Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2901. |
Money Supply is a flow concept |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE. MONEY SUPPLY is a stock concept as it is measured at a particular point of TIME. | |
| 2902. |
A consumer buys 18 units of a good at a price of Rs. 9 per unit. The price elasticity of demand for the good is (-)1. How many units the consumer will buy at a price of Rs. 10 per unit ? Calculate. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("Original Quantity (Q) = 18 unitsOriginal Price (P) = Rs. 9"),("New Quantity "(Q_(1))=? "New Price "(P_(1))=10),("Change in Quantity "(Delta Q)=? "Change in Price "(Delta P)=1),("ELASTICITY of Demand (ED) = "(-)1):}` `PED=(Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q)` `-1=(Delta Q)/(1)xx(9)/(18)` `-2=Delta Q` As New Price is increasing from 9 to 10, quantity demanded MUST decrease by `Delta Q`. New Quantity = INITIAL Quantity `+Delta Q=18+(-2)=16` At Price = 10, Quantity demanded = 16. |
|
| 2903. |
AD Curve starts : |
|
Answer» From the ORIGIN |
|
| 2904. |
Production in an economy is below to its potentiality due to unemployment. Government starts employment generation schemes. Explain its effects by using production possibility curve. |
|
Answer» Solution :Production POSSIBILITY curve is a curve which depicts all the possible combinations of goods which can be produced with given resources and technology in an ECONOMY i.e., producing goods at its full potentiality. Production below the potentialitymeans that total production in the economy is somewhere below the production possibility curve `P P_(1)`, for example, point U in the diagram. We know production below the production possibility curve HIGHLIGHTS unemployment. When GOVERNMENT starts employment generation schemes, the economy moves towards the full employment, thereby removes unemployment. So, economy comes back to its POTENTIAL level. Value: Analytic |
|
| 2905. |
How is BOP deficit solved? |
|
Answer» Solution :Deficit in BOP can be solved by: i) Import substiution. It implies domestic production of raw MATERIALS, consumer goods and capital goods that have otherwise been imported. ii) EXPORT promotion. It means exporting goods from India. To earn more foreign exchange, export promotion MEASURES should be taken. III) Depreciation of domestic currency. It means fall in the value of currency e.g., if exchange rate rises from Rs 60 for 1 DOLLAR to Rs 70 for one dollar. It encourages exports and discourages imports. |
|
| 2906. |
What do you mean by substitutes? Give examples of two goods which are substitutes of each other. |
Answer» Solution :(i) Substitute goods are those goods which can be used in place of ANOTHER goods and give the same satisfaction to a consumer.  (ii) There WOULD always EXIST a direct relationship between the price of substitute goods and demand for given commodity. (iii)It means with an increase in price of substitute goods, the demand for given commodity ALSO rises and vice-versa. (iv)For example, Pepsi and Coke, TEA and coffee are substitute to each other. |
|
| 2907. |
Explain the significance of 'minus sign' attached to the measure of price elasticity of demand in case of a normal good, as compared to the 'plus sign' attached to the measure of price elasticity of supply. |
| Answer» Solution :The measure of price elasticity of demand of normal good carries minus sign as there exists an inverse relationship between demand and price of the good. That is, other things REMAINING CONSTANT, as the price of a good RISES (or falls), the quantity demanded of the good falls (or rises). On the other hand, price elasticity of supply carries plus sign as there exists a positive relationship between the supply of a commodity and its price. To put in other words, when the price of a good rises (or falls), then the quantity supplied will increase (or decreases), other things remaining UNCHANGED. | |
| 2908. |
If supply curve touches Y-axis, elasticity of supply is less than one ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE : When supply curve touches Y-axis, `ES GT 1` | |
| 2909. |
Goods which are purchased for resale are |
|
Answer» FINAL goods |
|
| 2910. |
What function of money solves the barter'sproblem lack ofdouble coincidence ? |
| Answer» Solution :MONEY as medium of exchange SOLVES the BARTER's broblemof double COINCIDENCE . | |
| 2911. |
State the different phases of changes in Total Product and Marginal Product in the Law of Variable Proportions. Also show the same in a single diagram. |
|
Answer» Solution :The different phases of CHANGES in Total Product (TP) and Marginal Product (MP) can be understood with the help of Law of VARIABLE Proportions. As PER this law, if more and more of variable factor (labour) is COMBINED with the same quantity of fixed factor (capital), then initially the total product will increase but gradually after a point, the total product will become smaller and smaller. The following are the three phases (stages) of the Changes in the two variables. `1^(st)` Stage : Increasing returns to a factor This stage starts from the origin point 0 and continues till the point of inflexion (K) on the TP curve. During this phase, TP increases at an increasing rate and is also accompanied by rising MP curve (in figure ii). The MP curve attains its maximum point (U) corresponding to the point of inflexion. Throughout this stage, AP continues to RISE. `II^(nd)` Stage : Diminishing returns to a factor This stage starts from point K and continues till point B on the TP curve. During this stage, the TP increases but at a decreasing rate and attains its increases but at a decreasing rate and attains its maximum point at B, where it remains constant. On the other hand (in the figure (ii)), the MP curve continues to all and cuts AP from its maximum point Z, where MP equals AP. When TP attains its maximum point, corresponding to it, MP becomes zero. AP, in this stage initially rises, attains its maximum point at Z and thereafter starts falling. `III^(rd)` Stage : Negative Returns to a Factor This stage begins from the point B on the TP curve. Throughout this point, TP curve is falling and MP curve is negative. Simultaneously, the AP curve continues to fall and approaches the x-axis (but does not touch it). Like the first stage, this stage is also known as non-economic zone as any rational producer would not operate in this zone. This is because the addition to the total output by the additional labour unit (i.e. marginal product) is negative. This implies that employing more labour would not contribute anything to the total product but will add to cost of the production in form of additional wage. Hence, the cost of the additional labour input is greater the benefit of employing it. The law of variable proportion can be easily understood with the help to following schedule and diagram. 
|
|
| 2912. |
_ refer to thatportionoftotaldeposite of a commericialbankwhichit has to keepwith itself inthe formof liquidassets. |
|
Answer» CASH RESERVE ratio |
|
| 2913. |
Explain the distinction between 'autonomous investment' and 'induced investment'. |
| Answer» Solution :AUTONOMOUS investment is that investment which is independent of the level of INCOME or PROFIT.Thus, it is not INDUCED by any changes in income.Induced investment are done with the profit MOTIVE and are induced by changes in income. | |
| 2914. |
If the economy operates inside PPC, it shows full utilisation of resources. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE: If economy OPERATES inside PPC, it shows underutilsation of RESOURCES. | |
| 2915. |
Given MPC=0.9 and increase investment equal to Rs. 100 crore, calculate the value of multiplier and total increase in income. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2916. |
What is meant by balance of trade? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2917. |
There is given the price of a good , how does a consumer decide as to how much quality of the goods to buy? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) When purchasing a unit of a commodity a consumer compares its price with the expanted utility from the utility obtained is the benefit, and the pricepayable is the COST , the consumer compares benefit and the cost. He will by the unit of commodity only if the benefit is is greater than or at latest equal to the cost. (II) Equilibrium conditions for single commodity consumer Equilibrium . (a) Necessary Condition Marginal utility of Money = price `""...(1)` Or `(" Marginal Utility of a Product in Util " [MU_x])/("Marginal Utility of One Rupe "[MU_R]) " = Price of X"....(2)` In particular, the condition (1) saya that themarginal utility of a product in terms of Money should be equal to its price. Sometimes this is loosely stated as Marginal Utility is equal to price, i.e. ., MU = price . `"*"`If MU `gt`price `implies` As a rational consumer he willContinue to purchase an additional unit on a commodity as long as MU = price . `implies` MU `gt`Price IMPULSE benefit is greater than cost and when ever benefit is greater than cost the consumer keeps on CONSUMING additional unit of a commodity till MU = price . `implies` It is so because according to the law of diminishing marginal utility MU falls moreis purchased . As MU falls it is bound to become equal to the price at some point of purchase. `"*"` If MU `lt`Price `implies` As a rational consumer he will have to reduce the consumption of a commodity as long as MU = price . `implies MU lt`price implies when benefit is less than cost , never benefit is less than cost the dressing the additional unit of a commodity till MU = price. `implies` It is so because according to the law of diminishing marginal utility, MU rises as less units are consumed. As MU rises , it is bound to become equal to the price at some point of purchase . (b) Sufficient condition: Total gain falls as more is purchased after equilibrium . it means that consumer continues to purchase so long as total gain is increasing or at least CONSTANT. (iii) It can be explained with the help of the following schedule : 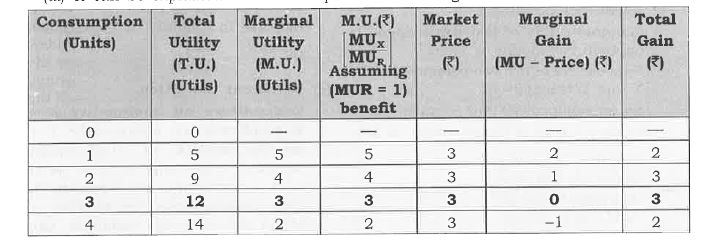 (a) Suppose , the price of commodity X in the market is Rs3 per unit .It means he has to pay Rs3 per unit for all the units he buys.Suppose, the unility obtained from the first unit is 5 utils(=Rs 5)The consumer will buy this unit because the utility of this unit is greater than the price and this process continues till Marginal utility = price as shown in the above schedule at quantity 3 . (b) Consumer will not buy the fourth unit utility of this unit is 2 unit because utility of this unit is 2 utils (= Rs 2)which is less than the price . It is not worth buying the fourth unit. The consumer will restrict his purchase to only 3 units. |
|
| 2918. |
What is meant by aggregate demand ? Explain the various components of aggregate demand. |
| Answer» Solution :AGGREGATE demand refers to the TOTAL demand for FINAL goods and services in the economy.There are 4 components of aggregate demand1. HOUSEHOLD consumption demand (C)2. Private investment demand (I)3. Government demand for goods and services (G)4. Net export demand (X-M) | |
| 2919. |
Consider the following statement-An economy always manages to meet all the needs of the people living in the country. |
| Answer» Solution :False: An ECONOMY always tries to provide MEANS of living to all the PEOPLE. It MAY be successful (as in most of the developed countries), or it may not be successful (as in many developing countries) to ACHIEVE its objective. | |
| 2920. |
Define consumption function |
| Answer» SOLUTION :CONSUMPTION FUNCTION or PROPENSITY refers to the functional releationship between consumption and national income. | |
| 2921. |
Are the following statements true or false ? Give reasons. The concept of normal resident applies to individuals only. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2922. |
APC can never be more than one |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2923. |
Calculate MPC from the following data about an economy which is in equilibrium: National income=2000, Investment expenditure=100, Autonomous consumption expenditure=200 |
|
Answer» Solution :`Y=C+I` `Y=(BAR(C )+By)+I` `B(2000)=1700 [At equiilbrium S=I=100 2. 1-b=MPS=0.3` `b(1700)/(2000)=0.85` Hence, MPC=0.85 |
|
| 2925. |
Define consumption function. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Itshows the functional relationship between consumption EXPENDITURE and level of NATIONAL INCOME. | |
| 2926. |
Which one of these is revenue expenditure ? |
|
Answer» PURCHASE of shares |
|
| 2927. |
Define deficit and surplus BOP. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :DEFICIT BOP = PAYMENTS for autonomous items gt Receipts from autonomous items. SURPLUS BOP = Receipts from autonomous items gt Payments for autonomous items. |
|
| 2928. |
Distinguish between factor income and transfer receipt. |
|
Answer» Solution :. Factor Income is a PAYMENT received in exchange of any good or service while as Transfer Income is received without rendering any service or good. Factor Income includes wages, rents, profit and interest while as Transfer Income COMPRISES gifts, subsidies, DONATIONS, PENSIONS, scholarships etc. |
|
| 2929. |
A 'resident' of a country is one : |
|
Answer» Who was born in that country |
|
| 2930. |
A consumer buys 10 units of a commodity at a price of Rs. 10 per unit. He incurs an expenditure of Rs. 200 on buying 20 units. Calculate price elasticity of demand by the percentage method. Comment upon the shape of demand curve based on this information. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("Initial PRICE (P) = 10","Initial Expenditure = 100","Initial Quantity (Q) = 10"),("New Price "(P_(1)),,),(=("Exp.")/("Quantity")=(200)/(20)=10,"New Expenditure = 200","New Quantity "(Q_(1))=20),(Delta P = 0,,Delta Q = 10):}` `PED = (Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q)=(10)/(0)xx(10)/(10)=(100)/(0)=oo` ED is perfectly ELASTIC as price does not change at all in response to the change in quantity demanded. Thus its DEMAND curve will be horizontal/parallel to x-axis. |
|
| 2931. |
Loans offered by commercialbanks are equalto depositsreceviedby them . |
| Answer» Solution :False : Through the function of money creation, commercial banks are ABLE to OFFER loans (or create CREDIT) which are in far excess of deposits RECEIVED. | |
| 2932. |
What are capital receipts in a government budget ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Capital receipts REFER to those receipts which EITHER create a liability or cause a reduction in the ASSETS of the GOVERNMENT . | |
| 2933. |
What does the the following represent ? |
|
Answer» REAL Flow |
|
| 2934. |
Under what conditions, a producer would like to supply less at a given price ? |
|
Answer» Solution :A DECREASE in supply means that producers now supply less at a given price level. The conditions are (a) Rise in the PRICES of remuneration of factors of the production. (b) Rise in the prices of other goods. (c ) When the technology becomes OUTDATED. (d) Change in the objective of producer (decrease supply at the same price) (e ) Taxation policy of GOVERNMENT RISES. 
|
|
| 2935. |
Budget set is - |
|
Answer» Right angled triangle formed by the BUDGET LINE with the axes. |
|
| 2936. |
A consumer buys 20 units of a good at a price of Rs. 5 per unit. He incurs an expenditure of Rs. 120 when he buys 24 units. Calculate price elasticity of demand using the percentage method. Comment upon the likely shape of demand curve based on this information. |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("Initial Price (P) = 5","Initial Expenditure = 100","Initial QUANTITY (Q) = 20"),("New Price "(P_(1)),,),(=("Exp.")/("Quantity")=(120)/(24)=5,"New Expenditure = 120","New Quantity "(Q_(1))=24),(Delta P = 0,,Delta Q = 4):}` `PED=(Delta Q)/(Delta P)XX(P)/(Q)=(4)/(0)xx(5)/(20)=(20)/(0)=oo` ED is perfectly elastic as price does not change at all in response to change in quantity demanded. Thus, its DEMAND curve will be horizontal/parallel to x - axis. |
|
| 2937. |
State whether the following statements are true or false. Give valid reasons for your answers. (i) Unplanned inventories accumulate when planned investment is less than planned saving. (ii) Deflationnry gap exists when aggregate demand is greater than aggregate supply at full employment level. (iii) Average prooensity to save can never be negative. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) True, as planned savings are more causing the Marginal PROPENSITY to Consume to reduce thus Aggregate Demand will FALL and producers will have accumulation of inventory. (ii) False, Inflationary Gap exists when actual Aggregate Demand is more than Aggregate Supply corresponding to full EMPLOYMENT level of output in the ECONOMY. (iii) False, at income levels which are lower than break-even point, Average propensity to save can be negative as there will be dissaving in the economy. |
|
| 2938. |
Steps taken through the government budget can influence : |
|
Answer» INEQUALITIES |
|
| 2939. |
What changes will take place in MR, when (i) TR increases at an increasing rate. (ii) TR increases at a diminishing rate. (iii) TR increases at a constant rate. |
|
Answer» Solution :The FOLLOWING changes will TAKE place in MR : (i) MR will increase (ii) MR will decrease, but will remain positive . (III) MR is CONSTANT. |
|
| 2940. |
Where will sale of machinery to abroad be recorded in the Balance of Payments Accounts? Give reasons. |
|
Answer» Solution :Sale of MACHINERY to abroad (exports) will be recorded as positive item in the current ACCOUNT of BOP, The current account of BOP is that account which maintains the records of imports and exports of goods and services as well as RECORD of unilateral transfers. Those transactions that result in an inflow of FOREIGN EXCHANGE in the country are recorded as positive items in the current account of BOP. On the other hand, those items that lead to an outflow of foreign exchange from the country are recorded as negative items in the current account of BOP. Therefore, as sale of machinery abroad leads to an inflow of foreign exchange in the country it will be recorded as a positive item in the current account of BOP. |
|
| 2941. |
Explain the effects of a price floor. ORWhat are the effects of price-floor (minimum price ceiling) on the market of a good? Use diagram. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i)When the government imposed lower LIMIT on the price (minimum price) that may be charged for a good or service which is higher than equilibrium price is called price floor. (ii) Price Floor is GENERALLY imposed on agricultural price support programmes and the minimum wage LEGISLATION. (iii) Since this price is above equilibrium price, there is EXCESS supply in the market. Since there is surplus, sellers can attempt to sell their PRODUCT at a price below the floor price. ` (##FM_M_ECO_XII_P1_C12_E02_022_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 2942. |
Increase in interest rate in the domestic economy leads to an appreciation of domestic currency. Your comments? |
| Answer» Solution :If domestic interest rises (SAY in India) and is higher than the interest rate in rest of the WORLD, the foreigners will be induced to shift their FUNDS to the Indian economy. Greater flow of funds from abroad for investment in domestic (Indian) economy will increase demand for Indian currency leading to its APPRECIATION in RELATION to foreign currency. | |
| 2943. |
How are following treated in the estimation of national income ? Expenditure by government in proving free education. |
| Answer» Solution :Yes, it will be INCLUDED in the national INCOME as it is a part of the GOVERNMENT FINAL consumption EXPENDITURE. | |
| 2944. |
Borrowing from IMF to recover from severe BOP crisis. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ACCOMMODATING | |
| 2945. |
What is revenue deficit |
| Answer» Solution :EXCESS of TOTAL revenue EXPENDITURE over the total receipts, of budget is called Revenue Deficit. | |
| 2946. |
What is a bartar system? What are its drawbacks? |
|
Answer» Solution :A barter system is an old method of exchange. Th is system has been used for centuries and long before money was invented. PEOPLE exchanged services and goods for other services and goods in return. The major limitations of Barter Exchange are: 1. Lack of Double Coincidence of Wants:Barter system can work only when both buyer and seller are ready to exchange each other’s goods. For example, A can exchange goods with B only when A has what Bwants and B has what A wants. However, such double coincidence is very rare. 2. Lack of Common Measure of Value:In the barter system, all commodities are not of equal value and there is no common measure (unit) of value of goods and services, in which exchange ratios can be expressed. For example, if A has wheat and B has rice, then it is difficult to decide, how much wheat is needed to exchange with one kilogram of rice. In the absence of common measure, the exchange ratio is fixed randomly, in which one of the party generally suffers.Barter system can work with few commodities in the primitive society. However, it is very difficult in the modern economy, where we NEED millions of exchange ratios for a large number of goods and services. 3. Lack of Standard of Deferred Payment:Under barter system, contracts involving future payments or credit TRANSACTIONS cannot take place with ease because of following reasons:(a) The borrower may not be able to arrange goods of exactly same quality at the time of repayment.(b) There may be conflicts regarding which specific commodity is to be used for repayment.(c) The commodity to be repaid may lose or gain its value at the time of repayment.So, it is very difficult to make deferred payments in the form of goods. 4. Lack of Store of Value:Under barter system, it is difficult for people to store wealth for future use because:(a) Most of the goods (like wheat, rice, vegetables, etc.) do not possess durability, i.e. their quality deteriorates with passage of time.(b) STORAGE of goods requires time and efforts.As a result, goods cannot be used to store the earnings for a long period.With so many difficulties, barter exchange could not continue for a long time. As a result, it was replaced by monetary exchange, i.e. buying and selling of goods with the help of ‘Money’. Money has been defined differently by different economists. The most acceptable definition of money can be stated in terms of all the functions of money. |
|
| 2947. |
When price of a commodity falls by Rs. 1 per unit, its quantity demanded rises by 3 units. Its price elasticity of demand is (-)2. Calculate its quantity demanded if the price before the change was Rs. 10 per unit. |
|
Answer» <P> SOLUTION :`{:("PED" =[-]2" GIVEN"),("Price before change [Initial Price] P = 10Initial Quantity "(Q)=?),("New Price "[P_(1)]=9 "New Quantity " (Q_(1))=?),(DELTA P=-1" [Given]" Delta Q=3):}``PED=(Delta Q)/(Delta P)xx(P)/(Q) "or" (-)2=(3)/((-)1)xx(10)/(Q)` `Q=(30)/(2)=15` So, the quantity demanded at price before change [P], i.e., 10, is equal to 15. |
|
| 2948. |
The value of MPC is double the value of MPS. Find the value of multiplier. |
|
Answer» Solution :GIVEN `MPC = 2 MPS` Add MPS on both sides `MPC + MPS = 2 MPS + MPS` Since `MPC + MPS = 1`, Substituting `3 MPS = 1` `MPS = (1)/(3)` `:. MPC = 1 - (1)/(3) = (2)/(3)` Multiplier `= (1)/(MPS) " or " (1)/(1-MPC)` `= (1)/((1)/(3)) " or " (1)/(1-(2)/(3)) = 3` |
|
| 2949. |
"Flow of income is circular in a two- sector economy". Comment |
| Answer» Solution :The given statement is correct, i.e. flow of income is circular in a two sector economy. The income RECEIVED by households from FIRMS for their factor services is spent by them on purchase of goods and services produced by the firms. Thus, income goes back from where it had come .This flow of income CONTINUES as production is a CONTINUOUS PROCESS. | |
| 2950. |
Current account records receipts and payments of transactions relating to visible items only. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False. Current ACCOUNT CONTAINS the RECEIPTS and payments relating to all TRANSACTIONS of visible items, invisible items and unilateral transfers. | |