Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2751. |
Are the following statements true or false ? Give reasons. In final goods , no value is to be added . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2752. |
Differentiate between revenue budget and capital budget. |
|
Answer» Solution :The main DIFFERENCE between the two are : (i) Revenue budget comprises only revenue receipts and revenue expenditures of the GOVERNMENT, while capital budget comprises of capital receipts and capital expenditures of the government . (ii) Revenue budget include all such FINANCIAL transactions which do not create any asset or LIABILITY for the government . On the other hand , TRANSACTION in capital budget do create assets or liabilities for the government . |
|
| 2753. |
Differentiate between full employment and under-employment equilibrium. |
| Answer» Solution :FULL employment EQUILIBRIUM is that equilibrium where all RESOURCES of the country are fully utilised (employed). Under-employment equilibrium is that equilibrium where all resources are not fully employed, i.e., Some resouroces are under-employed. | |
| 2754. |
Give reasons for the following statements: (i) Demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm is a horizontal straight line. (ii) Demand curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm is a downward sloping curve. (iii) Demand curve facing a monopoly firm is less elastic than that curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Under perfect COMPETITION, every firm is a price-taker firm. The price is set by industry demand and supply. Therefore, every firm faces a horizontal straight line demand CURVE indicating that it can SELL any quantity at the given price. (ii) A monopolistic competitive firm has to DESIGN its own pricing strategy. It can expect to sell larger quantity at a lower price, and vice-versa. Hence, its demand curve slopes downwards. (iii) A monopolist is the only producer of a good which has no close substitutes. A monopolistic competitive firm, on the other hand, produces a good that has several close substitutes. Hence, the demand curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm is more elastic than that faced by a monopoly firm. |
|
| 2755. |
Export and import of machines are recorded in capital account of the balance of payments account. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False. It will be RECORDED in the current account of the BALANCE of payments account. | |
| 2756. |
The sector which owns factor services : |
|
Answer» (a)producer |
|
| 2757. |
What do you mean by the production possibilities of an economy? |
| Answer» Solution :Production POSSIBILITIES of an ECONOMY REFER to different combinations of goods and serviceswhich an economy can produce from a given amount of resources and a given STOCK of technology. | |
| 2758. |
"GDP"_(mp) is : |
|
Answer» INCLUSIVE of depreciation |
|
| 2759. |
Define domestic territory. |
| Answer» Solution :DOMESTIC territory REFERS to the geographical territory WITHIN which PERSONS, goods and capital circulate freely. | |
| 2760. |
Draw consumption curve and saving curve in a single diagram and mark the 'break -even point' |
Answer» SOLUTION :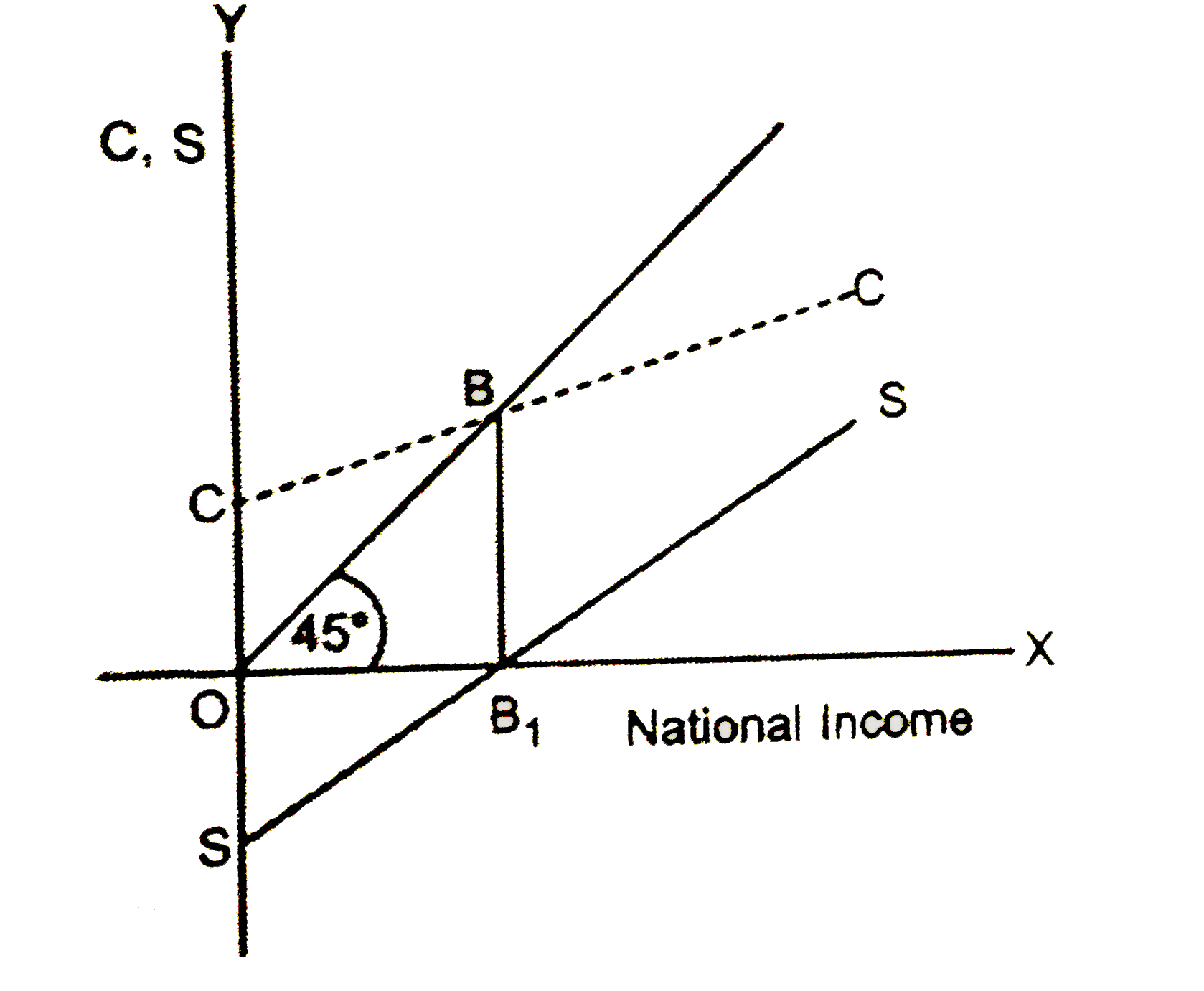 `B_(1)` is a BREAK -even POINT on S CURVE B is break -even point on C curve |
|
| 2761. |
Moneyflow involves exchange of : |
|
Answer» GOODS and services |
|
| 2762. |
State and explain the conditions of consumer's equilibrium in indifference curve analysis. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) To define consumer equilibrium, we use Interference Curve map and the budget line . Two conditions for consumer Equilibrium (a) Necessary Condition Marginal Rate of Substitution = Market Rate of Exchange `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` Or , `MRS_(x,y)=P_x//P_y` MRS ( Market Rate of Exchange ) MRE Or `MRS_(x,y) =MRE[(P_x)/P_y]` `"*" ` If `MRS_(x,y) gt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]` , At point T in FIGURE It means the consumer.s willingness to pay for commodity X is higher than what makes values for commodity X. So, the consumer should buy more of X and less of Y to get MRS `=P_x/P_y` 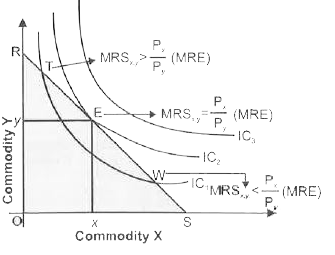 `"*"` If `MRS_(x,y) lt MRE [(P_x)/(P_y)]`, At point W in figure, It means the consumer willingness to pay for commodity X is LESSER than what market value for commodity X ,So, consumer should buy less of X and more Y to get MRS = `p_x/p_y` (b) Sufficient Condition `MRS_(x,y)` Diminishing (Convex) at a point of equilibrium i.E., when `MRS_(xy)=MRE[P_x/P_y]` (ii) The consumer will reach equilibrium when the budget line is tangential to the higher possible Indifference Curve, i.e. ., where necessary and sufficient condition satisfy . In the above diagram , the consumer will reach equilibrium at point E where budget line RS is tangential to the higher possible `IC_2` (iii) The consumer cannot move to Indifference Curve , i.e. ., `IC _3`as this is beyond this money income. (IV) Even on `IC_2` all the other points except E are beyond his means . (v) Hence , at point E, the consumer is in equilibrium where his satisfaction maximizes, given his income and prices of goods X and Y . In equilibrium at E , the slope of Budget line = the slope of Indifference Curve. Therefore `MRS_(xy)`is equal to the ratio of the price bof two goods `[(P_x)/(P_y)]` . |
|
| 2763. |
Tax rate on higher income group have been increased. Which economic value does it reflected ? Explain |
| Answer» Solution :Thiswill REDUCE the inequalities of INCOME as the DIFFERENCE between DISPOSAL INCOMES of higher income and lower income groups will fall. This will also provide more resource to the government for spending on welfare of the poor. | |
| 2765. |
What happens to the level of national income when aggregates supply exceeds aggregate demand? |
| Answer» Solution : If AGGREGATE supply does exceed (INTENDED) aggregate demand over a given period of time, there will be an involuntary build up in stocks (inventories) and national income (output) will have been GREATER than it otherwise WOULD have been. Typically, in the FOLLOWING time period, the equilibrium would be restored as excess stocks are subsequently run down, resulting in national income (output) being lower than it otherwise would have been. | |
| 2766. |
What is meaning of forward market ? |
| Answer» Solution : ForwardMarket REFERS to the market in which sale and puchase of foreign currency is SETTLED on a specified future DATE at a rate AGREED UPON today | |
| 2767. |
Reverse Repo Rate is therateat whichCentral Banks: |
|
Answer» Lends moneyto COMMERCIAL BANKS for short-term |
|
| 2768. |
Flow of Goods and services and factors of production across different sectors in barter economy is known as : |
|
Answer» Circular Flow |
|
| 2769. |
What is real GDP ? State three limitations of GDP as an index of economic welfare. |
| Answer» Solution :Real gross DOMESTIC product (GDP) is an inflation-adjusted measure that reflects the value of all goods and services produced by an economy in a given year, expressed in base-year prices, and is often referred to as "constant-price," "inflation-corrected" GDP or "constant dollar GDP."three LIMITATIONS of GDP as an index of economic welfare--GDP does not incorporate any measures of welfare.-GDP only INCLUDES market transactions-GDP does not DESCRIBE income distribution | |
| 2770. |
An increases in demand for imported goods raises the demand fro foreign exchange. |
| Answer» SOLUTION : True. Demand for foreign EXCHANGE will rise in order to make the PAYMENT for imported GOODS. | |
| 2771. |
Increase in foreign exchange rate leads to rise in supply of foreign exchange |
| Answer» SOLUTION :False. Increases in foreign EXCHANGE rate raises the supply of foreign exchange due to risein exports, foreign. INVESTMENT, treanfers from ABROAD and SPECULATIVE activites | |
| 2772. |
What does zero primary deficit mean ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Zero PRIMARY deficit means that the GOVERNMENT has to resort to borrowings only to MAKE interest PAYMENTS of previous years . | |
| 2773. |
Which bank controls the bankingand monatrystructureof India ? |
|
Answer» Reserve BANK of INDIA |
|
| 2774. |
Give examples of autonomous and accommodating items. |
|
Answer» Solution :Autonomous transactions do not take place with a VIEW to maintain balance I the country's BOP. These are recorded before CALCULATING deficit/surplus in BOP account. The main autonomous items are: i) Autonomous exports and imports of goods. ii) Autonomous exports and imports of SERVICES. iii) Autonomous unilaterla transactions (Receipts and payments). Autonomous capital transactions (Receipts and payments). Accommodating items. Refer to those which are taken up by the government in order to maintain BOP identity (balance). The main accommodating items are: i) Increasing or decreasing foreign EXCHANGE reserves. ii) Borrowing or LENDING. iii) Official reserve transactions. |
|
| 2775. |
What are time deposits in banks? |
| Answer» Solution :TIME deposits refer to those deposits, in which the AMOUNT is deposited with the bank for a fixed PERIOD of time. | |
| 2776. |
What is the shape of the demand curve faced by a firm under perfect competition? |
|
Answer» HORIZONTAL |
|
| 2777. |
Unforeseen obsolescence of fixed capital assets during production is : |
|
Answer» Consumption of Fixed Capital |
|
| 2778. |
Define MOC. Explain the concept with a hypothetical numerical example. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Marginal oppor-tunity COST is an addition to a cost in terms of a NUMBER of units of a commodity sacrificed to produce one ADDITIONAL unit of another commodity. (ii) Marginal opportunity cost can also be termed marginal RATE of transformation, Marginal rate of transformation is the ratio of number of units of a GOOD sacrificed to produce one additional unit of another commodity. `MRT_(X,Y)=("Amount of good Y sacrificed")/("Amount of good X gained")=(DeltaY)/(DeltaX)` 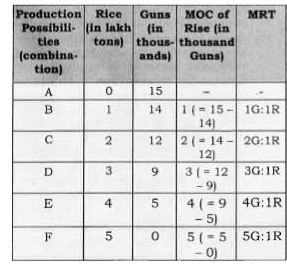
|
|
| 2779. |
State any three factors which lead to increase in demand. |
Answer» Solution :The CONDITIONS are : 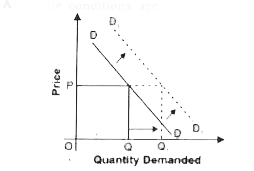 (i) Price of substitute GODS rises. (ii) Price of complementary GOODS falls. (iii) Income of a consumer rises in case of normal goods. (iv)Income of aconsumer falls in case of inferior goods. (V) When the preferences are FAVOURABLE. |
|
| 2780. |
Mention any three items that are excluded from GNP ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Three items excluded from GNP are : (i) Purely financial transactions, like sale and purchase of securities, bonds or transfer PAYMENTS. (ii) Transfer of second-hand goods. (III) Non-market transactions, like services of housewife, kitchen GARDENING , leisure TIME activities. |
|
| 2781. |
Starting from an initial situation of consumer's equilibrium state, how does increase in marginal utility of one rupee affect the quantity demanded of a product? |
Answer» Solution :QUANTITY demanded will decrease because of corresponding to higher MU of one RUPEE. MU of the commodity should also be higher which is possible only when CONSUMPTION (quantity demanded ). decrease It can be EXPLAINED with the help of the following SCHEDULE and diagram and assuming price of quantity X to be 1 and for consumer MU of a rupee is 20 units.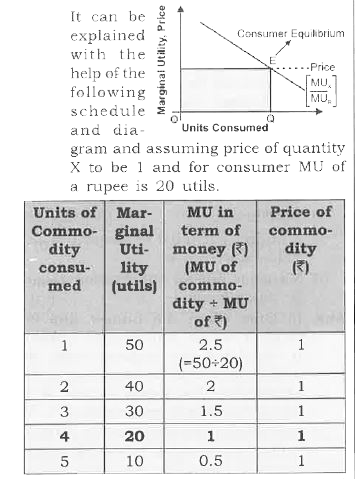 As is given in the question if marginal utility Rupee increases (let if increases to 30 units), then Quantity will decrease . It can be shown with the help of schedule and diagram . 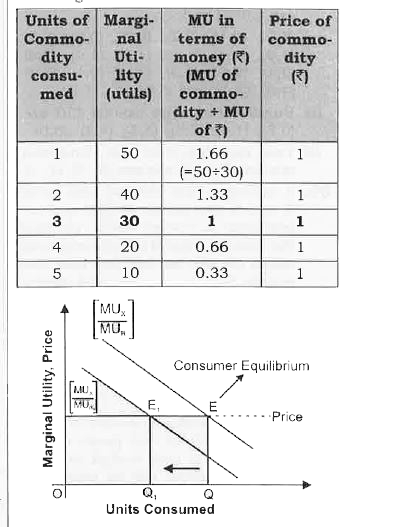
|
|
| 2782. |
What is foreign exchange? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FOREIGN exchange MEANS foreign currencies. For exmaple, Dollars, YEN, Pound are foreign exchange for INDIA. | |
| 2783. |
Revenue budget is an account of assets and liabilities of the government. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2784. |
Why is AC curve U-shaped in short run? |
|
Answer» Solution :Average COST is U-Shaped because of Law of variable proportion: (i) The SHAPE of average cost (AC) depends upon total cost (TC). (ii) Initially, total cost (TC) increases at a diminishing RATE (Total Product increases at INCREASING rate), which makes its average, i.e., average cost (AC) to fall, then reaches its minimum point.  (iii) Thereafter, total cost (TC) increases at increasing rate (Total Product increases at diminishing rate), which makes the average cost (AC) to RISE. This type of production behaviour shows operation of law of variable proportion. |
|
| 2785. |
When exchange rate falls : |
|
Answer» EXPORTS BECOME cheaper |
|
| 2786. |
Calculate GDP_("mp") and NDP_(fc) from following data. Asuume that there are only two sectors A and B in the economy: (i) Closing stock of sector A 20 (ii) Opening stock of sector B 5 (iii) Opening stock of sector A 30 (iv) Closing stock of sector B 15 (v) Sales by sector B 200 (vi) Sales by sector A 150 (vii) Goods and services tax paid by section A 15 (viii) Consumption of fixed capital by sector B 10 (ix) Consumption of fixed capital by sector A 10 (x) Subsidies to sector B 5 (xi) Intermediate consumption by sector A 70 (xii) Intermediate consumption by sector B 60 (xiii) Net factor income from abroad 10 |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2787. |
An increase in supply results in a fall both in equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price. |
| Answer» Solution :False: Increase in supply implies a RIGHTWARD SHIFT of the supply curve. New suPply curve will INTERSECT the given DEMAND curve at a lower price. The equilibrium price will fall, equilibrium quantity will RISE. | |
| 2788. |
Addition to the capital stock of an economy is termed as : |
|
Answer» Investment |
|
| 2789. |
What is meant by equilibrium ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Equilibrium means state of balance. In the context of AD and AS, equilibrium occurs when at a particular price level, aggregate DEMAND equals aggregate SUPPLY. For EXAMPLE, AD=AS. | |
| 2790. |
Define gross investment. |
| Answer» Solution :Gross inverstment refers to TOTAL INVESTMENT made IB a given period in an ECONOMY. It is the sun of gross domesric fixed capital formatio and change in ctocks. | |
| 2791. |
Foreign exchange transactions. dependent on other foreign exchange transactions are called |
|
Answer» CURRENT account TRANSACTIONS |
|
| 2792. |
Differentiate between consumption of fixed capital and capital loss. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 2793. |
What is the horizontal (X axis) intercept of budget line ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :HORIZONTAL intercept of BUDGET line `("Money income")/("Price of the COMMODITY on horizontal axis")=M/P_1` |
|
| 2794. |
What is inflationary gap? Explain the role of Cash Reserve Ratio in removing this gap. |
| Answer» Solution :An inflationary gap is a macroeconomic concept that describes the difference between the current LEVEL of real gross domestic product (GDP) and the anticipated GDP that would be experienced if an economy is at full employment. This is also referred to as the potential GDP. To correct the problem of inflationary gap, the Central Bank increases the Cash Reserve Ratio. It REDUCES the supply of money and credit CREATION capabilities of commercial banks. Due to LESSER supply of money, the Aggregate Demand comes down and the economy ATTAINS equilibrium situation | |
| 2795. |
The maximum value of multiplier is_ when the value of MPC is_ |
|
Answer» infinity,zero |
|
| 2796. |
Give two examples of revenue expenditure . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(i) PAYMENT of INTEREST (II) Payment of SALARIES . | |
| 2797. |
Transactions that take place to cover deficit or surplus are called _____transactions |
|
Answer» ACCOMMODATING |
|
| 2798. |
Distinguish between autonomous and accommodating transactions of balance of payments account.ORDistinguish between the autonomous transactions and the accommodating transactions in the Balance of Payments. What is the significance of this distinction? |
| Answer» Solution :~Autonomous ITEMS refer to those international economic TRANSACTIONS, which TAKE place due to some economic motive such as profit maximization. Accommodating items refer to the transactions that are undertaken to cover deficit or surplus in autonomous transactions.~Significance of Distinction: the deficit/surplus in Balance of Payments (BOP) is DETERMINED by autonomous transactions only. BOP is said to be in deficit when autonomous receipts fall SHORT of autonomous payments. | |
| 2799. |
The term PPP signifies : |
|
Answer» COMMON prices |
|
| 2800. |
Explain three properties of indifference curves. |
|
Answer» Solution :There are three properties of Indifference Curve. 1. Indifference curve are downward sloping to the right. Downward slope of the difference curve to the right implies that a consumer cannot simultaneously have more of both the GOODS. An INCREASE in the quantity of one good is associated with the decrease in the quantity of the other good. This is the accordance with the assumption of monotonic prefernces. 2. Higher IC represents higher utility - Higher IC represents more goods means more utility because of the assumption of monotonic preference. 3. SHAPE of Indifference Curve: As we more down along the Indifference curve to the right, the slope of IC (MRS) decreases. This is because as the consumer consumers more and more of one good, the marginal utility of the good falls. On the other hand, the marginal utility of the good which is sacrificed rises. In other words, the consumer is willing to sacrific less and less for each additional unit of the other good consumed. Thus, as we move down the IC, MRS diminishes. This suggests the convex shape of indifference curve.  In the above figure, IC is the Indifference Curve. AT point A, `MRS_(xy) = AD//DB` At point B, `MRS_(xy) = BE//EC` `BE//EC lt AD//DB` MRS at `B lt MRS` at A, so MRS has fallen. |
|