Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 3001. |
If th percentage change in supply is less than the percentage change in price, it is called _______. |
|
Answer» UNIT elasticity of SUPPLY |
|
| 3002. |
Distinguish between cash reseve ratio and statutory liquidity ratio. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Cash Reserve RATIO (CRR) REFERS to the minimumÂpercentage of net demand and TIME liabilities, to bekeptby commercial bankswiththe centralbanks. On theother hand, statutoryliquidityratio(SLR)refersto minimumpercentage ofnetdemandand timeliabilitiesin the from of DESIGNATED liquidassetswhichcommercial banks are requiredtomaintain with themselves. | |
| 3003. |
Describe briefly expenditure method. |
|
Answer» Solution :Expenditure method measures natonal income as the aggregate of all the final expenditure incurred in an economy, during a year. The main components of final expenditures are : (a) Private final CONSUMPTION expenditure refers to expenditure on the purchase of goods and services by households and private non-profit institutions serving households. (b) Government final consumption expenditure is the expenditure incurred by general government on various administrative services, e.g., law and ORDER, defence etc. (c) Gross Domestic capital formation refers to the addition to the existing capital STOCK of the economy. It is Gross Domestic fixed capital formation with change in stock. (d) Net exports is the difference between value of exports and imports of a COUNTRY, during the period of one year. `N NP_(FC)=a+b+c+d-"Dep."+NFIA-NIT` |
|
| 3004. |
Elasticity of supply is measured by dividing the percentage change in quantity supplied of a good by ______. |
|
Answer» PERCENTAGE CHANGE in income |
|
| 3005. |
Define current account and capital account of BOP. |
|
Answer» Solution :i) CURRENT account of BOP. It records all those transactions between residents of a COUNTRY and rest of the world which do not CAUSE a change in the asset or liability status of the residents of a country or its government. ii) CAPITAL account of BOP. It records all those transactions between residents of a country and rest of the world which cause a change in the asset or liability status of the residents of a country or its government. |
|
| 3006. |
Which of the following is not a component of operating surplus ? |
|
Answer» Interest |
|
| 3007. |
A city in north west India is hit by a massive earthquake causing huge loss of property. Life of people has come to a standstill. Government of India announces a compensation to earthquake victims to meet the needs of their food, clothes and shelter. (a) Is this expenditure included in national income ? (b) How does it impact life in the city ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) This expenditure by the government is not INCLUDED in national income as it is transfer payment and does not correspond to the flow of goods and services. (b) THI expenditure will help the people to get their LIVES back on track. It will add to their consumption expenditure. Also, if some expenditure is incurred to rebuild their houses, it will add to the CAPITAL formation in the city. |
|
| 3008. |
Distinguish between: (i) Balance of Trade and Balance of Payments, (ii) Current Account and Capital Account. |
| Answer» Solution :i)The key differences between balance of trade and balance of payments –Balance of trade can be CALCULATED by deducting the value of imports of goods from the value of exports of goods. Balance of payments, on the other hand, can be calculated by adding balance of payments at current account and balance of payments at capital account or by finding out the net balance between inflow of foreign exchange and outflow of foreign exchange.Balance of trade portrays a partial picture of foreign exchange. Balance of payments, on the other hand, provides a holistic picture.The net effect of balance of trade can be positive, NEGATIVE, or zero. The net effect of balance of payments would ALWAYS be zero.Capital and unilateral transfers are not INCLUDED in the balance of trade. Capital and unilateral transfers are major parts of balance of payments.Balance of trade is a sub-set of balance of payments. Without computing balance of trade, we would not be able to see the net effect of export and import in the balance of payments.ii) The following are the major differences between current account and capital account:Current account records the trading in goods and services in the current period. Capital Account records the MOVEMENT of capital in and out the economy.Current Account shows the net income of the country, whereas Capital Account shows the change in the ownership of the nation’s assets.Current Account is mainly concerned with receipts and payment of cash and non-capital items. Conversely, Capital Account has thoroughly considered the sources and application of capital.The key components of current account are export and import of goods and services, the investment the income and current transfers. On the other hand, foreign direct investment, portfolio investment and Loans by the government of one country to the government of another country are the key components of Capital Account. | |
| 3009. |
How does real flow consist of factor flow and product flow ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Real flow consists of two KINDS of flows: ("i") FACTOR flow : It is the flow of factor SERVICES from households to FIRMS. (ii)Product Flow : is the flow of goods and services from firms to households. |
|
| 3010. |
How would the following transactions affect the national income ? |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 3011. |
When the price of a good X is Rs. 5, the consumer buys 100 units of the good X. At what price would he be willing to purchase 140 units of good X ? The price elasticity of demand for good X is 2. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("Original Quantity (Q) = 100 unitsOriginal Price (P) = Rs. 5"),("New Quantity "(Q_(1))=140 " unitsNew Price "(P_(1))=?),("Change in Quantity "(Delta Q)=40 " unitsChange in Price "(Delta P)=?),("ELASTICITY of Demand (ED) = 2"):}` Price Elasticity of demand `(ED)=(Delta Q)/(Delta P)XX(P)/(Q)` `2=(40)/(Delta P)xx(5)/(100)=Delta P=Rs. 1` As the quantity demanded is increasing, price will decrease. It means that New Price = Original Price (P) - Change in Price `(Delta P)=5-1=Rs. 4` New Price = Rs. 4. |
|
| 3012. |
_refers to a situation when ADis equal to AS beyond the full employment level. |
|
Answer» FULL EMPLOYMENT Equilibrium |
|
| 3013. |
Why are tranfer payments not included in the estimation of National Income ? Do we arrive at the value that these are not important for the economy ? |
| Answer» Solution :Transfer payments are not included in National Income as these do not LEAD to corresponding flow of goods and services. These are not included because of LIMITATION of being ONE sided. These are very important for growth and WELFARE of economy like donations, old age pension, unemployment allowance, tax payments. These do promote SOCIAL and economic justice of those who receive these payments. | |
| 3014. |
What is barter system? |
| Answer» | |
| 3015. |
Break-even point is achieved when: |
|
Answer» NATIONAL INCOME = CONSUMPTION |
|
| 3016. |
Why people accept cheques when these are not legal tender ? |
| Answer» Solution :MONEY that has a legal sanction by the GOVERNMENT behind it is called legal tender. Thus seen cheques are not legal tender because a person can legally refuse to accept cheques for settling TRANSACTION. Still people accept cheques because of the trustin the person who has issued the CHEQUE. | |
| 3017. |
What is the difference between the spot rate and forward rate? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The rate at which current transaction take place is called SPOT rate. Whereas the exchange rate that prevails in a future CONTRACT for PURCHASE and sale of foreign exchange is called FORWARD rate. |
|
| 3018. |
What is meant by 'propensity to consume' ? Discuss the two types of propensities to consume. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Propensity to consume is the PROPORTION of total income or of an increase in income that consumers tend to spend on goods and SERVICES rather than to save.There are 2 TYPES of propensity to consume i.e1. APC2. MPC | |
| 3019. |
What are the three components of NFIA ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Net compensation of employees. (ii) Net income from PROPERTY and ENTREPRENEURSHIP. (III) Net retained earining of resident companies ABROAD. |
|
| 3020. |
Explain the role of cash reserve ratio in controlling credit creation |
| Answer» | |
| 3021. |
Why is interest received on loan a revenue receipt ? |
| Answer» Solution :Because it is an INCOME and it NEITHER CREATES a liability nor REDUCES any asset. | |
| 3022. |
Compare between monopoly and monopolistic competition. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 3023. |
Governmentof India hasrecentlylaunched 'Jan -Dhan Yojina' aimedat everyhouseholdin the countrytohave at leastone bankaccount. Explainhow depositemadeundertheplanare going to affect national incomeof the country. |
|
Answer» Solution :Thedeposits made under the plan are going to EFFECT national INCOME of the country in the followingway, Opening morebankaccountsmeansmore bankdeposit. More depositmeansincreasein thelendingcapacityof thecommercial BANKS. MoreIendingby banks means more INVESTMENT In the country Moreinvestment means more national income. |
|
| 3024. |
Which of the following is an example of Non-durable good ? |
|
Answer» MILK |
|
| 3025. |
What is the value of multiplier when Marginal Propensity to Save is zero? |
| Answer» Solution :MULTIPLIER(K)`=(1)/(MPS)=(1)/(0)="INFINITY"` | |
| 3026. |
The price of 1 US Dollar has fallen from Rs. 50 to Rs. 48. Has the indian currency appreciated or depreciated ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION : Indiancurrency has APPRECIATED. | |
| 3027. |
Who are produceers of money |
|
Answer» Solution :Producers o money refer to the suppliers of money .They are (i) The GOVT of the country (II) The banking system of a country INCLUDING both the COMMERICAL banks and the central bank (RBI) |
|
| 3028. |
An accounting statement that provides a systematic record of all the economic transactions, between residents of a country and the rest of the world is________. |
|
Answer» Balance of Payments |
|
| 3029. |
If the quantity supplied is exactly equal to the relative change in price then the elasticity of supply is |
|
Answer» LESS than one |
|
| 3030. |
Primary deficit is the difference between |
|
Answer» Fiscal DEFICIT and revenue deficit |
|
| 3031. |
Will the following be included in National Income of India? Give reassons for your answer. (i) Financial help given to flood victims. (ii) Profits earned by an Indian bank from its branches abroad. (iii) Salareis paid to non-resident Indians working in Indian emabassy in America. (iv) Interest received try an individual from banks. |
|
Answer» (II) Profit earned by an INDIAN bank from its branches abroad is factor income from abroad, and so included in national income. (iii) Salaries paid to NRI's working in INdian EMBASSY in America is factor income paid to abroad. it is deducted from India's national income. (iv) INTEREST recieved by an individual from bank is a factor payment by a productive enterprise. it is included in national income. |
|
| 3032. |
Why is interest termed as a revenue receipts? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Interest is a REVENUE because it neither creates any liability nor CAUSE a REDUCTION in the assets of the government . | |
| 3033. |
"All producer goods are not capital goods". Comment. |
|
Answer» Solution :A producer uses two types of goods or Producer goods include : (i) Raw materials, (ii) Fixed assets like plant and machinery. The first TYPE of producer goods (i.e., raw materials, like coal, wood, etc)., are not capital goods as they lose their identity in the production PROCESS. They are intermediate or single-use producer goods and cannot be used again in the production process. So, it can be SAID that all capital goods are producer goods, but all producer goods are not capital goods. The second type i.e., fixed assets can be used repeatedly in the production process, hence they are capital goods. |
|
| 3034. |
Foreign embassies in India are a part of |
|
Answer» ECONOMIC TERRITORY of India |
|
| 3035. |
For a consumer to be in equilibrium why must marginal rate of substitution be equal to the ratio of prices of the two goods? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) To define consumer equilibrium, we use Interference Curve map and the BUDGET line . Two conditions for consumer Equilibrium (a) NECESSARY Condition Marginal Rate of Substitution = Market Rate of Exchange `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` Or , `MRS_(x,y)=P_x//P_y` ( Market Rate of Exchange ) MRE Or `MRS_(x,y) =MRE[(P_x)/P_y]` `"*" ` If `MRS_(x,y) gt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]` , At point T in FIGURE It means the consumer.s willingness to pay for commodity X is higher than what makes values for commodity X. So, the consumer should buy more of X and less of Y to get MRS `=P_x/P_y` 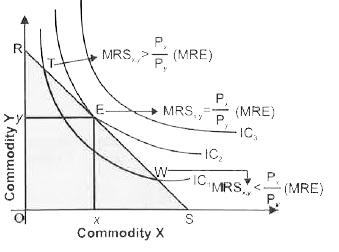 `"*"` If `MRS_(x,y) lt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]`, At point W in figure, It means the consumer willingness to pay for commodity X is lesser than what market value for commodity X ,So, consumer should buy less of X and more Y to get MRS = `p_x/p_y` (b) Sufficient Condition `MRS_(x,y)` Diminishing (Convex) at a point of equilibrium i.e., when `MRS_(xy)=MRE[P_x/P_y]` (II) The consumer will reach equilibrium when the budget line is tangential to the higher possible Indifference Curve, i.e. ., where necessary and sufficient condition satisfy . In the above diagram , the consumer will reach equilibrium at point E where budget line RS is tangential to the higher possible `IC_2` (iii) The consumer cannot move to Indifference Curve , i.e. ., `IC _3`as this is beyond this money income. (iv) EVEN on `IC_2` all the other points except E are beyond his means . (v) Hence , at point E, the consumer is in equilibrium where his satisfaction maximizes, given his income and prices of goods X and Y . In equilibrium at E , the slope of Budget line = the slope of Indifference Curve. Therefore `MRS_(xy)`is equal to the ratio of the price bof two goods `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` . |
|
| 3036. |
State one fiscal measure that can be used to reduce the gap between rich and poor. |
| Answer» Solution :Increasing the TAXES on RICH and using the same AMOUNT to benefit the POOR. | |
| 3037. |
What are two components of supply of money ? |
| Answer» Solution :(i) Currency with the public and (ii) Demand deposits in commercial BANK are the TWO COMPONENTS of money SUPPLY. | |
| 3038. |
An economy is in equilibrium. Find 'autonomous consumption' from the following : National income = 1,000 Marginal propensity to consume = 0.8 Investment expenditure = 100 |
|
Answer» Solution :GIVEN Y = 1,000 MPC (c ) =0.8 I=100 AUTONOMOUS consumption `(BARC)`=?? We know that at equilibrium, Y=C+I i.e. 1,000 = `barC`+cY+I implies `1,000=barC+0.8xx1,000+100` `implies 1,000=barC+900` `implies 1,000-900=barC` so, `barC=100` |
|
| 3039. |
Classify the following as intermediate goods or final goods : Mobile sets purchased by a mobile dealer. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INTERMEDIATE GOODS | |
| 3040. |
Domestic Income of a country can be more than its National Income. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3041. |
Which one of the following will be treated as labour in economics? Give a reason for each. (i) Preparation of food by a housewife. (ii) Singing for one's own pleasure. (iii) Driving his master's car by a driver. (iv) Playing cricket by Virat Kohli. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) and (II) do not generate any income. (iii) and (IV) CONSTITUTE LABOUR. These generate income. Value: Critical thinking |
|
| 3042. |
In case of constant MPS, saving function will be linear. |
|
Answer» Solution :True. : Slope of saving CURVE is indicated by MPS (i.e. `DeltaS//DeltaY`). Constant MPS means that saving curve is a straight LINE and HENCE, savings function will be linear. Note: As per CBSE guidelines, no marks will be given if REASON to the answer is not explained. |
|
| 3043. |
Increase in cash reserve ratio will lead to: |
|
Answer» Fall in AGGREGATE Demand |
|
| 3044. |
Given MPS equal to 0.25. What will be the increase in national income, if investment increases by 125 crore ? Calculate. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :500 CRORE | |
| 3045. |
How is exchange rate determined in the foreign exchange market ? Explain |
Answer» Solution :In the foreign exchange market, the equilibrium exchange rate is determined by the INTERSECTION of the demand curve for foreign currency and the supply curve of the foreign currency.  In this given diagram, DD is the demand curve for foreign currency and SS is the supply curve of foreign currency. The point E is the point of intersection, where the demand curve and the supply curve intersect. Thus, the point E represents the equilibrium exchange rate. OR is the equilibrium exchange rate adn OQ is the quantity demanded and supplied of the foreign currencies. If exchange rate rises to `OR_(1)`, then the supply of foreign currency exceeds the demand for foreign. This will then FORCE the exchange rate to fall back OR due to the excess supply. On the CONTRARY, if the exchange rate falls to `OR_(2)`, then there exists excess demand. Consequently, the rate of exchange rises from `OR_(2)` to OR. Thus, in the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply of the foreign exchange. In CASE of any mismatches between the demand and the supply, then such mismatchs are CORRECTED automatically by the invisible hands of the market i.e., demand and supply. |
|
| 3046. |
What is the basic reason for economic problemin all economies? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :It is SCARCITY of RESOURCES. | |
| 3047. |
Are the following statements true or false ? Give reasons. The fiscal deficit in the economy will be zero if there is no provision for borrowings in the budget. |
| Answer» Solution :TRUE. FISCAL DEFICIT is equal to total BORROWING requirements of the economy. | |
| 3048. |
In case of a straight line demand curve meeting the two axes, the price elasticity of demand at the midpoint of the line would be : |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 3049. |
Discuss the impact of injections and leakages (or withdrawals) on the level of equilibrium. |
|
Answer» Solution :Injections REFER to the government expenditure or exports or other such variables which cause increase in level of aggregate demand. Circular flow of income RISES. Leakages (or WITHDRAWALS) refer to the government taxes or imports or such variables which cause a decrease in AD. Circular flow of income falls. Due to injections, AD curve SHIFTS upwards while due to leakages, AD curve shifts downwards. In the diagram, (i) Due to an injection of government expenditure, AD INCREASES and equilibrium level of income shifts upwards from point `E "to" E_(1) or M "to" M_(1)`. Thus injections cause a positive multiplier effect. (i) Due to leakages in the form of taxes, AD decreases and equilibrium level of income shifts downwards from `E "to" E_(1) or M "to" M_(1)`. Thus leakages cause a negative multiplier effect. 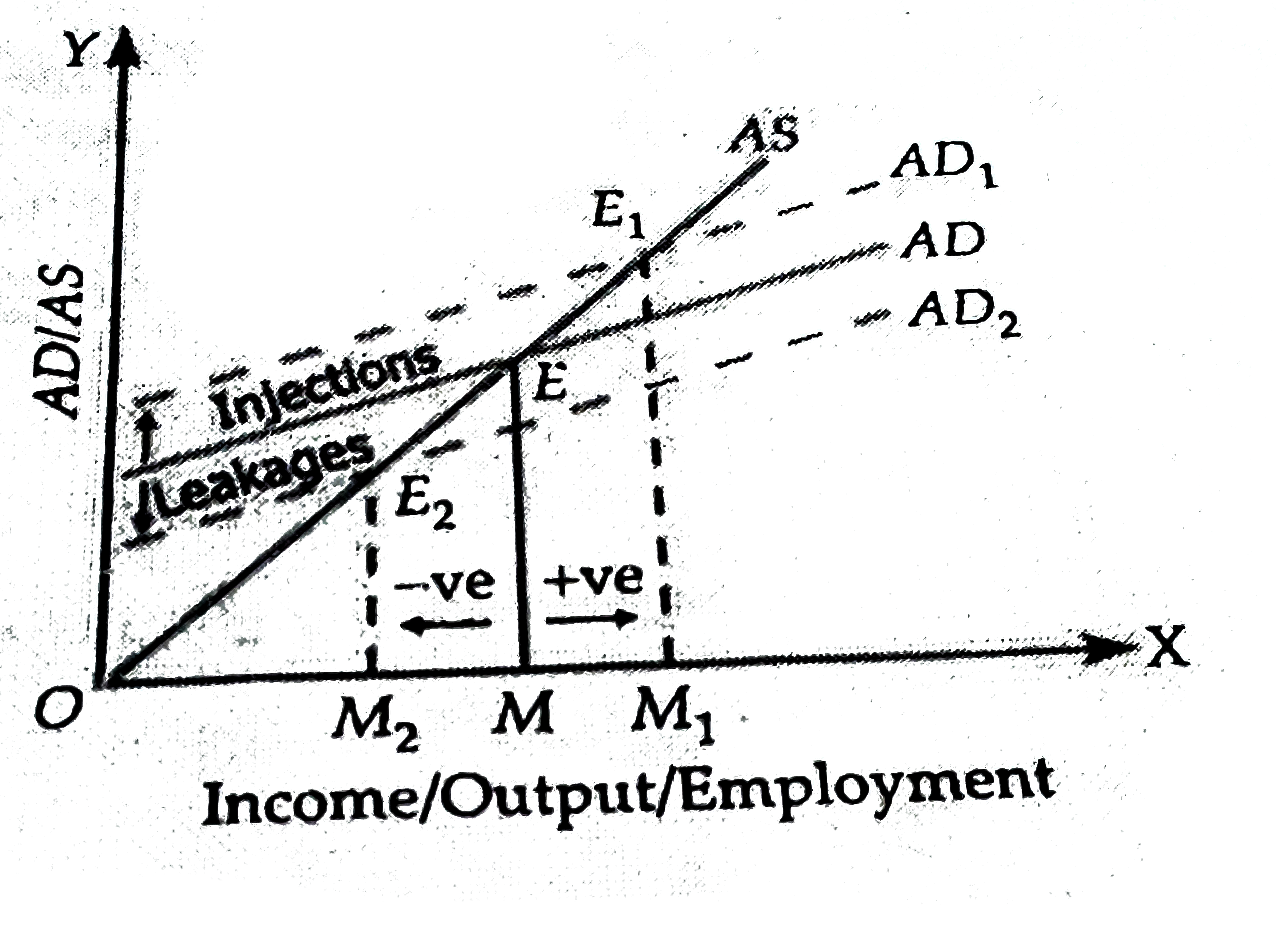
|
|
| 3050. |
From the given information , determine: (a) Capital Expenditure and (b) Interest Payments: |
| Answer» SOLUTION :{(a)₹15 , 000 CRORES ,(B)₹ 3 , 000 crores} | |