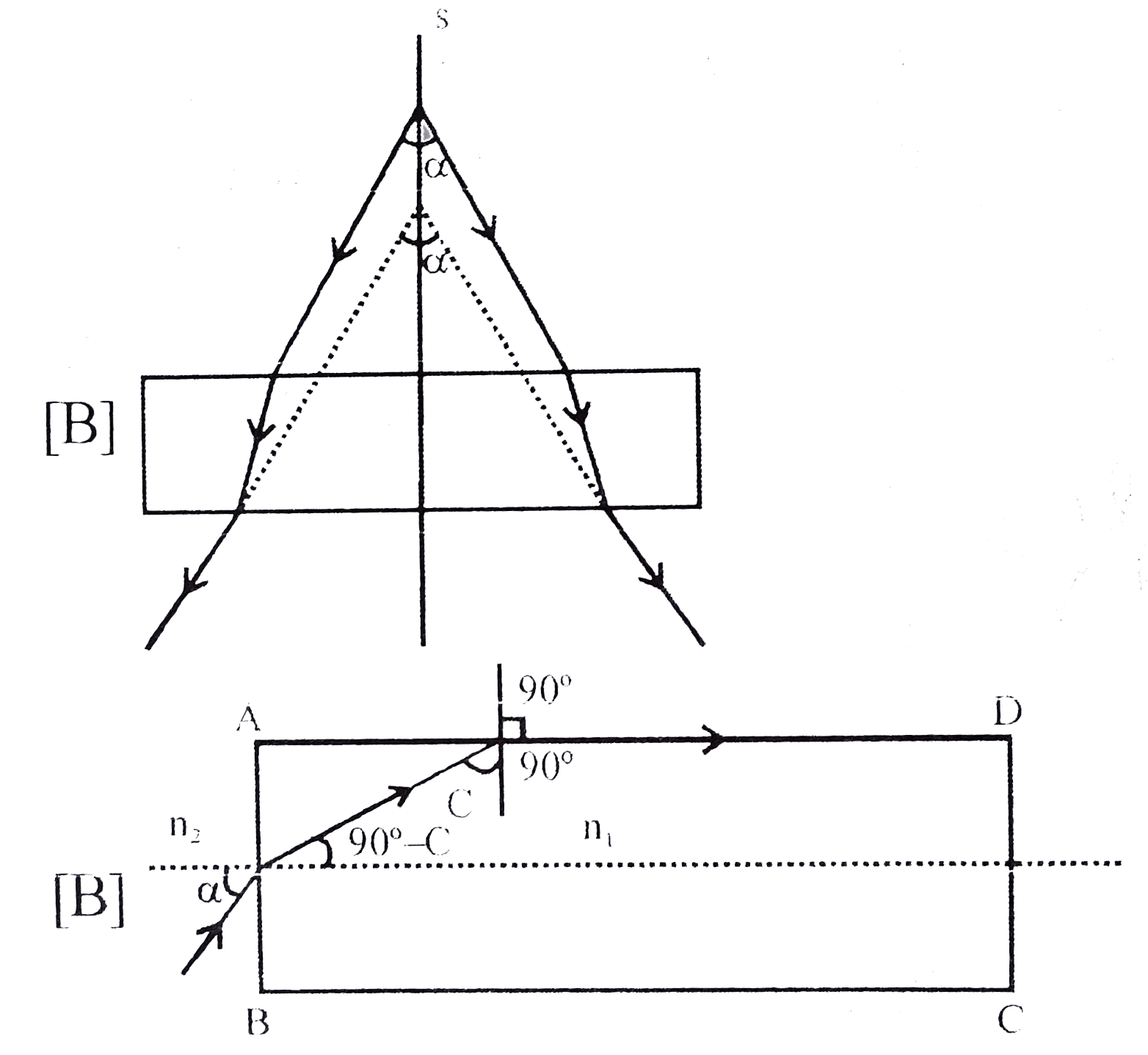 For critical angle at `A,D,`taking refraction at`AD` `n_(1)sinC=n_(2) RARR sinC=(n_(2))/(n_(1))rArr C="SIN"^(-1)(n_(2))/(n_(1)) ….(1)` taking refractor at AB`n_(2) sin alpha _(max)=n_(1) sin(90-C) rArr n_(2)sinalpha_(max)=n_(1)cosC` `rArr alpha_(max)="sin"^(-1)(n_(1))/(n_(2)) cosC ...(2)` from(1)&(2) `alpha_(max)=sin^(-1)[(n_(1))/(n_(2))"cos"("sin"^(-1)(n_(2))/(n_(1)))]` (c ) `[D](d//2)/(L) =(x)/(2L) rArr x=L` greastest distance=`2x+d` `=3d`  (d) [B] Behaviour of lens will be change when RAY INCIDENCE from optically denser medium . |
|
| 39686. |
"In hilly areas, sand is thrown on tracks covered with snow ". Why ? |
| Answer» Solution :HILLY areas, TRAIN COULD not be able to move upwards. By throwing SAND friction is INCREASED then the train would be able to move upwards. | |
| 39687. |
Which of the following functions of time represent (a) simple harmonic motion and (b) periodic but not simple harmonic? Give the period for each case. (1) sinomegat-cosomegat (2) sin^(2)omegat |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) `sinomegat-cosomegat` `=sinomegat-sin(pi//2-omegat)` `=2cos(pi//4)sin(omegat-pi//4)` `=sqrt2sin(omegat-pi//4)` This function represents a simple harmonic motion having a period `T=2pi//omega` and a PHASE angle `(-pi//4)` or `(7pi//4)` (b) `sin^(2)omegat` `=1//2-1//2cos2omegat` The function is periodic having a period `T = pi//omega`. It also represents a harmonic motion with the point of equilibrium OCCURRING at `1//2` INSTEAD of zero. |
|
| 39688. |
Briefly explain the concept of super position principle. |
|
Answer» Solution :When two or more waves in a medium overlap., their TOTAL displacement is the VECTOR sum of individual displacements. Let us consider two fucntions which CHARACTERIZE the displacement of the waves, for example, `y_(1)=a sin (kx- omegat)` and `y_(2)=A_(2)cos(kx- omegat)` SINCE both `y_(1) and y_(2)` satisfy the wave equation (solutions of wave equation) then their algebraic sum `y=y_(1)+y_(2)` also satisfies the wave equation. It is meant that, the displacement are additive. |
|
| 39689. |
The vector product of two vectors will have maximum magnitude when theta is equal to |
| Answer» | |
| 39690. |
Can the couple acting on a rigid body produce translatory motion? |
| Answer» Solution :No, the couple ACTING on a rigid BODY cannot rotatory MOTION as the RESULTANT force is zero. | |
| 39691. |
A square lead slab of side 50 cm and thickness 10 cm is subject to a shearing force on its narrow face) of 9.0 xx 10 ^(4) N.The lower edge is riveted to the floor. How much will the upper edge be displaced ? Shear modulus of lead G=5.8 xx 10 ^(9) N//m^(2) |
Answer» Solution :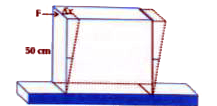 The load slab is FIXED and the force is applied parallel to the narrow face. The AREA of the face parallel to which this force is applied is, `A=l xx B` `= 50 cm xx 10 cm = 0.5 m xx 0.1 m` `therefore A = 0.05 m ^(2)` Stress = `("Force")/("Area")= (9 xx 10 ^(4))/(0.05) =1.8 xx 10 ^(6) Nm ^(-2)` Shear modulus `(G) =("Stress")/("Shear strain")` `therefore` Shear strain`= ("Stress")/(G)` ` (Delta x)/(L) = ("Stress")/(G)` `therefore Deleta x = ("Stress")/(G) xx l` `therefore Delta x = (1.8 xx 10 ^(6))/(5.6 xx 10 ^(9)) xx 0.5` `therefore Delta x =0.1607 xx 10 ^(-3)` `therefore Delta x ~~ 1.6 xx 10 ^(-4) m = 0.16 mm` |
|
| 39692. |
The force on a body executing SHM is 2N when the displacement is 2cm. If the amplitude of oscillation is 5cm, what is the total energy associated with the SHM? |
|
Answer» `1.25 XX 10^(-2) J` |
|
| 39693. |
StatementI: A quasi -static process is so called bacause it is a sudden and large change of the system. Statement II: An adiabatic process is not quasi- static because it is a sudden and large change of the system. |
|
Answer» Statement I: is true, StatementII is true and Statement II is the correct explanation for Statement I. |
|
| 39694. |
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown if Fig. A to B : Volume constant B to C : adiabatic C to D : volume constant D to A : adiabatic V_(C) = V_(D) = 2V_(A)=2V_(B) ( a) In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside? (b) In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine? (c) What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of P_(A),P_(B) V_(A) . (d) What is the efficiency of the engine? [gamma=5/3" for the gas "],[C_(v)=3/2R" for one mole"] |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) A to B since each one is an isochoric PROCESS ( b) C to D ( c) `W_(AB)=int_(A)^(B)pdV=0,W_(CD)=0` Similarly `W_(BC) =[int_(B)^(C)pdV=k int_(B)^(C)(DV)/(V^(gamma) )= (V^(-gamma+1))/(-gamma+1)]_(V_(B))^(V_(C))` `=1/(1-gamma) (P_(c )V_(c)-P_(B)V_(B))` [ work done during ADIABATIC process ] Similarly, `W_(DA)==1/(1-gamma)(P_(A)V_(A)-P_(D)V_(D))` Now `P_(C)=P_(B)((V_(B))/(V_(C)))^(gamma) =2^(-gamma)P_(B)[ :. V_(C )=2V_(B)] ` Similarly, `P_(D) =P_(A)2^(-gamma)` , Total work done ` = W_(BC)+W_(DA)` `=1/(1-gamma) [P_(B)V_(B)(2^(-gamma+1)-1)P_(A)V_(A)(2^(-gamma+1)-1)]` `1/(1-gamma) (2^(1-gamma)-1) (P_(B)-P_(A))V_(A) ""( :. V_(A)=V_(B))` `=3/2 (1-(1/2)^(2//3))(P_(B)-P_(A))V_(A)` Heat supplied during process A,B `dQ_(AB)=dU_(AB)` `Q_(AB)=3/2nR(T_(B)-T_(A))=3/2(P_(B)-P_(A))V_(A)` Efficiency = `("Net Work done")/("Heat Supplied") =(1-(1/2)^(2//3))` |
|
| 39695. |
The co-ordinates of centre of mass of letter E which is cut from a uniform metal sheet are (Take origin at bottom left corner and width of letter 2 cm every where): |
|
Answer» (2 CM, 4 cm) |
|
| 39696. |
Two waves with wavelength lamda have phase difference of 60° at the point of superposition. Find path difference between them. |
|
Answer» `lamda/6` `THEREFORE (PI )/(3) = (2pi )/( lamda ) (Delta x)` `therefore Delta x = (lamda )/(6)` |
|
| 39697. |
Select the correct pair from the following pairs with reference to acceleration due to gravity (g). |
|
Answer» G is minimum at poles and it is maximum at equator. |
|
| 39698. |
A block slides down a frictionless incline kept on the floor of a chamber . Find the acceleration of the block relative to the incline when the chamber is carried by a helicopter with upward acceleration a at inclination theta with the vertical . Consider the special cases when theta = 0 ^(@) and theta = 90^(@) . The inclination of the plane is 90^(@) - alpha to the vertical in the same sense as theta . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39699. |
The main difference between liquid surface and an elastic membrane is |
|
Answer» Hook.s law is not obeyed by LIQUID SURFACE |
|
| 39700. |
At what height from the surface of Earth the gravitational force will be reduced by 10% if the radius of Earth is 6400 km? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Gravitational FORCE on the Earth surface `F_(s)=(GMm)/(R_(E)^(2))` Gravitational force at HEIGHT h `F_(h)=(GMm)/((R_(E)+h)^(2))` `THEREFORE(F_s)/(F_h)=((R_(E)+h)^(2))/(R_(E)^(2))=(10)/(9)` `3(R_(E)+h)=3.162R_(E)` `3h=(3.162-3)R_(E)` `=0.162R_(E)` `(R_(E)+h)/(R_E)=(3.162)/(3)` `therefore` Height h `=(0.162xx6400)/(3)` (or) h = 345.6 KM |
|