Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Derive the law of demand from the two commodity equilibrium condition " Marginal Utility = price ratio through utility approach''. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The law states that a consumer is in equilibrium when the ratio of MU to price in CASE of each good consumed is the same. In of goods, X and Y , a consumer is in equilibrium when , `(MU_x)/P_x =(MU_y)/P_y` (ii) Given that the consumer is in equilibrium and price of X falls. It can be seen from the figure that figure B is derived from Figure A 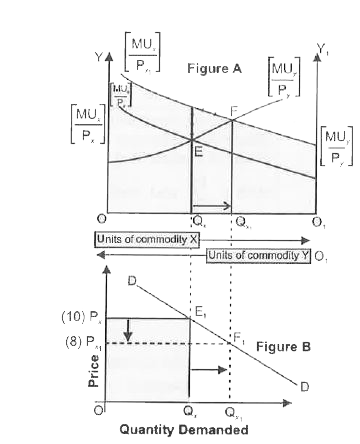 (iii) In figure A, initially , the consumer equilibrium is attached at point E where `(MU_x)/(P_x)=(MU_y)/P_y`(Assuming, `P_x=10`) Corresponding to point E , we derive point E, in figure B . (iv) DUE to FALL in price (suppose from 10 to 8),`(MU_x)/(P_x)gt(MU_y)/P_y`at the given QUANTITY Q . It means , marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X is more than marginal utility from the last rupees spent on commodity Y . So , to attain the equilibrium the consumer must increase the quantity of X , which decreases the `MU_x` and decreases the `MU_y`Increase in quantity of Y continue till`(MU_x)/(P_x)= (MU_y)/P_y`and the new consumer equilibrium will be attached at point F. Corresponding to point F ,we derive the point `F_1` in figure B, So , by JOINING point `E_1 and F_1`. we derive the demand curve . |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Increase in stock of goods held by a consumer will contribute to capital formation.
- Explain the meaning of diminshing marginal rate of substitution with the help of a numercial example
- Explain the meaning of inflationary gap and deflationary gap . Explain any one measure by which these gaps can b e reduced.
- Distinguish between average propensity to consume and marginal propensity to consume. The value fo which of these two can be greater than oneand when ?
- Componenet of current account in BOP
- How are exports affected by depreciation of foreign currency ? Explain
- (a) State any two precautions that must be taken into consideration while estimating national income by value added method. In an economy following transcations took place. Calculate value of output value added by Firm B: (i) Firm A sold to firm B goods of 80 crore, to firm C 50 crore to household 30 crore and goods of value 10 crore remains unsold (iii) Firm B sold firm C goods of 70 crore, to firm D 40crore, goods of value 30 crore were exported and goods of value 5 crore was gold to government Or Differentiate betweeen National Current Places and National Income at Constant Prices. Which of the two presents a better view of the economic growth of economy and why?
- A firm gets maximum profits only if difference between average revenue and average cost is the maximum.
- Reserve repo rate is the rate at which Central Bank lends funds to banks.
- Commerical banksdo not contributeto quantumof moneysupplyin the economyas they do nothavenote- issuingauthority.